Whereas the Earth absorbs plenty of vitality from the sun, plenty of it’s mirrored again into space. The daylight mirrored from Earth is named Earthshine. We will see it on the darkish portion of the moon throughout a crescent moon. The Farmer’s Almanac stated it was once known as “the new moon within the previous moon’s arms.”
Earthshine is one occasion of planetshine, and after we take a look at the sunshine from distant exoplanets, we’re trying instantly at their planetshine with out it bouncing off one other object.
If distant astronomers had been Earthshine the best way we take a look at exoplanet shine, would the sunshine inform them our planet is rippling with life?
Within the subsequent few years, plenty of superior telescopes will come on-line. Along with the JWST, they’re going to give us the forms of photographs scientists have been eagerly anticipating for many years. Due to the ground-based European Extraordinarily Giant Telescope and Big Magellan Telescope, and the upcoming LUVOIR space telescope, we’ll enter an age of directly-imaged exoplanets. Scientists want to arrange for all these observations and knowledge so that they’ll be ready to interpret them.
These future telescopes will enable astronomers to characterize increasingly Earth-like exoplanets, we hope. However the one approach our characterizations of those planets will be correct is that if our fashions are correct. Since Earth is the one planet we all know of that hosts life and the one liveable planet with identified properties, it is our solely check case and the one useful resource astronomers must validate their fashions.
That is the place Earthshine is available in.
In a brand new paper, a staff of researchers examined how Earthshine can be utilized to construct correct fashions of planetshine. The paper is “Polarized Signatures of a Liveable World: Evaluating Fashions of an Exoplanet Earth with Seen and Close to-infrared Earthshine Spectra.” The lead creator is Kenneth Gordon, a graduate pupil on the Planetary Sciences Group on the College of Central Florida. The paper’s been accepted into The Astrophysical Journal.
We’re discovering a rising variety of rocky planets in probably liveable zones round exoplanets. However to get nearer to understanding in the event that they’re liveable, we have to characterize their surfaces. Astronomers have restricted instruments to try this, largely by finding out the sunshine from the planets as they transit in entrance of their star or detecting the flux instantly from the planet.
These strategies work for big, gaseous planets. However they’re troublesome for rocky planets, and rocky planets are what we’re inquisitive about. Giant gaseous planets have puffy atmospheres that make spectroscopic research simpler. And so they emit or mirror extra mild because of their dimension, giving them a better flux in direct imaging. However rocky planets have a lot smaller atmospheres which might be tougher to review spectroscopically. As a result of they’re smaller, their flux can be decrease, making them troublesome to picture instantly.
As our telescopes change into extra highly effective, they’re going to overcome a few of these obstacles to characterizing rocky exoplanets. This new paper is a part of how the astronomy group is making ready.
Of their paper, the authors level out how even the highly effective JWST is hampered in its efforts to completely characterize Earth-like exoplanets. Characterizing the atmospheres of those planets round cool dwarf stars requires lengthy durations of statement. In a earlier paper, a separate staff of researchers confirmed that the JWST would wish to watch greater than 60 transits of one of many well-known TRAPPIST-1 rocky exoplanets to detect Earth-like ranges of ozone.
“Utilizing JWST’s Close to-InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI), they discovered that >60 transits for 1b and >30 transits for 1c and 1d can be required to detect present-day Earth ranges of ozone (O3) on these planets,” the authors write. That is a major expenditure of observing time.
The JWST may even wrestle with what astronomers name degeneracies. “… plenty of degeneracies will nonetheless exist within the characterizations of liveable worlds by JWST, resembling differentiating between the optical thicknesses and particle-size distributions of clouds,” they write.
The researchers give attention to polarimetry of their work. In a nutshell, polarimetry is the measurement of polarized mild that is been affected one way or the other by materials that it passes by way of, displays off, or is refracted or diffracted by. Polarimetry can be the interpretation of the measurements.
Polarimetry may very well be key to breaking the impasse between our superior telescopes and the small, rocky planets we need to research. It might scale back the wanted statement time, too. “Polarimetry is a robust method that has the power to interrupt these degeneracies because it assesses bodily elements of sunshine not measured in non-polarimetric photometry or spectroscopy.”
Polarimetry is highly effective as a result of it’s totally delicate to the properties of exoplanet atmospheres. It is confirmed its effectiveness in finding out our personal solar system, together with shrouded-by-clouds Venus. “Polarimetry has helped to characterize our bodies within the solar system, together with the clouds of Venus and the fuel giants, in addition to the differing icy circumstances of the Galilean moons,” the authors clarify. Polarimetry has been so efficient in finding out Venus that some need to construct a polarimetric radar to review the planet extra absolutely.
The issue is astronomers haven’t got fine-tuned polarimetric fashions of exoplanets to assist them perceive what they’re seeing once they research polarimetric planetshine. Fashions exist, however they must be examined and validated towards actual planets, and that is the place Earth is available in. “Thus far, the Earth is the one identified and noticed liveable “Earth-like’ planet, thus serving as a benchmark to deduce the biosignatures of life as we all know it at this time,” the authors state.
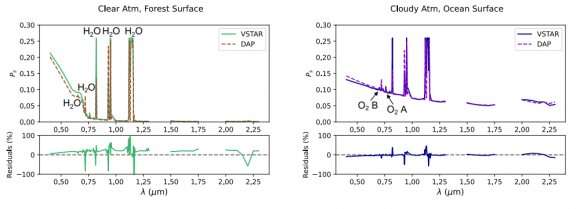
Earthshine is vital to this, in keeping with the researchers. “Research of the optical and near-infrared (NIR) earthshine flux spectra reveal diagnostic biosignatures of the Earth, together with the vegetation pink edge (VRE), the ocean glint, and spectral options of atmospheric O2 and H2O.” Different research have additionally proven what an efficient contribution polarimetry could make in these observations.
The sunshine that displays off the Earth is polarized, however after bouncing off the moon, it is depolarized. The authors corrected that of their work. They thought-about 5 various kinds of planetary surfaces underneath each a cloudless and a cloudy sky. Additionally they thought-about various kinds of clouds with completely different particle sizes.
The principle level of the research was to match two completely different present fashions that astronomers can use to interpret polarimetry and gauge their accuracy. One’s known as DAP, and the opposite’s known as VSTAR. The staff used each to interpret their polarimetric knowledge after which in contrast them.
This type of analysis illustrates how a lot work goes into scientific endeavors. Whereas astronomy headlines would possibly make issues sound easy, it is sophisticated. There’s much more to it than simply pointing highly effective telescopes at distant objects after which trying on the photos. It takes a devoted effort from hundreds of individuals over a long time to make astronomy work. There’s loads at stake, and if sometime a staff of astronomers will get to say, “We did it! We found a planet with life!” it’s going to be due to detailed, intricate work like this that does not generate many headlines.
Extra info:
Kenneth E. Gordon et al, Polarized Signatures of a Liveable World: Evaluating Fashions of an Exoplanet Earth with Seen and Close to-infrared Earthshine Spectra, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2301.05734
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
May next-generation telescopes see that Earth has life? (2023, January 19)
retrieved 19 January 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-01-next-generation-telescopes-earth-life.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




