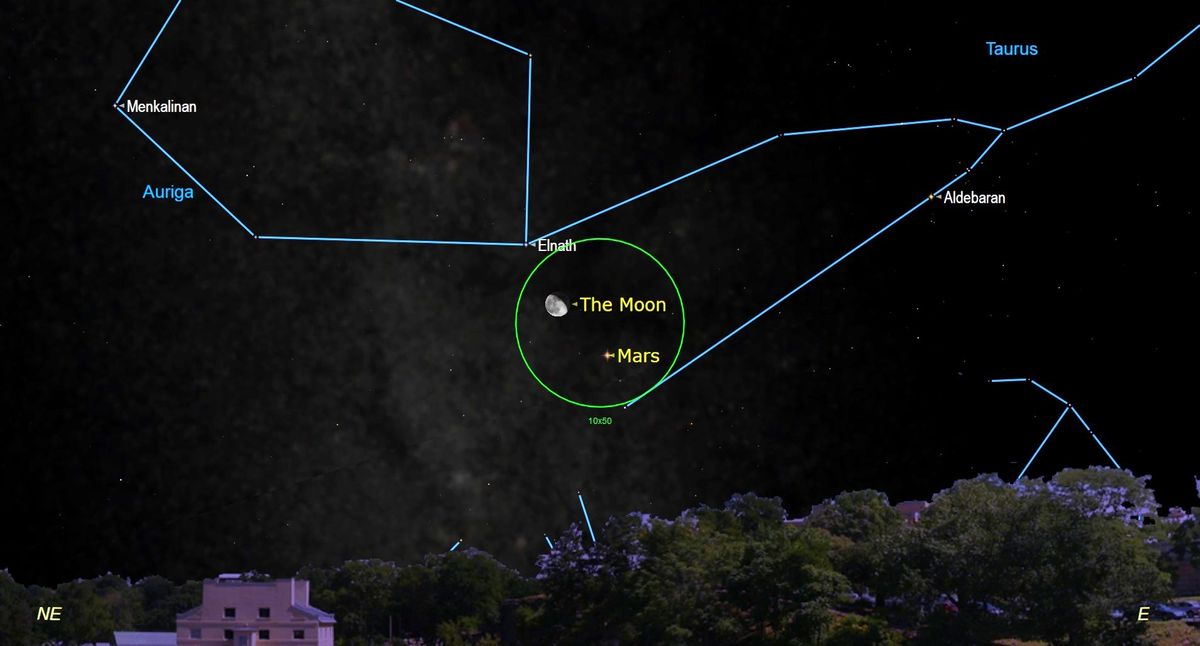
Throughout the late night hours of Friday (Oct. 14), those that are outdoors will little doubt be aware of a waning gibbous moon, 74 p.c illuminated and simply 2 and a half days from its half or final quarter phase.
However there may even be one other object, showing to hover to the decrease proper of the moon; glowing like an orange luminary at midnight of the evening. That object shouldn’t be a star, however one in every of our planetary neighbors: Mars. Its proximity to the moon will little doubt haven’t just a few of us asking the query, “Simply what’s that fiery-colored factor that is glowing under the moon?”
Actually, I wouldn’t be shocked if just a few individuals dial their native police stations to report a UFO.
Associated: Total lunar eclipse: How to prepare for next month’s eclipse of the moon
In somewhat below eight weeks, Mars will likely be at opposition to the sun, when it will likely be within the sky all evening; rising at sundown, reaching its highest level within the south in the course of the evening and setting at dawn. Now, nonetheless, Mars doesn’t rise till simply after 9 p.m. native daylight occasions and will not attain its highest level till 5 a.m.
Oppositions of Mars happen on a mean of about each 2.2 years. However not all Martian oppositions are alike. Certainly, the oppositions later on this decade will lean ones for observers of Mars. Those that witnessed its spectacular method to inside 35.78 million miles (57.58 million km) of Earth in July 2018 should accept more and more poorer views of the crimson planet because the Earth-Mars orbital geometry turned extra unfavorable within the coming years forward.
Learn extra: Amazing Photos: The ‘Blood Moon’ Eclipse and Mars Opposition of July 27, 2018
In stark distinction to 2018, Mars will come no nearer to Earth than 59.7 million miles (96.1 million km) in 2025, 63.0 million miles (101.4 million km) in 2027 and 60.2 million miles (96.8 million km) in 2029.
However earlier than this stretch of lean years arrives, we’ve yet another “first rate” Mars. Later this fall, on Nov. 30 at 9:17 p.m. EDT (0117 GMT on Dec. 1) , Mars will make its closest method to Earth till Could 11, 2031 coming to inside 50.61 million miles (81.43 million km).
On Friday (Oct. 14) at 9:45 p.m. EDT (0145 GMT on Oct. 15), the moon will go closest – 2.9 levels – to the higher left of Mars. Because the evening wears on, the moon and Mars will slowly get progressively farther aside. By 5 a.m., Mars and the moon will likely be actually hovering excessive within the southern sky, however they may now be greater than 4 levels aside. (To gauge levels within the sky, lengthen your arm and make a fist; your fist’s width equals about ten levels).
Mars at the moment shines at magnitude -0.9, making it brighter than any star within the sky save for Sirius the Dog Star, the brightest star within the sky. (The decrease an object’s magnitude, the brighter it seems to the attention.) However as Mars attracts progressively nearer to Earth – about 316,000 miles (509,000 km) every day, its brightness will enhance markedly. By Nov. 10, it’ll surpass Sirius in brilliance and when it arrives at opposition on the evening of Dec. 7, it’ll attain a peak magnitude of -1.9.
That is greater than twice as vivid than it seems now!
One thing for you to consider if you watch its rendezvous with the moon on Friday night.
Joe Rao serves as an teacher and visitor lecturer at New York’s Hayden Planetarium (opens in new tab). He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine (opens in new tab), the Farmers’ Almanac (opens in new tab) and different publications. Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) and on Facebook (opens in new tab).