China’s authorities has formally authorized three robotic moon missions that can lay groundwork for a everlasting lunar base.
The Chang’e program missions in growth are progressing effectively, the China Nationwide Area Administration (CNSA) introduced on Sept. 10, with the following spacecraft, Chang’e 6, nearly full.
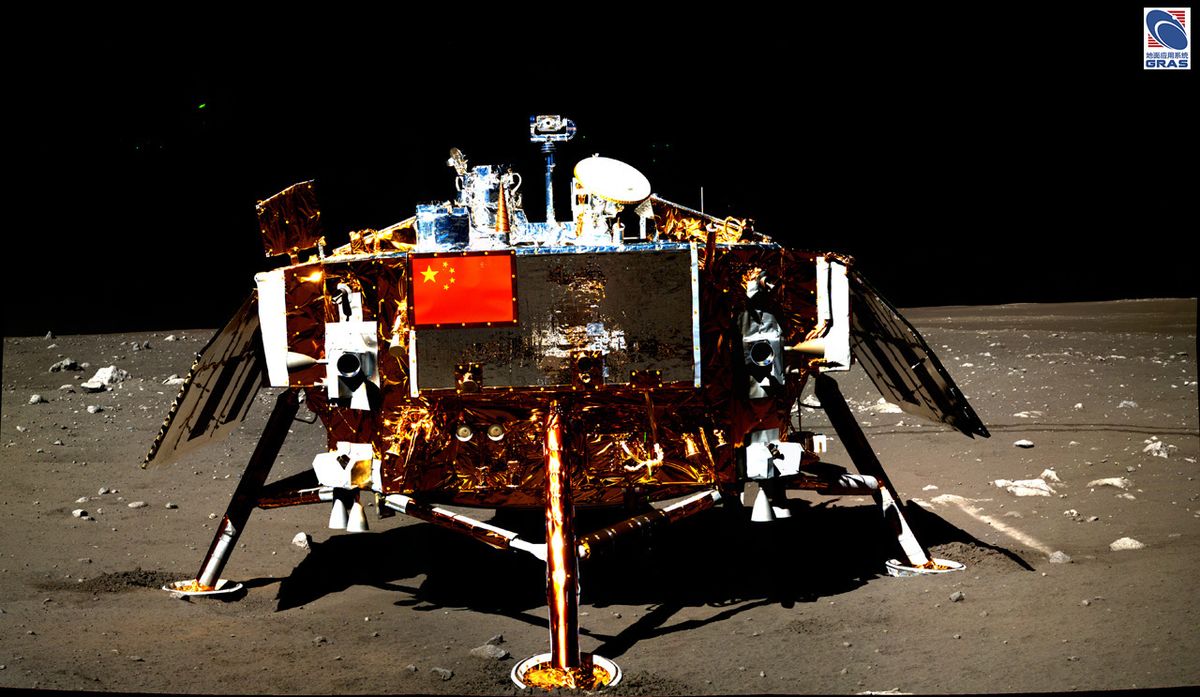
China has made a lot of leaps in lunar exploration since starting its robotic moon program in 2004. In successive missions, the nation has efficiently launched first a pair of orbiters, then a lander and a rover; performed the one far-side lunar landing thus far; and most just lately executed a posh sample-return mission.
Associated: China’s Yutu 2 rover spots cube-shaped ‘mystery hut’ on far side of the moon
Liu Jizhong, director of CNSA’s Lunar Exploration and Area Program Middle, advised CCTV (opens in new tab)that the overarching objective of those missions is to put a basis for a lunar analysis station.
“There are quite a lot of technological points to be tackled” Liu stated. “Nevertheless, with the muse we have constructed up and a very good staff, I imagine we are going to succeed.”
The primary of the brand new missions will likely be Chang’e 6, which was initially constructed as a backup to the 2020 Chang’e 5 lunar sample-return mission. Chang’e 5 was profitable, so the spacecraft is being repurposed for the first-ever try at amassing samples from the far aspect of the moon. CNSA has not supplied a timeline for the mission, regardless of the superior levels of growth of the spacecraft.
Subsequent, Chang’e 7 will goal the lunar south pole. The mission will encompass an orbiter, lander, rover, relay satellite and a small detector that may hop into craters to hunt for water.
Chang’e 8 will launch later within the decade and is meant to check applied sciences for 3D printing and for utilizing native assets.
China is planning a undertaking named the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) in collaboration with Russia for the 2030s and is searching for companions to affix the endeavor.
Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.