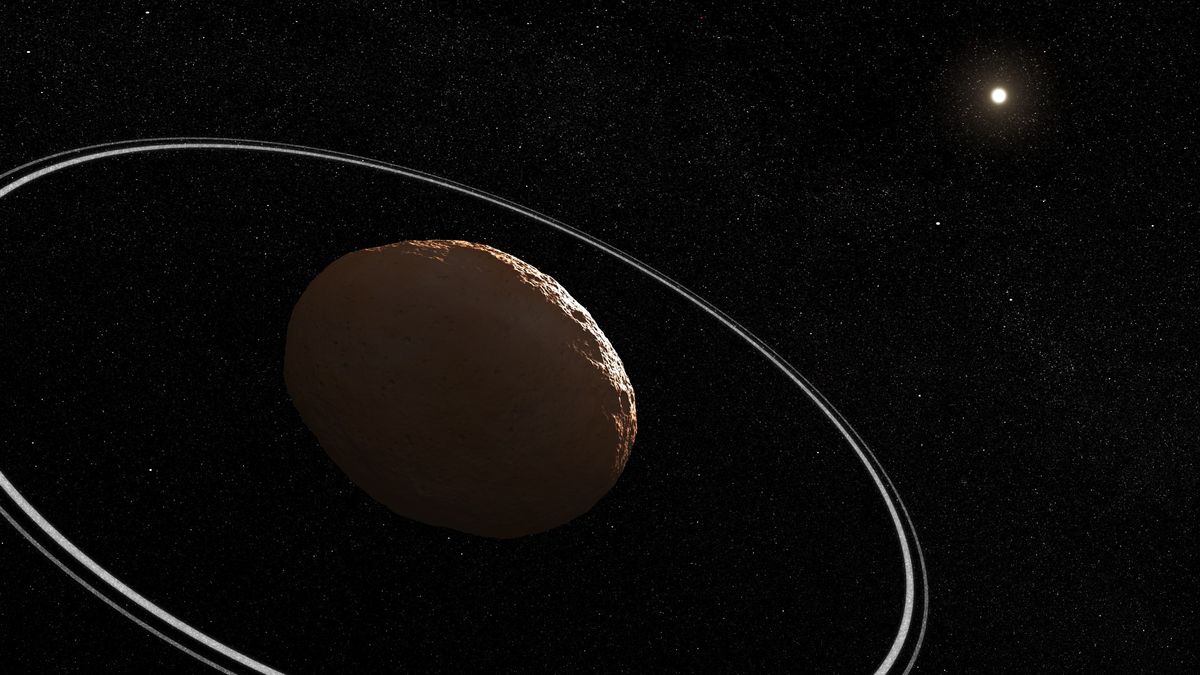
Probably the most complete plans want a sprinkle of luck, even in space.
In October 2022, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or Webb) watched as Chariklo, a tiny ringed asteroid, eclipsed a star. This occasion, referred to as an occultation, marked a primary for Webb. On the month’s finish, Webb turned towards Chariklo once more and notched one other victory: For the primary time, astronomers analyzing the telescope’s information noticed clear indicators of water ice, the presence of which was solely hinted at till now. These observations will information astronomers to raised perceive the character and conduct of tiny our bodies within the outer reaches of our solar system.
However the two feats virtually didn’t occur.
Associated: Asteroid Chariklo Has Rings: Images of a Space Rock Oddity (Gallery)
Though it’s the largest of its sort, Chariklo continues to be too small and too far for even the mighty Webb to {photograph} immediately. As an alternative, astronomers determined to check it by means of occultation, which is an oblique however highly effective technique to check small our bodies like Chariklo. However the workforce didn’t know if and when a star — with out which an occultation wouldn’t happen — would fall into Webb’s area of view. This made Chariklo a part of Webb’s target of opportunity (opens in new tab) program: If the asteroid occurred to cross in entrance of a star, this system would enable astronomers to briefly interrupt the telescope’s schedule to watch the occasion.
