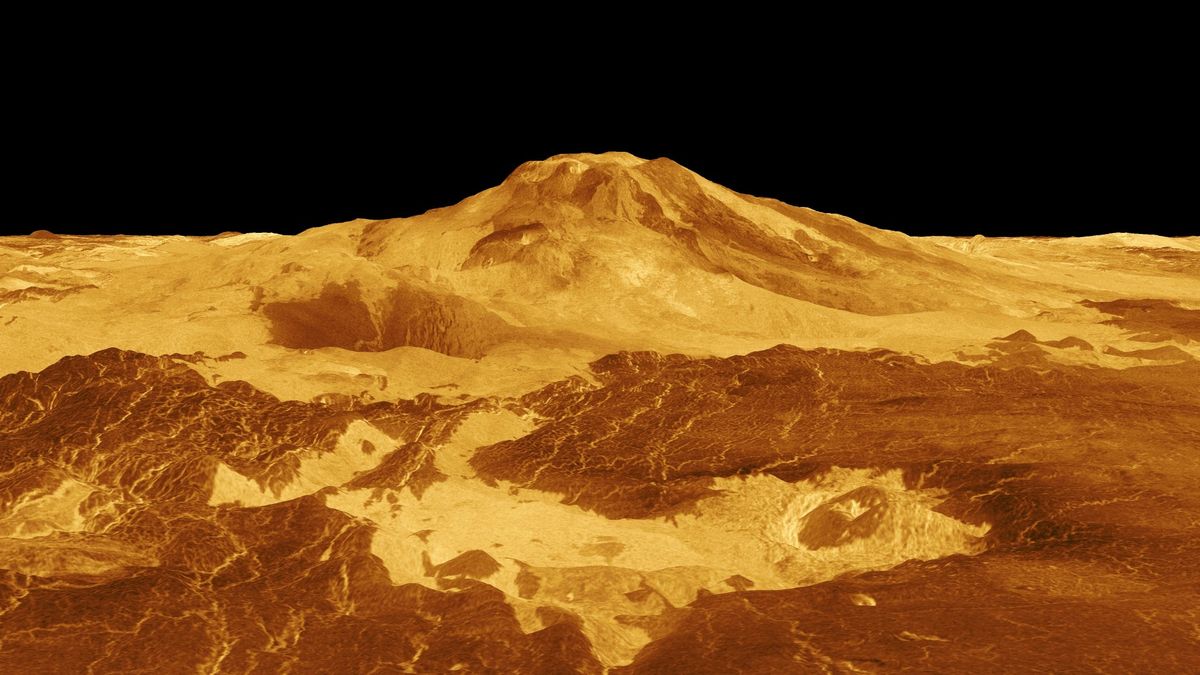
Huge international volcanism that coated 80% of Venus’ floor in lava might have been the deciding issue that reworked Venus from a moist and gentle world into the suffocating, sulfuric, hellish planet that it’s in the present day.
The floor temperature on Venus is a sweltering 867 levels Fahrenheit (464 levels Celsius), sizzling sufficient to soften lead, and there is a crushing stress of 90 atmospheres beneath the dense clouds of carbon dioxide laced with corroding sulfuric acid. Typically decried as Earth‘s “evil twin,” Venus is a sufferer of a runaway greenhouse effect, little question amplified by Venus being about 25 million miles (40 million kilometers) nearer to the sun than Earth and subsequently receiving extra warmth.
But, there’s growing evidence that Venus wasn’t at all times this fashion, and will have as soon as been a temperate world considerably much like Earth — maybe extra just lately, in geological phrases, than anticipated.
Associated: NASA’s Parker Solar Probe captures stunning Venus photo during close flyby
Michael Manner, of NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart in Maryland, has led a lot of the analysis creating this new imaginative and prescient of Venus. Of their newest paper, he and his crew argue that Venus’ volcanism may have in the end been what pushed the planet over the sting by sending huge quantities of carbon dioxide — as we all know, a potent greenhouse fuel — billowing into Venus’ atmosphere.
Within the Nineties, NASA’s Magellan spacecraft radar-mapped the floor of Venus, which is in any other case obscured by the planet’s dense ambiance, and located that a lot of the floor was coated in volcanic basalt rock. Such “massive igneous provinces” are the results of tens of 1000’s, if not lots of of 1000’s of years’ value of massive volcanism that occurred in some unspecified time in the future previously billion years.
Particularly, a number of of those occasions coming within the space of one million years, maybe, and every masking lots of of 1000’s of sq. miles or kilometers in lava, may have endowed Venus’ ambiance with a lot carbon dioxide that the local weather would have been unable to manage. Any oceans would have boiled away, including moisture to the ambiance, and since water vapor can be a greenhouse fuel, accelerating the runaway greenhouse impact. Over time, the water would have been misplaced to space, however the carbon dioxide, and the inhospitable world, remained.
“Whereas we’re not but positive how typically the occasions which created these fields occurred, we must always be capable to slender it down by learning Earth’s personal historical past,” Manner stated in a statement.
The frequency with which large volcanic occasions forming massive igneous provinces have occurred on Earth implies that it’s possible that a number of such occasions may have occurred on Venus inside one million years. These incidents may have scarred Venus endlessly.
Earth itself has had some shut calls. So-called “super-volcanoes” have been linked to quite a few mass-extinction occasions on Earth over the previous half-a-billion years. For instance, the Late Devonian period mass extinction 370 million years in the past has been attributed by some to super-volcanism in what’s now Russia and Siberia, in addition to to a separate super-volcanic eruption in Australia. The Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction is extensively blamed on the formation of the largest of Earth’s massive igneous provinces, the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province, 200 million years in the past. Even the loss of life of the dinosaurs 65 million years in the past might have been attributable to the double whammy of an asteroid strike and super-volcanism within the Deccan Traps, a big igneous province in India.
For unknown causes, comparable volcanic occasions on Venus had been far more widespread and instigated a runaway greenhouse impact that reworked the planet. In the meantime on Earth, the carbon-silicate cycle that acts because the planet’s pure thermostat, exchanging carbon dioxide and different greenhouse gases between the mantle and the ambiance over hundreds of thousands of years, was in a position to stop Earth from following the identical path as Venus.
Two future NASA missions will endeavor to reply a few of these questions. DAVINCI, the Deep Environment Venus Investigation of Noble Gases, Chemistry and Imaging mission will launch later this decade, to be adopted by VERITAS, the Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography and Spectroscopy mission within the early 2030s. The European House Company’s EnVision mission additionally targets launch someday within the 2030s, whereas China has proposed a attainable mission known as VOICE, the Venus Volcano Imaging and Local weather Explorer, that if launched would attain Venus in 2027 to check the planet’s ambiance and geology.
“A main aim of DAVINCI is to slender down the historical past of water on Venus and when it might have disappeared, offering extra perception into how Venus’ local weather has modified over time,” Manner stated.
The findings had been printed within the Planetary Science Journal earlier this yr.
Comply with Keith Cooper on Twitter @21stCenturySETI. Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.