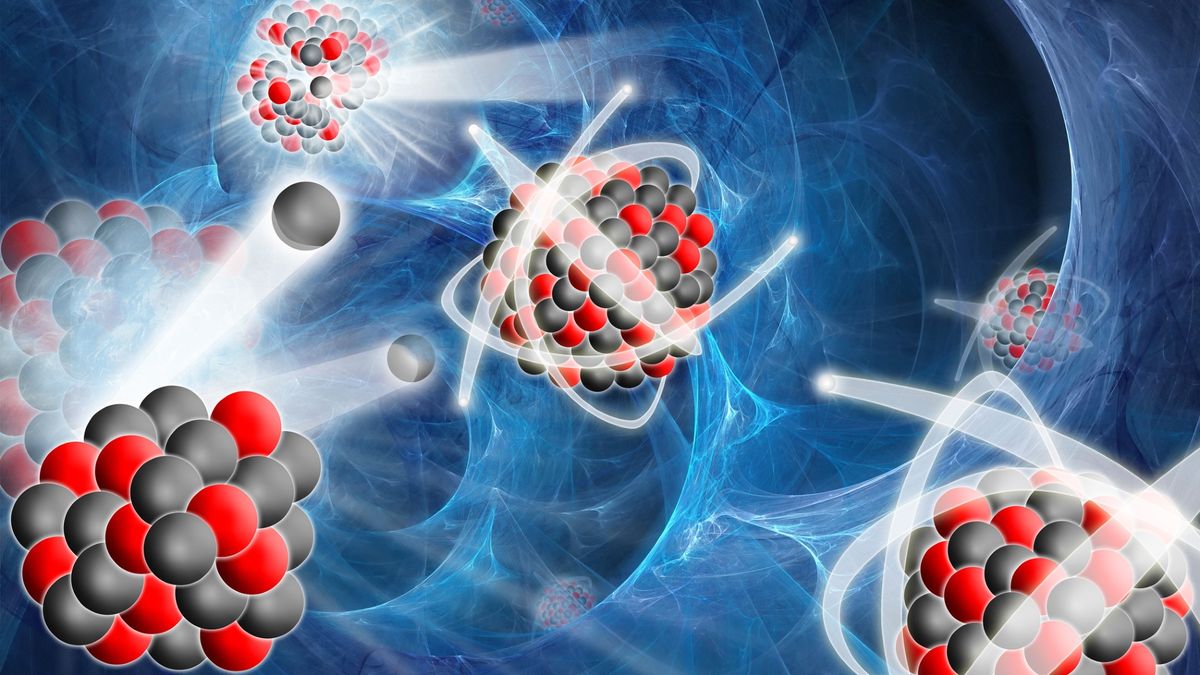
Nuclear fission is the method of breaking massive atomic nuclei into smaller atomic nuclei to launch a considerable amount of power.
This course of is normally performed by forcing the nuclei to soak up neutrons — the particle normally discovered within the atomic nucleus with protons. The phenomenon has been harnessed by humanity to each present power by way of nuclear power vegetation, but in addition to energy nuclear weapons.
Fission is a type of nuclear transmutation, which means that the beginning atoms usually are not the identical components because the resultant — or daughter — product atoms. The fission course of can happen spontaneously as a kind of radioactive decay however that is uncommon, extremely sluggish, and restricted to very heavy chemical components.
Associated: What is nuclear fusion?
Robert Lea holds a bachelor of science diploma in physics and astronomy from the U.Okay.’s Open College. Robert has contributed to House.com for over a decade, and his work has appeared in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Journal, All About House and extra.
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is the method of splitting atomic nuclei into smaller nuclei, releasing massive quantities of power in consequence. Nuclear fission may also help humankind meet its power wants when chain reactions are managed in reactors. Nuclear energy now gives an estimated 85 p.c of the electrical energy we use.