The workforce calculated solely a 50% likelihood that Webb would spot a star shiny sufficient with an fascinating object like Chariklo crossing in entrance. After its launch in 2021, as Webb went by means of routine course corrections to carry it regular in its parking spot in space, the workforce continued predicting and revising its checklist of doable occultations. Late final yr, astronomers ended up on the favorable aspect of that fifty% once they found “by exceptional good luck” that Chariklo was on monitor to occult a star that additionally fell into Webb’s view.
“This was the primary stellar occultation tried with Webb,” the workforce wrote in a NASA statement (opens in new tab) printed Wednesday (Jan. 25). “A whole lot of laborious work went into figuring out and refining the predictions for this uncommon occasion.”
On Oct. 18, 2022, Chariklo and its system of two rings crossed in entrance of a star. Utilizing Webb’s near-infrared digicam (NIRCam), astronomers monitored the star’s brightness for an hour. Ensuing information confirmed two dips within the star’s brightness as anticipated: When the asteroid’s rings first hid the star because the eclipse started, and once more when the final of its rings wrapped up the occultation.
“The shadows produced by Chariklo’s rings have been clearly detected,” the workforce wrote within the assertion, “demonstrating a brand new approach of utilizing Webb to discover solar system objects.”
Learn extra: How the James Webb Space Telescope works in pictures
Objects like Chariklo are referred to as centaurs, because of their hybrid nature. (Centaurs are mythological horse-human hybrids.) They appear like asteroids however behave like comets — complete with visible tails. Their residence, an unstable orbit between Jupiter and Neptune, hosts 1000’s of centaurs of various styles and sizes. As fascinating as they’re, their small measurement and huge distance make them troublesome to check. The composition of even the largest centaur, Chariklo — which continues to be tiny at simply 160 miles (250 km) in diameter and distant at a whooping 2 billion miles (3.2 billion km) from us — is poorly understood. Additionally, past research hinted at water ice someplace in Chariklo’s system, however had but to conclusively detect it.
On this newest analysis, astronomers pointed Webb at Chariklo once more. This time, they used the telescope’s Close to-infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) instrument to measure the daylight mirrored by Chariklo and its two rings. The ensuing spectrum confirmed three absorption bands of water ice, marking the primary clear indication of crystalline ice.
The presence of crystalline ice seemingly signifies that Chariklo is topic to fixed bombardment, in keeping with Dean Hines, an astronomer on the Area Telescope Science Institute in Maryland. “As a result of high-energy particles remodel ice from crystalline into amorphous states, detection of crystalline ice signifies that the Chariklo system experiences steady micro-collisions that both expose pristine materials or set off crystallization processes,” Hines stated in NASA’s assertion.
