Photo voltaic crusing generally is a comparatively slow-motion affair, however progress within the nascent area is shortly gaining steam.
The thought is to not use typical “fuel guzzling” propulsion however quite to make use of ever-present and energetic solar photons to journey via space. Over time, this steady thrust from sunlight can speed up a spacecraft to very excessive speeds.
Harnessing this know-how, which is now being pursued by a number of nations, may enable probes to effectively discover the outer solar system and even interstellar space, advocates say.
However the know-how has been a piece in progress for a few years — and it hasn’t at all times been clean crusing.
Associated: What is a solar sail?
Troubled tech demo
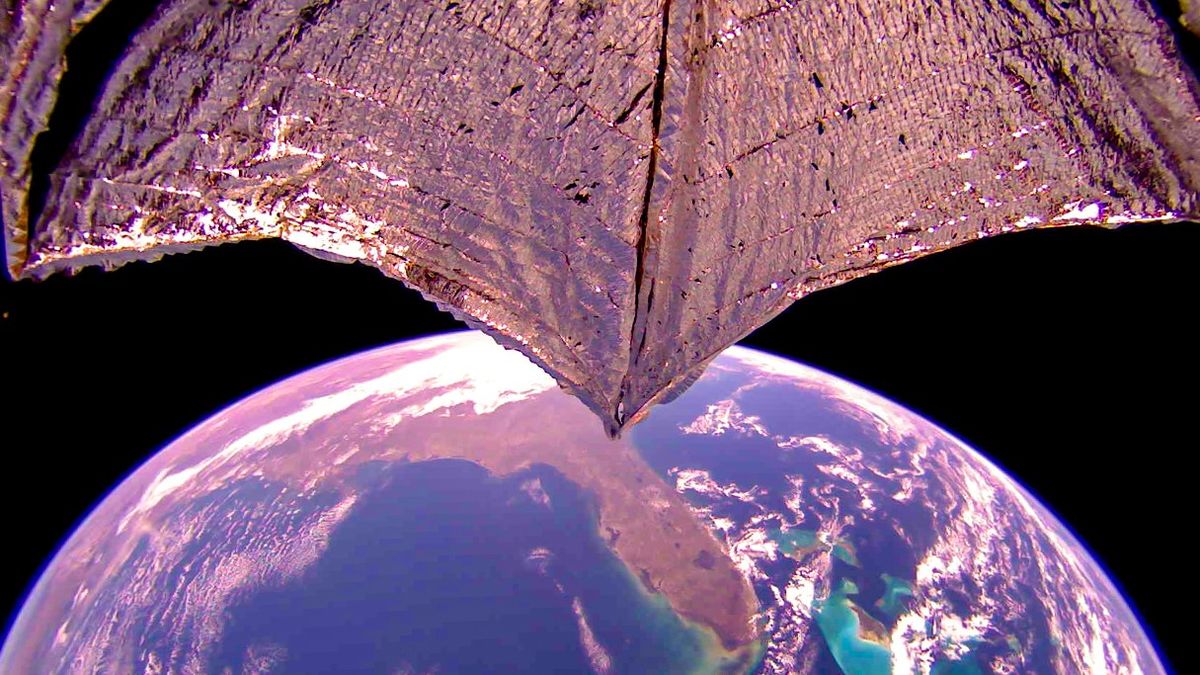
NASA’s Artemis 1 moon mission, which launched in November 2022, despatched the company’s Orion capsule on an uncrewed shakeout cruise to lunar orbit and again. However Artemis 1 additionally lofted 10 tiny ridealong cubesats, one in every of which was a solar sailer — NASA’s Close to-Earth Asteroid (NEA) Scout.
NEA Scout was developed underneath NASA’s Superior Exploration Techniques division. The cubesat was designed and developed by two NASA facilities, the Marshall Area Flight Middle in Alabama and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
NEA Scout carries an ultra-thin sail that, when absolutely deployed through lengthy booms, covers 925 sq. ft (86 sq. meters). That is pretty small for a solar sail, however it must be sufficiently big for the cubesat cruise via deep space, displaying that the propulsion know-how is prepared for prime time — one of many mission’s chief objectives.
“I emphasize that NEA Scout is a know-how demonstration and likewise a science mission,” the mission’s principal investigator, Les Johnson of NASA Marshall, informed Area.com.
NEA Scout goals to sail to a small asteroid named 2020 GE and research it up shut. The cubesat deployed as deliberate shortly after Artemis 1’s Nov. 16 liftoff, however it soon ran into trouble: The mission group has thus far been unable to speak with NEA Scout.
“We’re not but involved with the spacecraft, although we’re utilizing the Deep Space Network each day making an attempt,” Johnson, who has been engaged on the mission for almost a decade, informed Area.com. “We nonetheless have hope and are nonetheless making an attempt!”