When this course of is allowed to run unchecked, nevertheless, it provides rise to a strong and damaging drive. The detonation of so-called ‘atom bombs’ is signified by the sight of a mushroom cloud — a dreadful reminder of the facility of the atom and of fission itself.
When was nuclear fission found?
The invention of induced fission would not have been potential with out the strides made by Ernest Rutherford and Niels Bohr towards a coherent image of the atom through the 1910s.
This led to the invention by Henri Becquerel, Marie Curie, Pierre Curie, and Rutherford that the atoms of components might ‘decay’ and transmute to a different factor by way of the emission of an alpha particle.
Two years after the invention of the neutron in 1932 by James Chadwick, Enrico Fermi and his colleagues in Rome started pelting these newly discovered particles at uranium with different physicists additionally reaching the conclusion the particle would make an excellent probe of the atomic nucleus.
In 1933, Hungarian physicist Leó Szilárd first formalized the concept neutron-driven fission of heavy atoms might be used to create a nuclear chain response having generated power by utilizing protons to separate lithium the yr earlier than.
Lastly, in December 1938, physicists Lise Meitner and Otto Frisch realized that isotopes of barium that appeared mysteriously throughout neutron-uranium bombarding experiments performed by colleague Otto Hann had been the results of the uranium nuclei present process fission.
(opens in new tab)
How does nuclear fission produce power?
