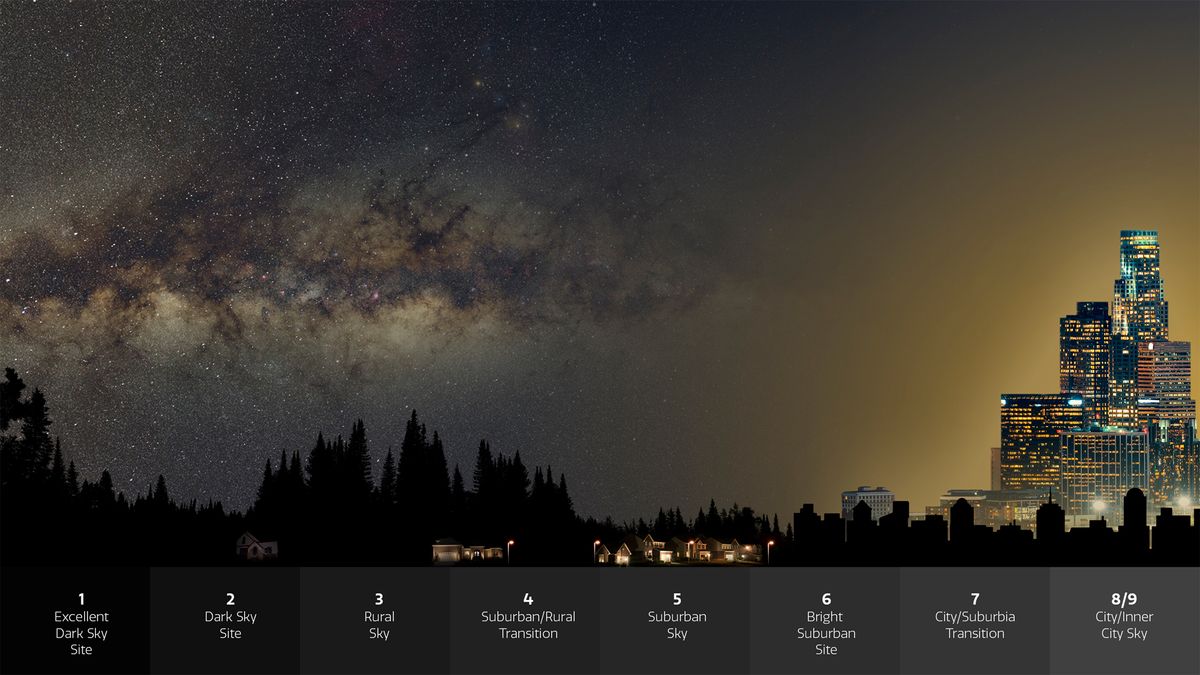
Mild air pollution is brightening up the night time sky so quick that stars are just about disappearing in entrance of sky-watchers’ eyes, a brand new examine has revealed.
The place 18 years in the past, a star gazer would see on common 250 specks of sunshine illuminating the darkness overhead. Right now, solely 100 could be seen, in response to the examine that relied on data from 1000’s of citizen scientists everywhere in the world.
The rationale behind this unprecedented star loss is the rise in light pollution, the impact of synthetic city lightning that, in response to the examine, results in a mean 9.6% world annual rise within the brightness of the sky. This tempo of sky-brightening is sort of a bit sooner than satellite measurements have indicated beforehand, the examine’s authors stated in a statement (opens in new tab).
The sky is brightening up at a unique charge in several elements of the world. In Europe, the tempo seems barely slower at 6.5% per 12 months, whereas in North America the night time glow of the sky will increase by 10.4% yearly, the examine discovered.
Associated: Challenge for astronomy: Megaconstellations becoming the new light pollution
“The speed at which stars have gotten invisible to folks in city environments is dramatic,” Christopher Kyba, of the GFZ German Analysis Centre for Geosciences and lead creator of the examine, stated within the assertion.
The examine was performed by researchers from the GFZ German Analysis Middle for Geosciences, the Ruhr-Universität Bochum and the US Nationwide Science Basis’s NOIRLab. The evaluation, dubbed the “Globe at Evening” Citizen Science Challenge, included 50,000 bare eye night time sky observations made by volunteers between 2011 and 2022 .
The dearth of darkness at night time is regarding for much extra folks than simply skilled astronomers and astronomy lovers. In line with Constance Walker, co-author of the examine and head of the Globe at Evening mission of NSF’s NOIRLab, the unceasing publicity to mild impacts all people in addition to animals residing in affected areas.
“Skyglow impacts each diurnal [active during the day] and nocturnal animals and likewise destroys an vital a part of our cultural heritage,” Walker stated within the assertion.
The nighttime glow of the sky has not beforehand been measured globally, the researchers stated, however estimates exist primarily based on satellite measurements. These measurements, nonetheless, have beforehand indicated that the rise in mild air pollution has plateaued and is even mildly lowering in probably the most affected areas in Europe and North America. The brand new findings present that these earlier estimates had been doubtless unsuitable.
“Satellites are most delicate to mild that’s directed upwards in direction of the sky. However it’s horizontally emitted mild that accounts for many of the skyglow,” Kyba stated. “So, if commercials and facade lighting turn out to be extra frequent, greater or brighter, they may have a big effect on skyglow with out making a lot of a distinction on satellite imagery.”
On prime of that, satellite sensors are much less delicate to LED lighting that has turn out to be extra frequent lately, which glows in hues of blue, in comparison with the orange-glowing sodium vapor lamps that had been dominant prior to now.
“Our eyes are extra delicate to blue mild at night time, and blue mild is extra prone to be scattered within the environment, so it contributes extra to skyglow,” Kyba stated. “However the one satellites that may picture the entire Earth at night time usually are not delicate within the wavelength vary of blue mild.”
The researchers famous that one shortcoming of the examine is that it did not have sufficient information from the creating world the place modifications could also be occurring at a good sooner charge.
The study (opens in new tab) was revealed on Thursday (Jan. 19) within the journal Science.
Comply with Tereza Pultarova on Twitter @TerezaPultarova. Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.