Associated: The 10 greatest images from NASA’s Artemis 1 moon mission
Mega-sail
Johnson has been spearheading solar sail work for 20 years, on and off, given the ebb and circulate of growth {dollars}.
The know-how has “come a good distance, and we’re engaged on the subsequent one, Photo voltaic Cruiser,” stated Johnson.
Photo voltaic Cruiser’s sail is a whopping 17,800 sq. ft (1,650 sq. meters) in dimension — giant sufficient to cowl greater than six tennis courts. Photo voltaic Cruiser has accomplished a preliminary design assessment, and the challenge is eying a flight alternative for later on this decade.
A latest unfurling of 1 quadrant (a take a look at article) of Photo voltaic Cruiser’s big sail occurred at Marshall, spotlighting the evolution of the mega-sail design.
Photo voltaic Cruiser, which is sponsored by the Photo voltaic Terrestrial Probes Program in NASA’s Heliophysics Division, may lay the muse for future crusing missions that enhance space weather monitoring and prediction and assist reply questions concerning the sun, its interplay with Earth and different components of the heliosphere.
Large modifications have occurred over Johnson’s 20 years of solar sail work, due largely, he stated, to the smartphone revolution: Industrial micro-technology has spilled over into spacecraft, making them lighter weight. “The miniaturization of spacecraft instantly makes solar sails extra viable,” Johnson stated.
Leslie McNutt, NASA’s deputy challenge supervisor for Photo voltaic Cruiser, voiced comparable sentiments, saying that solar crusing has developed previously 20 years from concept to actuality. NASA and business companions are engineering progressive sail applied sciences to assist push the boundaries of what small satellites can do in space and the way far they’ll go, she informed Area.com.
“One of many hardest challenges with solar sails is deploying them in space. You understand how your tape measure retracts while you push the button? Think about reversing that course of in space to unspool a sail as tall and extensive as a 10-story constructing from a container the scale of a compact fridge,” McNutt stated.
The Photo voltaic Cruiser challenge group has got down to reveal a bigger solar sail than any flown earlier than. “We have taken the idea previous the drafting board and into growth … after years of exhausting work,” stated McNutt, “paving the best way for bigger and extra advanced solar sails to take flight.”
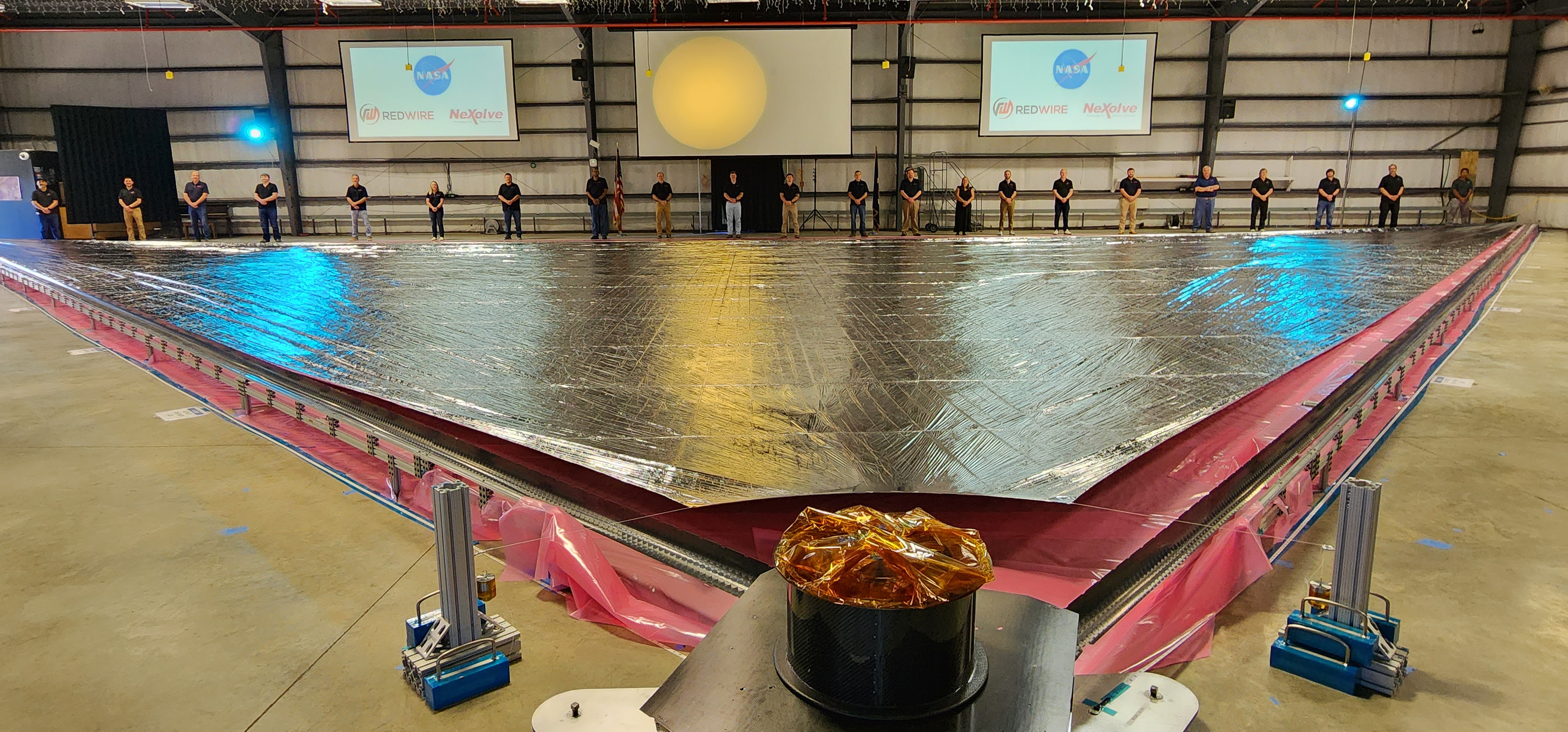
Classes realized
Additionally pioneering solar crusing is The Planetary Society, the general public space exploration advocacy group. Again in 2015, the nonprofit’s LightSail 1 unfurled its sail in Earth orbit in a landmark take a look at. LightSail 1 did not carry out any precise crusing, however its successor did: LightSail 2 went up in 2019 and circled our planet for almost 3.5 years, lastly reentering Earth’s atmosphere this previous November.
“Funded fully by greater than 50,000 on a regular basis space fans from around the globe, the LightSail program demonstrated the primary managed solar crusing mission utilizing a small cubesat-sized spacecraft. LightSail 2 raised the profile of solar crusing as a viable propulsion methodology for small spacecraft to discover the solar system,” stated Bruce Betts, chief scientist for The Planetary Society.