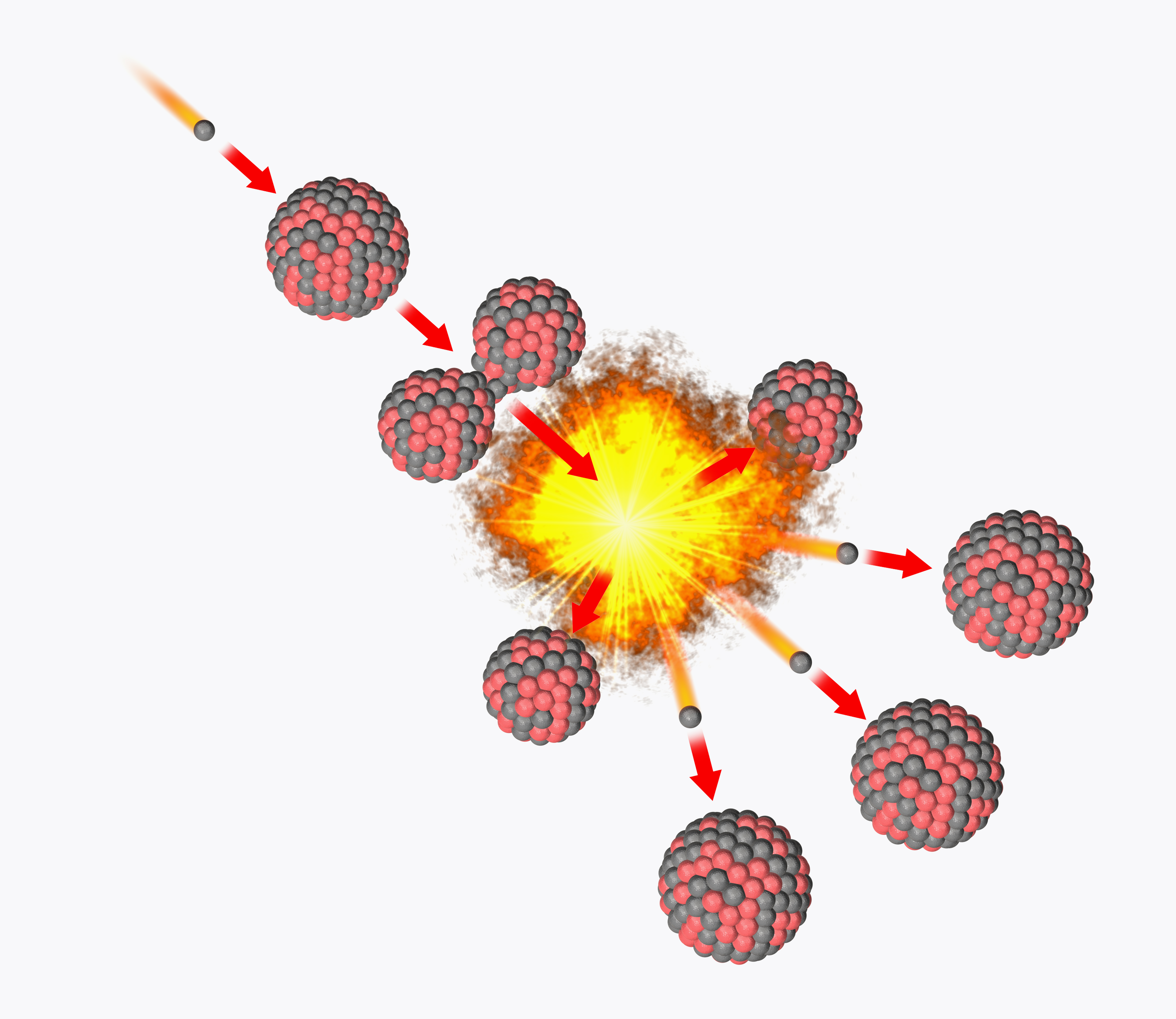
Induced nuclear fission happens when a particle — generally a neutron — passes a big goal atomic nucleus and is captured by it. In nuclear reactors, that is an isotope — an atom with a special neutron rely in its nucleus — of the heavy components uranium or plutonium.
The power wanted to kick begin fission is round 7 to eight million electronvolts (MeV), and when a neutron carrying this degree of power or extra strikes the goal nucleus, the power it imparts deforms the nucleus right into a double-lobed peanut-like form.
The hole between the lobes created by neutron seize finally exceeds the purpose at which the strong nuclear force — which binds protons and neutrons collectively within the atomic nucleus and is highly effective solely throughout tremendously small ranges — can maintain them collectively.
Because of this, the nucleus fractures into smaller fragments , normally round half the mass of the beginning particle, additionally releasing not less than two, generally three, neutrons.
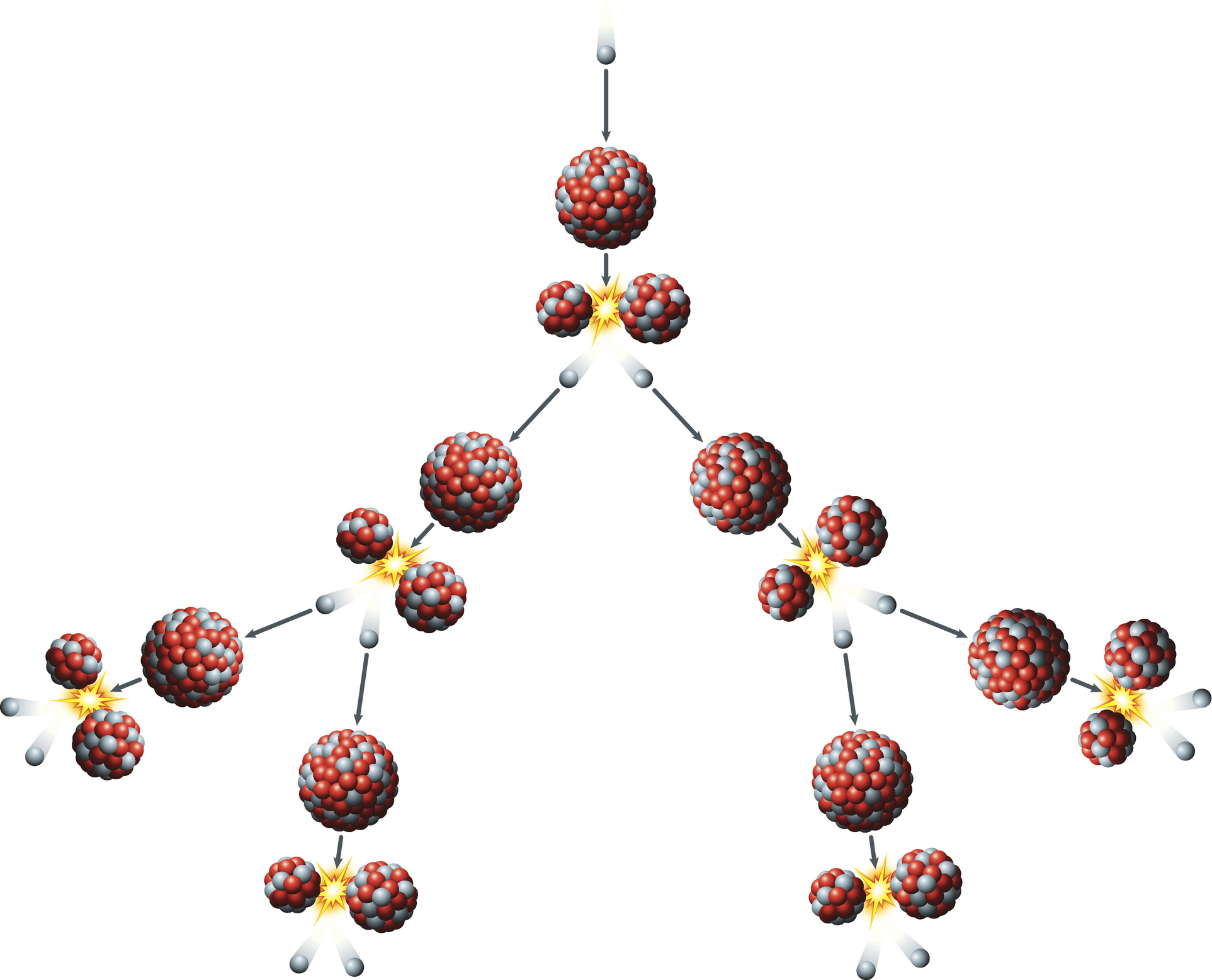
The daughter particles are quickly pushed aside because of their constructive costs repelling each other. The launched neutrons touring at a velocity of round 33 million ft per second (10 million meters per second, or about three p.c of the velocity of sunshine) — go on to strike two extra nuclei, inflicting them to separate and launch 4 neutrons. These neutrons are then ejected, placing different nuclei.
