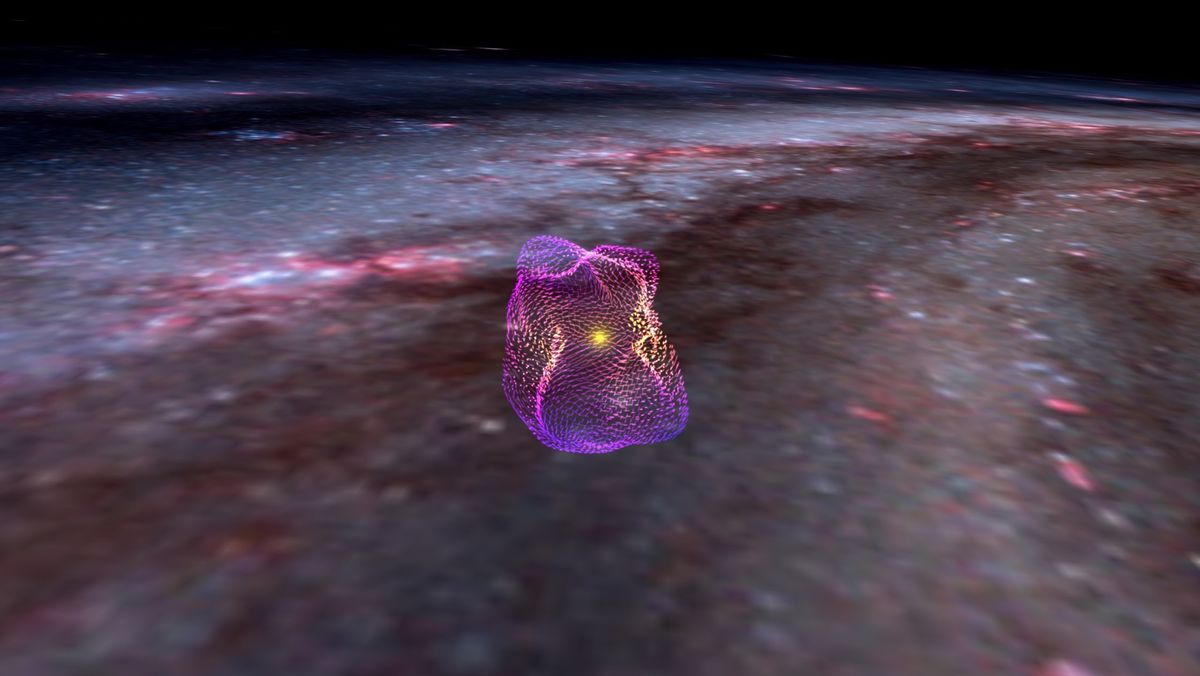
Interstellar cartographers have for the primary time mapped in 3D the magnetic subject swept up by the Native Bubble.
The Native Bubble is a cavity a minimum of 1,000 light-years huge within the interstellar gasoline across the solar system — a ‘superbubble’ in interstellar space. The Native Bubble was blown out by a sequence of supernovas between 10 million and 20 million years in the past, and is considered one of many such bubbles within the interstellar medium that riddle our Milky Way galaxy and others just like the cavities in Swiss cheese.
“Placing collectively this 3D map of the Native Bubble will assist us look at superbubbles in new methods,” Theo O’Neill, who used knowledge from the European House Company’s (ESA) Gaia and Planck missions to assemble the map, stated in an announcement. O’Neill was an undergraduate scholar on the College of Virginia when he made the map throughout a summer season analysis camp on the Harvard–Smithsonian Heart for Astrophysics, beneath the tutelage of Harvard astrophysicist Alyssa Goodman.
Associated: Hear the sounds of starquakes across the Milky Way from Gaia probe
“We have lengthy identified that magnetic fields should play essential roles in lots of astrophysical phenomena,” Goodman stated within the assertion.
“However finding out these magnetic fields has been notoriously tough,” she stated. “As we speak’s pc simulations and all-sky surveys may lastly be ok to start out actually incorporating magnetic fields into our broader image of how the universe works, from the motions of tiny dust grains on as much as the dynamics of galaxy clusters.”
The important thing to mapping the magnetic-field construction of the Native Bubble is interstellar dust, notably charged particles that may comply with magnetic subject strains throughout space. Specifically, ESA’s Planck mission, which studied the cosmic microwave background radiation between 2009 and 2013, was additionally delicate to polarized microwave emission from this charged dust. The polarization tells of the orientation wherein the dust is emitting microwaves; this orientation is affected by the magnetic-field strains. In the meantime, observations by ESA’s Gaia spacecraft, which launched in 2013, charted the situation of interstellar dust on the floor of the Native Bubble, which is increasing and sweeping up each dust and magnetic subject strains which are strewn all through space.
To begin, O’Neill assembled a 2D map of magnetic fields on the sky, earlier than performing a geometrical evaluation to show it right into a 3D illustration. Previous research by Goodman had discovered that many of the younger stars and areas of star formation within the neighborhood of the sun are to be discovered on the sting of the increasing Native Bubble, the place dust and gasoline is compressed. O’Neill’s map reveals that certainly the magnetic-field strains do coincide with massive websites of star formation on the floor of the Native Bubble, such because the Orion Molecular Cloud that’s house to the well-known Orion Nebula, positioned 1,344 light-years away from Earth.
There are some caveats, nonetheless, resulting in the map being considerably tough across the edges. “We have made some large assumptions to create this primary 3D map of a magnetic subject; it is under no circumstances an ideal image,” Goodman stated.
The 2 essential assumptions are first that the dust producing the polarized emission is on the floor of the Native Bubble and never farther away, and second that magnetic-field strains are being swept up onto the sting of the Native Bubble because it expands. Nevertheless, as each pc modeling and scientists’ understanding of superbubbles improves, so too will the accuracy of the map.
As within the Native Bubble, astronomers consider that superbubbles basically play a major position within the means of star formation.
“House is filled with these superbubbles that set off the formation of recent stars and planets and affect the general shapes of galaxies,” O’Neill stated. “By studying extra in regards to the precise mechanics that drive the Native Bubble, wherein the sun lives in the present day, we will study extra in regards to the evolution and dynamics of superbubbles basically.”
O’Neill offered the analysis on the 241st assembly of the American Astronomical Society, being held this week in Seattle and just about.
Comply with Keith Cooper on Twitter @21stCenturySETI. Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.