Throughout the LightSail program, Betts stated that there have been a lot of detailed classes realized concerning the challenges of working a solar sail mission.
“The LightSail mission helped us discover the challenges of controlling spacecraft orientation, methods for normal actions to optimize deliberate rotations of the spacecraft and, no less than for LightSail 2, the significance of usually recalibrating the gyroscopes used to find out rotation charges of the spacecraft,” Betts informed Area.com.
The Planetary Society is sharing LightSail data with NASA and different solar crusing missions “that are actually lining as much as tackle the subsequent, extra advanced generations of solar crusing,” stated Betts.
Excessive crusing
One mission headed for its day within the sun is NASA’s Superior Composite Photo voltaic Sail System, or ACS3. It’s a know-how demonstration utilizing a mixture of supplies for ACS3’s light-weight booms that roll out from a cubesat.
Then there’s the “excessive solar crusing” growth work being performed by Artur Davoyan of the College of California, Los Angeles and sponsored by NASA’s Revolutionary Superior Ideas (NIAC) program.
“We envisage a brand new technology of breakthrough science missions that weren’t doable earlier than, from probing elementary legal guidelines of nature on the outskirts of our solar system to peering into distant worlds,” Davoyan defined in a NIAC briefing about his work.
Fabrication and testing of novel ultra-lightweight sail “metamaterials” able to withstanding the intense output by the sun’s outer atmosphere, or corona, is one factor of Davoyan’s analysis.
The NIAC-funded research has blueprinted two breakthrough mission ideas. One is the Quick Transit Interstellar Probe, which goals to ship a spacecraft 500 astronomical items (AU) from Earth in simply 10 years of spaceflight. (One AU is the Earth-sun distance, about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers. For perspective, Neptune orbits about 30 AU from the sun on common.)
The opposite is Corona-Web, a possible precursor mission that will ship a formation of utmost solar sails to scrutinize the internal heliosphere at excessive inclinations, removed from the sun.

Quick transit
One other NIAC-funded effort proposes using “diffractive solar crusing.” This challenge, led by Amber Dubill of the Johns Hopkins College’s Utilized Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, would use diffracted quite than mirrored daylight to propel a craft. This variation may result in a smaller sail, much less advanced steering, navigation and attitude-control schemes and lowered energy wants, amongst different attributes.
Dubill envisions circumnavigating the sun with a constellation of diffractive solar sails to offer measurements of the solar corona and magnetic fields.
Les Johnson sees the thought of solar crusing and what it gives — a propulsion know-how and science supplier — as gaining wider acceptance within the scientific and engineering communities.
“Something that’s requiring fixed low-thrust over years is the place solar sails actually shine,” he stated. “Sure, pun supposed.”
Leonard David is creator of the e-book “Moon Rush: The New Space Race (opens in new tab),” printed by Nationwide Geographic in Might 2019. A longtime author for Area.com, David has been reporting on the space business for greater than 5 a long time.Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or on Facebook (opens in new tab).