This results in a series response of splitting nuclei, producing a doubling of fission reactions every time a nucleus is break up. Which means by the tenth ‘technology,’ there are 1,024 fissions, and by technology 80 there are 6 x 10²³ fission reactions.
(opens in new tab)
The explanation this course of releases power is said to Albert Einstein’s discovery that mass and power are interchangeable. In its easiest type, that is encapsulated by arguably the world’s most well-known equation: power equals mass occasions the velocity of sunshine squared or e=mc².
When a fissile materials absorbs a neutron and breaks aside, the mass going into the response is barely larger than the mass than emerges from it. The distinction in mass between the beginning particle and its daughter particles is tiny — about 0.1 p.c of the unique mass.
That is when the time period c² turns into vital as this tells us that even a tiny quantity of mass liberates lots of power.
Round 85 p.c of this power liberated in fission reactions is launched as kinetic power granted to the daughter nuclei. This power is then transformed to warmth. The remainder of the power is transferred as kinetic power to the launched neutrons or carried away by high-energy radiation within the type of gamma rays.
The exact daughter merchandise created in fission cannot be precisely predicted, as the method is topic to a excessive diploma of probability and variation. In truth, a lot in order that there is not any agency assure the seize of a neutron will occur or that this can even result in fission.
One sure factor is that the variety of protons and neutrons that goes into the method will probably be preserved at its conclusion.
