A couple of days after formally beginning science operations, the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb House Telescope propelled astronomers right into a realm of early galaxies, beforehand hidden past the grasp of all different telescopes. Webb is now unveiling a really wealthy Universe the place the primary forming galaxies look remarkably totally different from the mature galaxies seen round us at this time.
Researchers have discovered two exceptionally shiny galaxies that existed roughly 300 and 400 million years after the Massive Bang. Their excessive brightness is puzzling to astronomers. The younger galaxies are reworking fuel into stars as quick as they’ll they usually seem compacted into spherical or disk shapes which are a lot smaller than our Milky Way galaxy. The onset of stellar start might have been simply 100 million years after the Massive Bang, which occurred 13.8 billion years in the past.
“Every part we see is new. Webb is exhibiting us that there is a very wealthy Universe past what we imagined,” mentioned Tommaso Treu of the College of California at Los Angeles, a co-investigator on one of many Webb packages. “As soon as once more the Universe has shocked us. These early galaxies are very uncommon in some ways.”
The outcomes are from Webb’s GLASS-JWST Early Launch Science Program (Grism Lens-Amplified Survey from House), and Cosmic Evolution Early Launch Science Survey (CEERS). Two analysis papers, led by Marco Castellano of the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics in Rome, Italy, and Rohan Naidu of the Heart for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and the Massachusetts Institute of Expertise in Cambridge, Massachusetts have been revealed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
In simply 4 days of research, researchers discovered two exceptionally shiny galaxies within the GLASS-JWST photographs. These galaxies existed roughly 450 and 350 million years after the Massive Bang (with redshifts of roughly 10.5 and 12.5, respectively), which future spectroscopic measurements with Webb will assist verify.
“With Webb, we have been amazed to search out essentially the most distant starlight that anybody had ever seen, simply days after Webb launched its first knowledge,” mentioned Rohan Naidu of the extra distant GLASS galaxy, known as GLASS-z12, which is believed thus far again to 350 million years after big bang. The earlier file holder is galaxy GN-z11, which existed 400 million years after the large bang (redshift 11.1), and recognized in 2016 by Hubble and Keck Observatory in deep-sky packages.
“Based mostly on all of the predictions, we thought we needed to search a a lot larger quantity of space to search out such galaxies,” mentioned Castellano.
“These observations simply make your head explode. It is a complete new chapter in astronomy. It is like an archaeological dig, when instantly you discover a misplaced metropolis or one thing you did not learn about. It is simply staggering,” added Paola Santini, fourth writer of the Castellano et al. GLASS-JWST paper.
“Whereas the distances of those early sources nonetheless have to be confirmed with spectroscopy, their excessive brightnesses are an actual puzzle, difficult our understanding of galaxy formation,” famous Pascal Oesch of the College of Geneva in Switzerland.
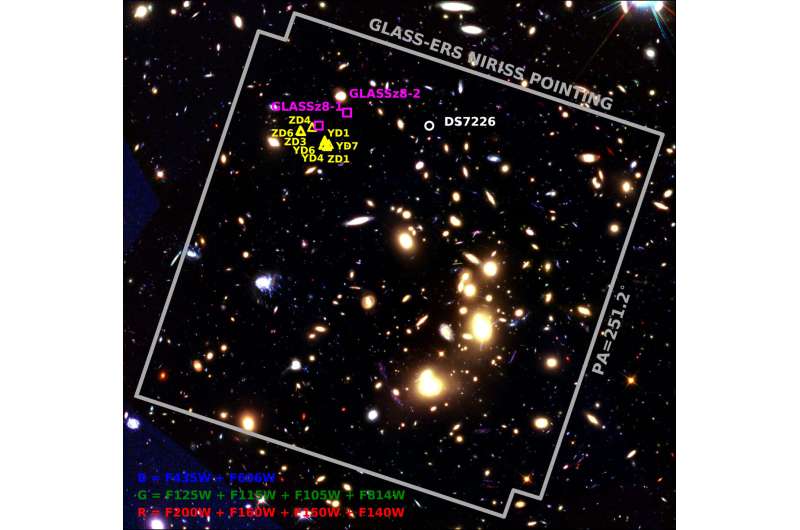

The Webb observations nudge astronomers towards a consensus that an uncommon variety of galaxies within the early Universe have been a lot brighter than anticipated. This may make it simpler for Webb to search out much more early galaxies in subsequent deep sky surveys, say researchers.
