Microbes carried by laser-propelled sails may function interstellar probes that may construct communications stations to telephone dwelling from Alpha Centauri, suggests a scientist identified for eager to resurrect extinct woolly mammoths and use DNA to detect dark matter.
This idea from George Church, a geneticist at Harvard College, builds upon efforts to tremendously velocity up spaceflight. Present spacecraft often take years to make journeys inside the solar system; for instance, NASA’s New Horizons probe took almost 10 years to achieve Pluto.
In idea, spacecraft utilizing standard rockets would require 1000’s of years to finish an interstellar voyage. As an example, Alpha Centauri, the closest star system to Earth, is situated about 4.37 light-years away — greater than 25.6 trillion miles (41.2 trillion kilometers), or greater than 276,000 occasions the gap from Earth to the sun. NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft, which launched in 1977 and reached interstellar space in 2012, would take about 75,000 years to achieve Alpha Centauri even when the probe had been headed in the best route, which it isn’t.
The interstellar problem
The issue that every one rocket thrusters face is that the propellant they carry with them has mass. Lengthy journeys want a whole lot of propellant, which makes spacecraft heavy. This, in flip, requires extra propellant, making them heavier, and so forth.
Earlier analysis has steered that “mild crusing” could be one of many solely possible methods to get a spacecraft to a different star inside a human lifetime. Though mild doesn’t exert a lot strain, scientists have lengthy steered that what little strain it does apply may have a significant impact. Certainly, many experiments have proven that “solar sails” can depend on daylight for propulsion if the spacecraft is mild sufficient and has a large enough sail.
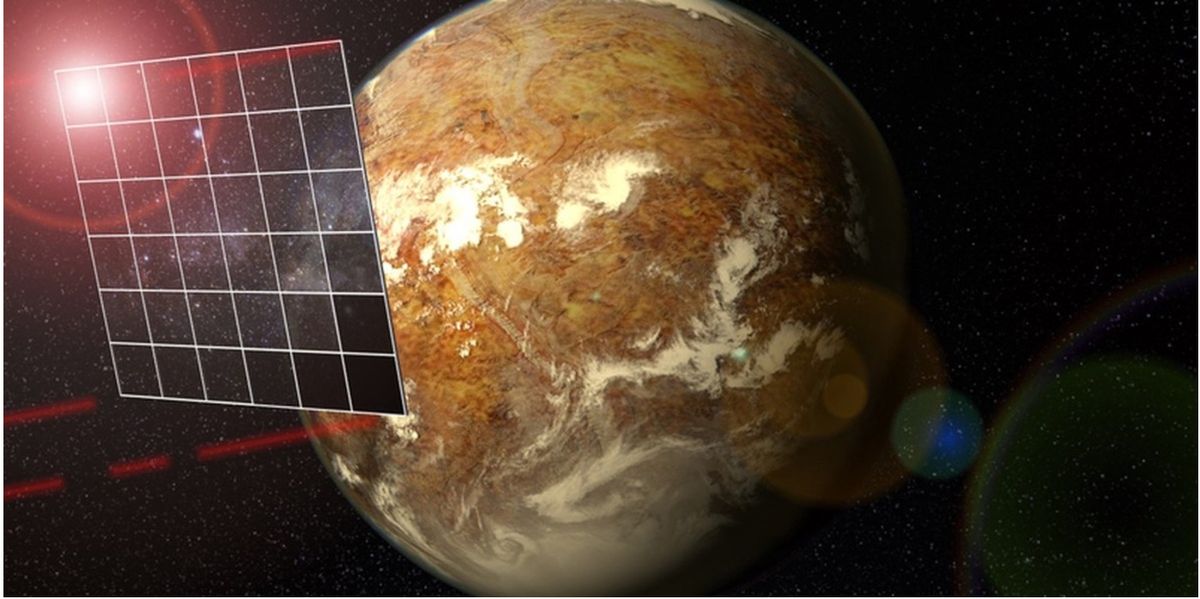
Certainly, the $100 million Breakthrough Starshot initiative, introduced in 2016, plans to launch swarms of microchip-size spacecraft to Alpha Centauri, every of them geared up with terribly skinny, extremely reflective sails propelled by essentially the most highly effective lasers ever constructed. The plan has them flying at as much as 20% the velocity of sunshine, reaching Alpha Centauri in about 20 years.
Nonetheless, Starshot faces many technical challenges. These embrace building lasers powerful enough for propulsion and creating sails that can withstand extraordinary forces and stay on track to their targets.
George Church, Ph.D., is a genetics professor at Harvard Medical Faculty and the Founding Core School and Lead for Artificial Biology on the Wyss Institute of Harvard College. He’s additionally a Professor of Well being Sciences and Know-how at Harvard and the Massachusetts Insitute of Know-how and serves as Director for each the U.S. Division of Vitality Know-how Heart and Nationwide Institutes of Well being Heart of Excellence in Genomic Science.
As well as, even when Starshot efficiently launches “space-chips” at Alpha Centauri, with out one other laser at that vacation spot, there isn’t any method for them to decelerate. This probably limits Starshot missions to flybys as a substitute of landings.
Any Starshot probe try to land would probably show catastrophic. Though the spacecraft are designed to be terribly light-weight — every simply 0.035 ounces (1 gram) or so — when touring at 20% the velocity of sunshine, they’d every pack as a lot power as one-eight the atom bomb dropped on Hiroshima in World Conflict II, Church famous.
As a substitute, Church steered utilizing probes a billion occasions lighter. In the event that they did make impression, it might solely pack as a lot power as half a meals calorie, he famous.