One frequent response in nuclear reactors is the seize of a neutron by uranium-235 which creates two daughter neutrons and atomic nuclei of barium-144 and krypton-90. This response releases about 200 megaelectronvolts (MeV) which is equal to only 0.000000000032 Joules.
It is these created neutrons which are liable for making fission a viable energy-generating mechanism. However this must be strictly managed.
Chain reactions and significant mass
Not the entire neutrons created in fission can be found to drive additional reactions, as some might be misplaced as fission proceeds. If sufficient neutrons might be maintained, nevertheless, the fission response turns into self-sustaining with this level described as ‘crucial mass.’
This self-sustaining crucial mass level in nuclear fission is decided by a number of components throughout the fissile materials itself together with its composition, its density, how pure it’s, and even the bodily form it’s organized in.
Spheres have been discovered to reduce neutron loss that may forestall crucial mass from being reached, which will also be lowered by surrounding the fissile materials with a ‘neutron reflector’ which bounces again any stray neutrons.
One of many key features of creating fission secure is controlling the chain response and the speed of fission. If lower than one neutron from a fission response causes an additional response, this will result in fission operating uncontrolled and an explosion.
Which means limiting the variety of neutrons obtainable to go on to create additional fission reactions. In lots of reactors, that is performed by introducing materials that may ‘take in’ neutrons, permitting the chain response to be sustained whereas additionally stopping fission from operating uncontrolled.
‘Management rods’ composed of boron or cadmium — components which are robust neutron absorbers — or a mixture of each are a standard mechanism for controlling energy ranges in fission reactors. Energy might be elevated by barely withdrawing management rods and permitting neutrons to drive up reactions. when the specified energy degree is reached, management rods might be re-inserted to stabilize reactions.
In some reactors, water infused with boron is used as a coolant with its focus lowered as fission created neutron absorbing by-products.
Associated: US military wants to demonstrate new nuclear power systems in space by 2027