“We have nailed one thing that’s extremely fascinating. These galaxies would have needed to have began coming collectively perhaps simply 100 million years after the Massive Bang. No person anticipated that the dark ages would have ended so early,” mentioned Garth Illingworth of the College of California at Santa Cruz. “The primal Universe would have been only one hundredth of its present age. It is a sliver of time within the 13.8-billion-year-old evolving cosmos.”
Naidu/Oesch workforce member Erica Nelson of the College of Colorado famous that “our workforce was struck by having the ability to measure the shapes of those first galaxies; their calm, orderly disks query our understanding of how the primary galaxies fashioned within the crowded, chaotic early Universe.” This exceptional discovery of compact disks at such early occasions was solely potential as a result of Webb’s photographs are a lot sharper, in infrared gentle, than Hubble’s.
“These galaxies are very totally different from the Milky Way or different huge galaxies we see round us at this time,” mentioned Treu.
Illingworth emphasised that the 2 shiny galaxies discovered by these groups have quite a lot of gentle. He mentioned one choice is that they might have been very huge, with numerous low-mass stars, like later galaxies. Alternatively, they might be a lot much less huge, consisting of far fewer terribly bright stars, often known as Inhabitants III stars.
Lengthy theorized, they’d be the primary stars ever born, blazing at blistering temperatures and made up of solely primordial hydrogen and helium; solely later would stars prepare dinner up heavier components of their nuclear fusion furnaces. No such extraordinarily scorching, primordial stars are seen within the native Universe.
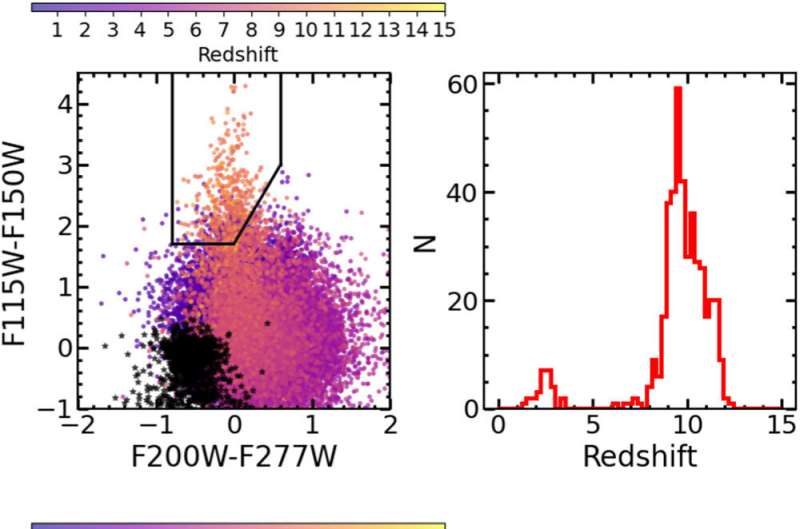
“Certainly, essentially the most distant supply could be very compact, and its colours appear to point that its stellar inhabitants is especially devoid of heavy components and will even comprise some Inhabitants III stars. Solely Webb spectra will inform,” mentioned Adriano Fontana, second writer of the Castellano et al. paper and a member of the GLASS-JWST workforce.
Current Webb distance estimates to those two galaxies are based mostly on measuring their infrared colours. Finally, follow-up spectroscopy measurements exhibiting how gentle has been stretched within the increasing Universe will present impartial verification of those cosmic yardstick measurements.
Extra info:
Marco Castellano et al, Early Outcomes from GLASS-JWST. III. Galaxy Candidates at z ∼9–15*, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2022). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac94d0
Guido Roberts-Borsani et al, Early Outcomes from GLASS-JWST. I: Affirmation of Lensed z ≥ 7 Lyman-break Galaxies behind the Abell 2744 Cluster with NIRISS, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2022). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac8e6e
Supplied by
European Space Agency
Quotation:
Webb attracts again curtain on universe’s early galaxies (2022, November 17)
retrieved 17 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-webb-curtain-universe-early-galaxies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