“A probe that lands is tremendously extra beneficial than one which flies by at nice distance and for a really temporary time,” Church informed House.com.
Picogram interstellar probes
How may such an extremely mild probe show helpful? In the event that they carried genetically modified microbes, they might construct themselves gear upon touchdown, Church steered.
Beforehand, Church has made plenty of radical proposals that sound like science fiction. For instance, he steered DNA could help detect dark matter, the invisible and largely intangible substance that researchers recommend makes up about five-sixths of all matter within the universe. He additionally desires to resurrect extinct beasts such as the woolly mammoth.
Nonetheless, Church can also be a pioneering biologist. In 1984, he developed the primary direct genomic sequencing technique, which resulted within the first genome sequence, that of Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium usually discovered within the human abdomen. He additionally helped provoke the Human Genome Venture in 1984 to completely map the roughly 3 billion letters contained in human DNA.
Church famous that he took an interest on this new thought due to how he grew up in Florida within the shadow of Cape Canaveral rocket launches, and since he teaches a course at MIT known as “How To Develop Nearly Something.” As such, he was “in search of tasks that push that envelope,” he mentioned.
Beforehand, scientists have steered creating interstellar “von Neumann” probes that may replicate themselves and gear. The idea is known as after mathematician John von Neumann, who proposed the thought of self-replicating machines in 1948, Church famous.
Church primarily based his new proposal each on his expertise in biology and the pioneering analysis carried out for Starshot. Since his probes are solely about one-billionth the mass of Starshot craft, he steered {that a} billion of his probes could possibly be launched for the same value to a single Starshot mission.
Starshot additionally requires a 100-gigawatt laser array, which might be by far be essentially the most highly effective laser humanity has ever constructed. Since Church steered terribly tiny probes, a comparatively modest laser may suffice, he mentioned. For instance, a mothership about 0.0014 ounces (40 mg) in mass with a 1.3-foot-diameter (0.4 meter) sail that carries many tiny probes may solely require a 2-gigawatt laser array.
Starshot’s probes often call for a sail about 108 sq. ft (10 sq. meters) in dimension with a mass of lower than 0.035 ounces (1 gram). Compared, given how a typical bacterium has a mass of about 1 picogram, or one-trillionth of a gram, it might solely require a sail about 15 millionths of a sq. inch (0.0001 sq. centimeters) in dimension with a mass of about 7.6 picograms, Church mentioned. He added that mild sails about 8.8 millionths of an oz (0.25 milligrams) in mass have already been examined in vacuum and in microgravity.
“Deceleration is difficult even for picogram scale, however not even into account for gram scale,” Church mentioned.
Interstellar probes would probably expertise impacts that might cripple or destroy them — from dust grains, and even hydrogen atoms. Nonetheless, the truth that one may launch a billion or so microbial probes for the price of one Starshot craft implies that shedding probes won’t show a significant setback.
A dwelling probe with ‘biolaser’
A probe that lands is tremendously extra beneficial than one which flies by at nice distance and for a really temporary time.
George Church, Ph.D.
After the probes reached their vacation spot, Church steered that genetically modified microbes may construct themselves communications modules. One technique to speak could be bioluminescence, with which microbes may emit mild utilizing the sorts of molecules present in fireflies or different naturally bioluminescent organisms. Though this mild could be comparatively dim, Church famous that given no predators and perfect rising circumstances, microbes may cowl a completely planetary floor in simply 124 hours.
For a extra compact method, Church steered a dwelling probe may create a “biolaser” able to changing starlight right into a communication beam. He famous that the gold beetle (Aspidimorpha tecta) can construct reflective surfaces doubtlessly helpful for creating such an natural gadget, though Church conceded that constructing it “can be an fascinating laboratory problem.”
Church steered the communications array these probes construct may transmit flashes again at Earth. These beams may encode knowledge in regards to the vacation spot web site equivalent to temperatures, strain and pH.
Associated: A Wild ‘Interstellar Probe’ Mission Idea Is Gaining Momentum
It would show tough to search out locations for these interstellar seeds to develop. “That is why we wish hundreds of thousands of photographs on hundreds of thousands of goal websites,” Church mentioned. Scientists may additionally depend on so-called “extremophile” microbes identified to outlive extremes of temperature, pH, strain and different circumstances on Earth, Church mentioned.
Church famous that one potential goal could be the closest identified exoplanet—Proxima Centauri b, a rocky world within the Alpha Centauri system. Nonetheless, it receives solely 3% of the type of mild helpful for photosynthesis, which may make it tough for any microbial probes to thrive there. It may additionally doubtlessly expertise 10,000 extra flares from its star able to stripping off any ambiance, making it a hostile place to try to stay.
Different potential targets embrace worlds that will exist across the sun-like stars Alpha Centauri A and B within the Alpha Centauri system. These will not be rocky planets—as a substitute, they could be extra much like Uranus and Neptune, and lined in water and ammonia. Nonetheless, there are microbes on Earth that might survive in such locales, equivalent to micro organism present in deep-ocean hydrothermal vents.
One main concern can be planetary safety points — on this case, ensuring that Earth microbes don’t inflict injury on any alien life which may exist at locations. Probes might be designed to “intention for strictly restricted quantity of development,” Church steered. An “completely excessive precedence” can be testing any potential interstellar probes at targets inside the solar system first to see how effectively they carry out, he added.
Church detailed his idea (opens in new tab) Dec. 6 within the journal Astrobiology.
Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or on Facebook (opens in new tab).