(opens in new tab)
Water will also be used to strip the power away from quick neutrons launched with an excessive amount of kinetic power. This makes these neutrons extra more likely to go on to set off fission or to be absorbed by management rods.
Delayed neutrons — created at any time after fission starting from just a few milliseconds to minutes — are additionally vital in stopping chain reactions from operating uncontrolled.
Produced in small quantities, delayed neutrons have much less power than instantly emitted ‘immediate neutrons,’ and with out them the fission chain response could be unbalanced, resulting in a nearly instantaneous and uncontrollable rise or fall within the neutron inhabitants.
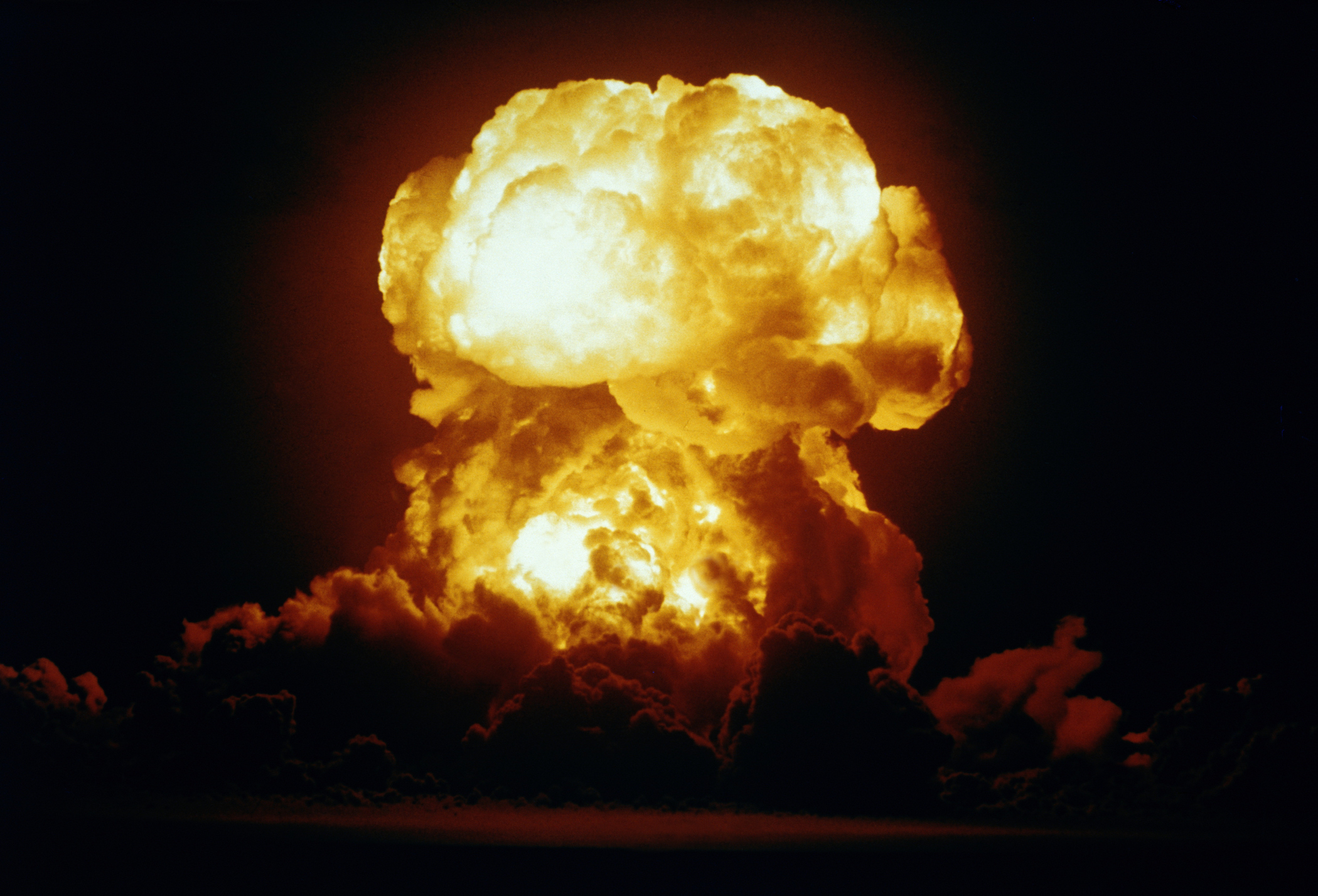
Atom bombs are powered by a mass of fission nuclei assembled instantaneously and held collectively for a few millionth of a second. This enables the chain response to quickly unfold by way of the fissile materials exhibiting what occurs when chain reactions usually are not managed.

(opens in new tab)
Is nuclear fission secure?
After the world witnessed the detonation of atomic bombs and the destruction and lack of life that they wrought within the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, it’s little surprise that most people is cautious of nuclear energy.
Regardless of outstanding and well-known examples of nuclear fission accidents all through historical past akin to these at Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima, this supply of power is safer than ever.
In 2022, Our World in Information reported that for each terawatt-hour of power generated by fission there are just 0.07 deaths (opens in new tab), in comparison with 32.7 deaths for a similar quantity of power generated by fossil fuels.
Even these notorious accidents themselves could have claimed fewer lives than their horrible stain on historical past would have most of us imagine.
The World Nuclear Affiliation says that the 2011 Fukushima accident, triggered when a magnitude-9 earthquake triggered a 50-foot (15-meter) tsunami that disabled the plant’s energy provide and cooling mechanisms, claimed zero lives as the results of radioactive materials leaks.
Likewise, in response to the World Nuclear Affiliation, the 1979 Three Mile Island accident in Pennsylvania triggered no deaths because of the leak of radioactive fuel brought on by a cooling malfunction.