Learn extra: Centaurs Rising: NASA Eyes Missions to Weird Asteroid-Comet Hybrids
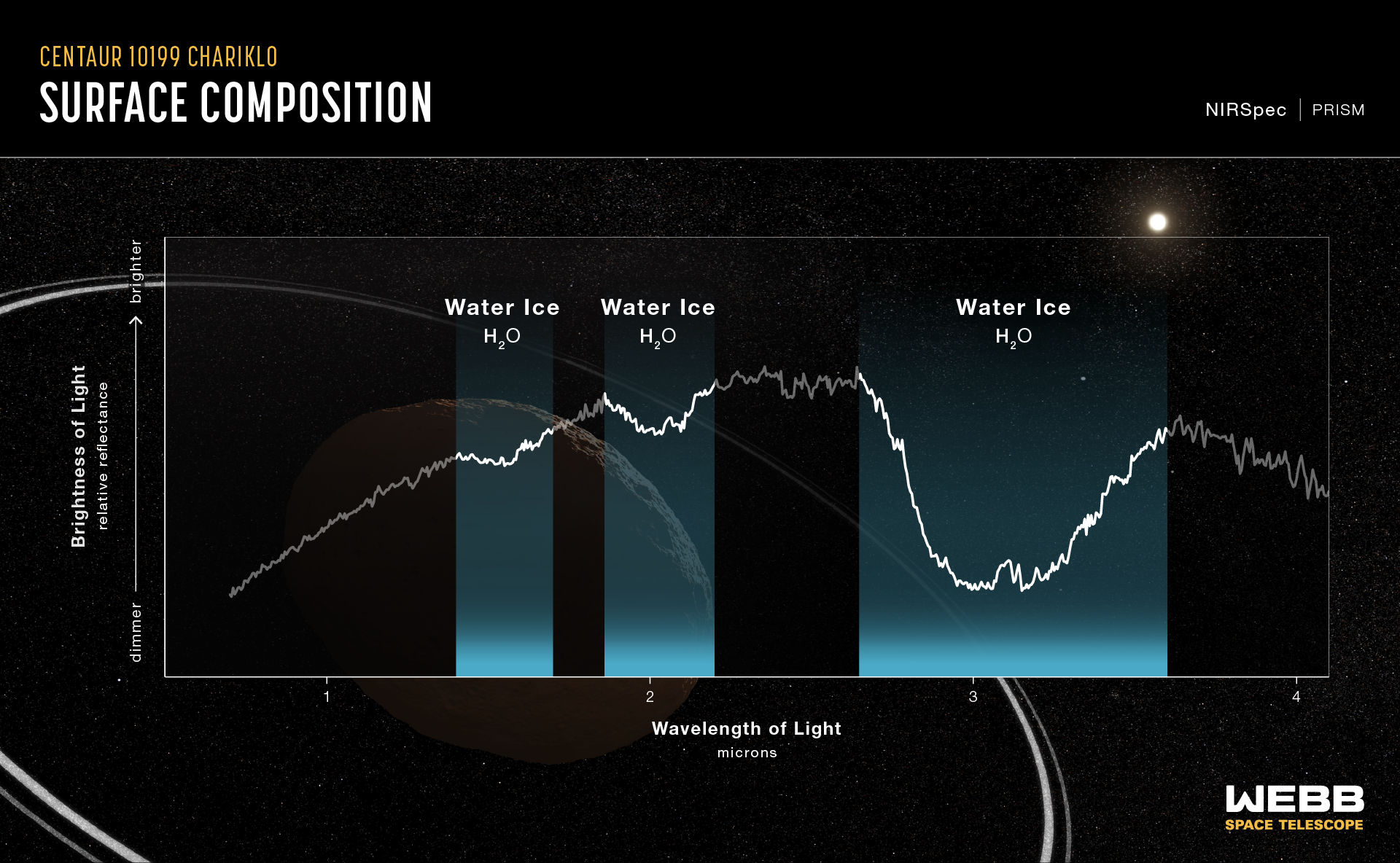
Astronomers have gotten one step nearer to learning the Chariklo system, however there’s nonetheless a lot that is still unknown concerning the centaur. The spectrum analyzed within the newest analysis contains details about the system as an entire, however in the mean time, it’s troublesome to differentiate the info between Chariklo and its two rings.
For instance, though astronomers noticed the primary clear indicators for crystalline water ice, they don’t but know for positive the place within the asteroid’s system the ice is current. Within the coming months, researchers hope to make use of Webb’s excessive sensitivity to dig up particular person options of Chariklo and its two rings, Pablo Santos-Sanz, an astronomer on the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía in Spain who took half on this analysis, stated within the assertion.
“We hope [to] achieve perception into why this small physique even has rings in any respect, and maybe detect new fainter rings,” Santos-Sanz stated.
Observe Sharmila Kuthunur on Twitter @Sharmilakg (opens in new tab). Observe us @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab), or on Facebook (opens in new tab) and Instagram (opens in new tab).




