Northwestern College astrophysicist Farhad Zadeh has been fascinated and puzzled by a household of large-scale, extremely organized magnetic filaments dangling within the middle of the Milky Way ever since he first found them within the early Eighties.
Now, 40 years later, Zadeh stays simply as fascinated—however maybe barely much less puzzled.
With a brand new discovery of comparable filaments situated in different galaxies, Zadeh and his collaborators have, for the primary time, launched two potential explanations for the filaments’ unknown origins. In a brand new paper, printed earlier this month in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Zadeh and his co-authors suggest the filaments may consequence from an interplay between large-scale wind and clouds or may come up from turbulence inside a weak magnetic subject.
“We all know quite a bit concerning the filaments in our personal Galactic Heart, and now filaments in exterior galaxies are starting to indicate up as a brand new inhabitants of extragalactic filaments,” Zadeh stated. “The underlying bodily mechanisms for each populations of filaments are comparable regardless of the vastly completely different environments. The objects are a part of the identical household, however the filaments exterior the Milky Way are older, distant cousins—and I imply very distant (in time and space) cousins.”
An knowledgeable in radio astronomy, Zadeh is a professor of physics and astronomy in Northwestern’s Weinberg Faculty of Arts and Sciences and a member of the Heart for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Analysis in Astrophysics (CIERA).
‘One thing common is occurring’
The primary filaments that Zadeh found stretched as much as 150 light years lengthy, towering close to the Milky Way’s central supermassive black hole. Earlier this yr, Zadeh added almost 1,000 extra filaments to his assortment of observations. In that batch, the one-dimensional filaments seem in pairs and clusters, typically stacked equally spaced, aspect by aspect like strings on a harp or spilling sideways like particular person ripples in a waterfall.
Utilizing observations from radio telescopes, Zadeh found the mystifying filaments comprise cosmic ray electrons gyrating alongside a magnetic subject at near the velocity of sunshine. Though he’s placing collectively the puzzle of what the filaments are fabricated from, Zadeh nonetheless puzzled the place they got here from. When astronomers found a brand new inhabitants exterior our personal galaxy, it supplied new alternatives to research the bodily processes within the space surrounding the filaments.
The newly found filaments reside inside a galaxy cluster, a concentrated tangle of hundreds of galaxies situated one billion light-years from Earth. A number of the galaxies inside the cluster are energetic radio galaxies, which seem like breeding grounds for the for formation of large-scale magnetic filaments. When Zadeh noticed these newly uncovered filaments for the primary time, he was amazed.
“After learning filaments in our personal Galactic Heart for all these years, I used to be extraordinarily excited to see these tremendously stunning constructions,” he stated. “As a result of we discovered these filaments elsewhere within the universe, it hints that one thing common is occurring.”
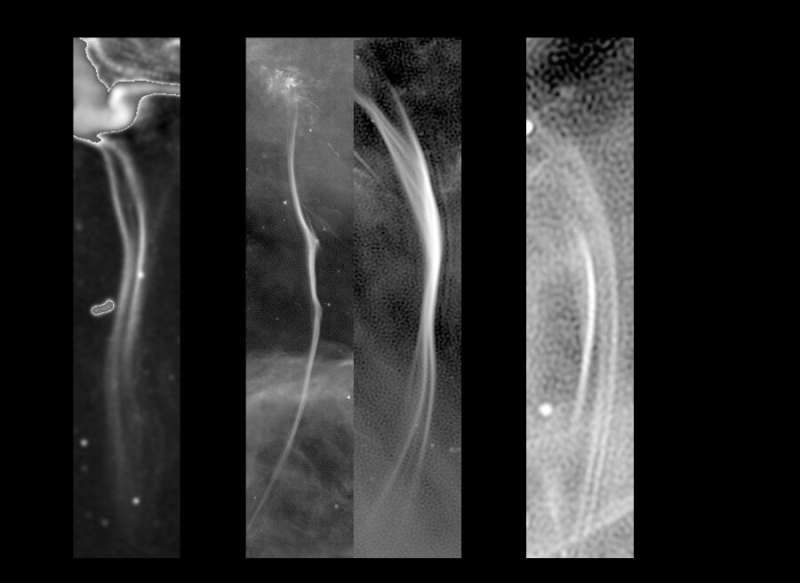
Galactic giants
Though the brand new inhabitants of filaments appears to be like much like these in our Milky Way, there are some key variations. The filaments exterior the Milky Way, for instance, are a lot larger—between 100 to 10,000 instances longer. In addition they are a lot older, and their magnetic fields are weaker. Most of them curiously grasp—at a 90-degree angle—from a black hole’s jets into the huge nothingness of the intracluster medium, or the space wedged between the galaxies inside the cluster.
However the newly found inhabitants has the identical length-to-width ratio because the Milky Way’s filaments. And each populations seem to move power by the identical mechanisms. Nearer to the jet, the filaments’ electrons are extra energetic, however they lose power as they journey farther down the filament. Though the black hole’s jet may present the seed particles wanted to create a filament, one thing unknown have to be accelerating these particles alongside astonishing lengths.
“A few of them have wonderful size, as much as 200 kiloparsecs,” Zadeh stated. “That’s about 4 or 5 instances larger than the dimensions of our complete Milky Way. What’s exceptional is that their electrons keep collectively on such a protracted scale. If an electron traveled on the velocity of sunshine alongside the filament’s size, it will take it 700,000 years. They usually do not journey on the velocity of sunshine.”
Promising prospects
Within the new paper, Zadeh and his collaborators hypothesize that the filaments’ origins might be a easy interplay between galactic wind and an impediment, comparable to a cloud. Because the wind wraps across the impediment, it creates a comet-like tail behind it.
“Wind comes from the movement of the galaxy itself because it rotates,” Zadeh defined. “It is like while you stick your hand out of a window from a shifting automotive. There is not any wind exterior, however you are feeling the air shifting. When the galaxy strikes, it creates wind that might be pushing by locations the place the cosmic ray particles are pretty unfastened. It sweeps the fabric and creates a filamentary construction. “
Simulations, nevertheless, provide one other viable chance. When researchers simulated an energetic, turbulent medium, lengthy, filamentary constructions materialized. As radio galaxies transfer round, Zadeh defined, gravity can have an effect on the medium and stir it. The medium then kinds spots of swirling eddies. After the weak magnetic subject wraps round these eddies, it may well get stretched, folded and amplified—ultimately turning into elongated filaments with robust magnetic subject.
Though many questions stay, Zadeh nonetheless marvels on the new discoveries.
“All of those filaments exterior our galaxy are very outdated,” he stated. “They’re virtually from a unique period of our universe and but signaling the Milky Way inhabitants {that a} widespread origin exists for the formation of the filaments. I believe that is exceptional.”
Extra info:
F. Yusef-Zadeh et al, Populations of Magnetized Filaments within the Intracluster Medium and the Galactic Heart, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2022). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac982a
Supplied by
Northwestern University
Quotation:
The Milky Way’s mysterious filaments have ‘older, distant cousins’ (2022, November 18)
retrieved 18 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-milky-mysterious-filaments-older-distant.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