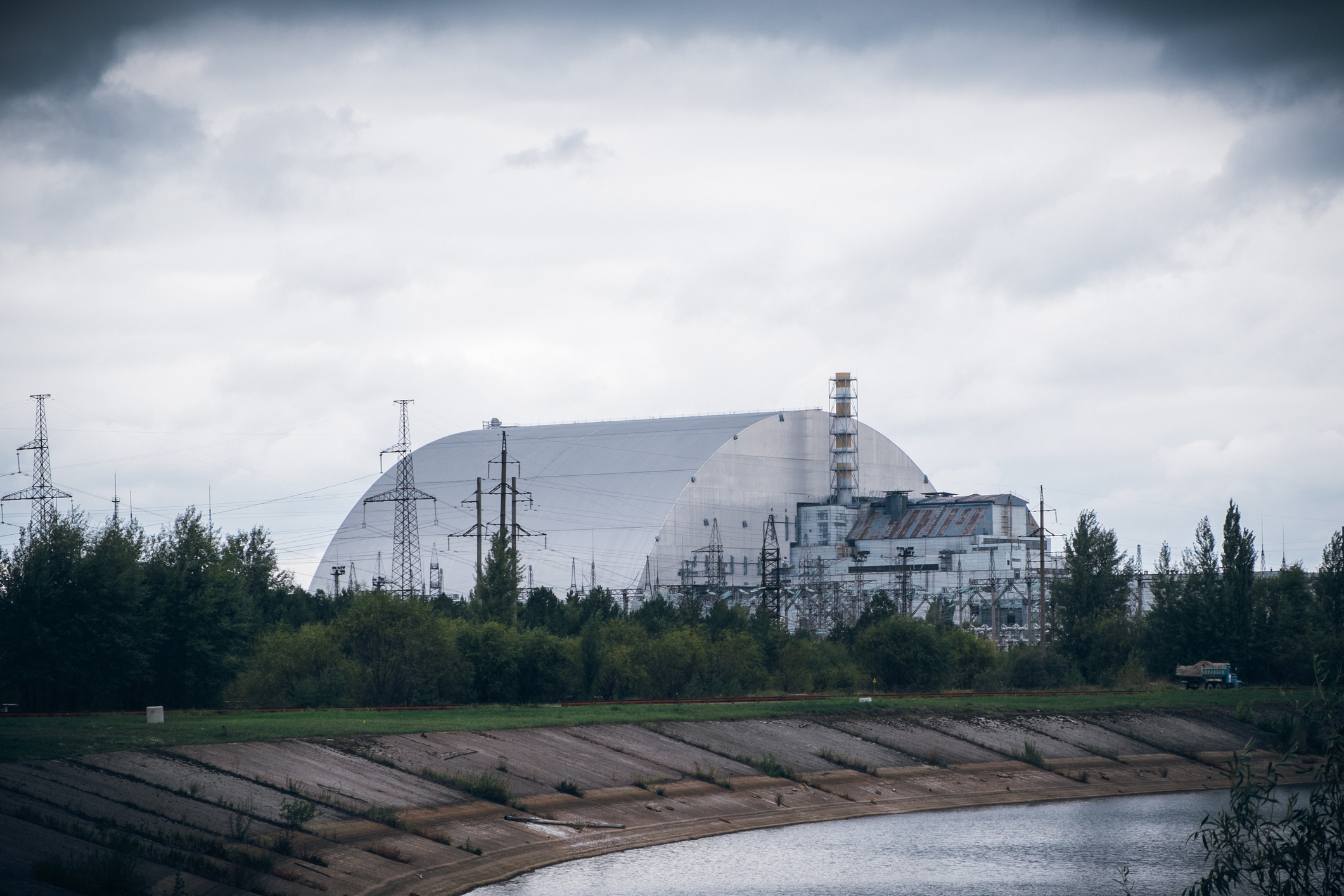
Arguably the world’s most well-known nuclear accident occurred on the Chernobyl Nuclear Energy Plant, close to town of Pripyat in Ukraine in 1986 because of a flawed reactor design that was operated with inadequately educated personnel.
