Since 2018, when the NASA InSight Mission deployed the SEIS seismometer on the floor of Mars, seismologists and geophysicists at ETH Zurich have been listening to the seismic pings of greater than 1,300 marsquakes. Repeatedly, the researchers registered smaller and bigger marsquakes.
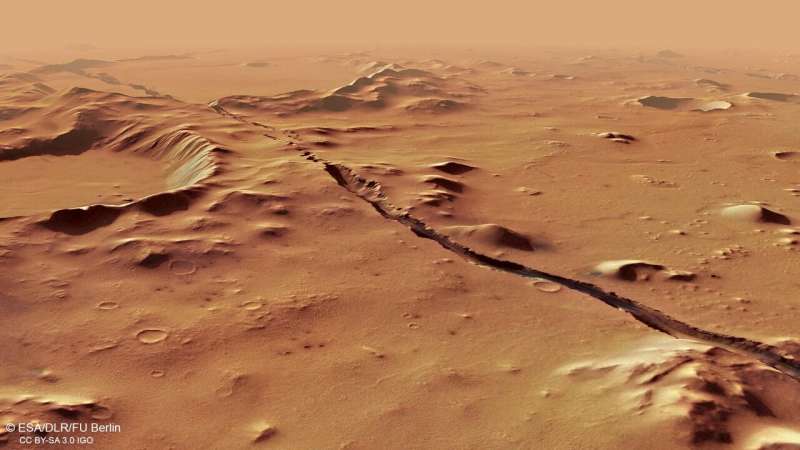
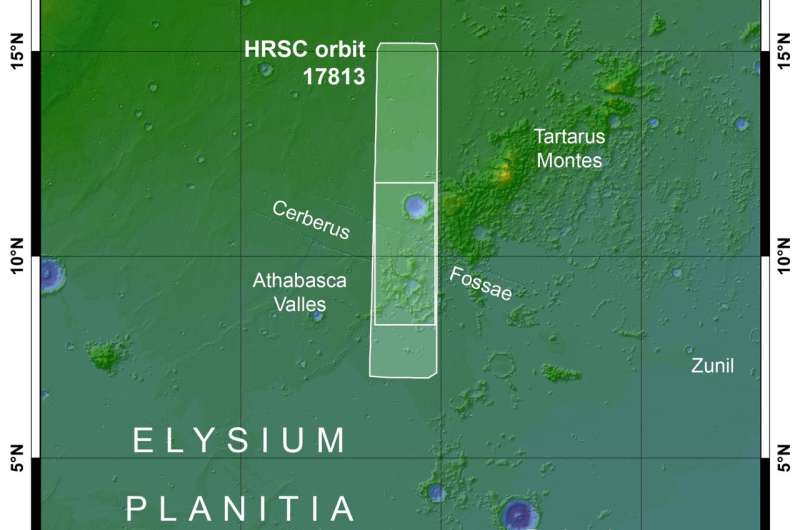
An in depth evaluation of the quakes’ location and spectral character introduced a shock. With epicenters originating within the neighborhood of the Cerberus Fossae—a area consisting of a collection of rifts or graben—these quakes inform a brand new story. A narrative that means volcanism nonetheless performs an energetic position in shaping the Martian floor.
Mars exhibits indicators of life and youth
A world workforce of researchers, led by ETH Zurich, analyzed a cluster of greater than 20 latest marsquakes that originated within the Cerberus Fossae graben system. From the seismic knowledge, scientists concluded that the low-frequency quakes point out a doubtlessly heat supply that may very well be defined by current day molten lava, i.e., magma at that depth, and volcanic activity on Mars. Particularly, they discovered that the quakes are situated principally within the innermost a part of Cerberus Fossae.
After they in contrast seismic knowledge with observational photographs of the identical space, additionally they found darker deposits of dust not solely within the dominant path of the wind, however in a number of instructions surrounding the Cerebus Fossae Mantling Unit.
“The darker shade of the dust signifies geological proof of more moderen volcanic exercise—maybe inside the previous 50,000 years—comparatively younger, in geological phrases,” explains Simon Staehler, the lead creator of the paper, which has now been revealed within the journal Nature Astronomy. Staehler is a Senior Scientist working within the Seismology and Geodynamics group led by Professor Domenico Giardini on the Institute of Geophysics, ETH Zurich.

Why examine the terrestrial neighbor?
Exploring Earth’s planetary neighbors is not any simple process. Mars is the one planet, apart from Earth, wherein scientists have ground-based rovers, landers, and now even drones that transmit knowledge. All different planetary exploration, to date, has relied on orbital imagery.
“InSight’s SEIS is essentially the most delicate seismometer ever put in on one other planet,” says Domenico Giardini. “It affords geophysicists and seismologists a possibility to work with present knowledge exhibiting what is going on on Mars right this moment—each on the floor and in its inside.” The seismic data, together with orbital photographs, ensures a higher diploma of confidence for scientific inferences.
One in all our nearest terrestrial neighbors, Mars is essential for understanding related geological processes on Earth. The crimson planet is the one one we all know of, to date, that has a core composition of iron, nickel, and sulfur that may have as soon as supported a magnetic subject. Topographical proof additionally signifies that Mars as soon as held huge expanses of water and presumably a denser environment. Even right this moment, scientists have realized that frozen water, though presumably principally dry ice, nonetheless exists on its polar caps. “Whereas there may be far more to be taught, the proof of potential magma on Mars is intriguing,” Anna Mittelholz, Postdoctoral Fellow at ETH Zurich and Harvard College.
Final remnants of geophysical life
Taking a look at photographs of the huge dry, dusty Martian panorama it’s troublesome to think about that about 3.6 billion years in the past Mars was very a lot alive, not less than in a geophysical sense. It spewed volcanic particles for an extended sufficient time to provide rise to Tharsis Montes area, the biggest volcanic system in our solar system and the Olympus Mons—a volcano practically 3 times the elevation of Mount Everest.
The quakes coming from the close by Cerberus Fossae—named for a creature from Greek mythology often called the “hell-hound of Hades” that guards the underworld—counsel that Mars is just not fairly useless but. Right here the burden of the volcanic area is sinking and forming parallel graben (or rifts) that pull the crust of Mars aside, very similar to the cracks that seem on the highest of a cake whereas its baking. In accordance with, Staehler “it’s potential that what we’re seeing are the final remnants of this as soon as energetic volcanic area or that the magma is true now transferring eastward to the following location of eruption.”
This examine concerned scientists from ETH Zurich, Harvard College, Nantes Université, CNRS Paris, the German Aerospace Heart (DLR) in Berlin, and Caltech.
Simon Stähler, Tectonics of Cerberus Fossae unveiled by marsquakes, Nature Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-022-01803-y. www.nature.com/articles/s41550-022-01803-y
Quotation:
Magma on Mars doubtless, examine finds (2022, October 27)
retrieved 27 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-magma-mars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