This resulted in two staff being killed in an explosion and an additional 28 folks dying inside weeks of the accident. The World Nuclear Affiliation additionally attributes over 5,000 thyroid most cancers circumstances, together with 15 fatalities, to the accident. To this day, a 1,000-square-mile (2,600-square-kilometer) uninhabited exclusion zone stays across the former plant.

(opens in new tab)
One of many causes for the spectacular security of present fission energy vegetation is that high-profile accidents like these listed above have prompted the event of improved designs and security options.
The present iteration of fission vegetation are Generation III reactors (opens in new tab). These are notable for a number of options, notably a lowered chance of core-melt accidents.
Many security options are inherent to the designs of those reactors, for instance, quick neutron reactors function utilizing a system that slows as temperature will increase.

(opens in new tab)
What about nuclear waste?
One frequent fantasy about nuclear energy is that ‘nuclear waste,’ the radioactive by-products of fission processes, lasts without end.
Whereas there is no such thing as a doubt that the secure storage and disposal of fission by-products is a priority, a lot of this materials is definitely recyclable and has been responsibly managed because the onset of civil nuclear energy.
The World Nuclear Affiliation (WNA) says fission reactors create a small quantity of waste that is available in three varieties, ranked primarily based on their degree of radioactivity from low, to intermediate, to high-level.
The group provides that 90 p.c of fission waste suits within the first low radioactivity class. Excessive-level nuclear waste accounts for 3 p.c of total waste however releases 95 p.c of the radioactivity of fissile waste.
Regardless of the image of hazardous nuclear waste popularized by “The Simpsons” and different pop-culture staples, this waste is not a glowing inexperienced ooze. Somewhat most of that is ‘spent gasoline’ within the type of steel rods containing ceramic pellets of enriched uranium.
Spent nuclear gasoline might be recycled to create new gasoline and byproducts, with the Workplace of Nuclear Power suggesting that it retains 90 percent of its potential energy (opens in new tab) even half a decade after use in a reactor.
At present, whereas international locations like France recycle spent nuclear gasoline, america would not do that, although plans are underway for reactors that might function with spent gasoline.
In america, used gasoline rods are enclosed in steel-lined concrete swimming pools of water or are encased in metal and concrete containers after which saved at 76 totally different reactor websites throughout 34 states. This spent gasoline waits right here for a everlasting disposal resolution.
Further Studying
Humanity should never neglect the potential for destruction offered by nuclear fission. Father John A. Siemes, professor of recent philosophy at Tokyo’s Catholic College, provides an eyewitness account (opens in new tab) of the detonation of an atom bomb over Hiroshima.
The final boson of the usual mannequin to be found, the Higgs boson, determines how different particles get their mass.
Bibliography
“Nuclear Fission: Basics (opens in new tab).” Atomic Archive (2022).
“Nuclear fission (opens in new tab).” Britannica (2022).
“Fissile Elements: Supply and Demand (opens in new tab).” MIT (2022).
“Physics of Uranium and Nuclear Power.” World Nuclear Affiliation (2022).
“Physics and Kinetics of TRIGA Reactors (opens in new tab).” IAEA (2022).
“Fukushima Daiichi Accident (opens in new tab).” World Nuclear Affiliation (2022).
“Three Mile Island Accident (opens in new tab).” World Nuclear Affiliation (2022).
“Chernobyl Accident 1986 (opens in new tab).” World Nuclear Affiliation (2022).
“What is nuclear waste, and what do we do with it (opens in new tab)? World Nuclear Affiliation (2022).
“5 Fast Facts about Spent Nuclear Fuel (opens in new tab)” Workplace of Nuclear Power (2022).
“Nuclear Energy (opens in new tab).” Our World in Information (2022).
“This Month in Physics History (opens in new tab).” APS Physics (2007).
Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or on Facebook (opens in new tab).