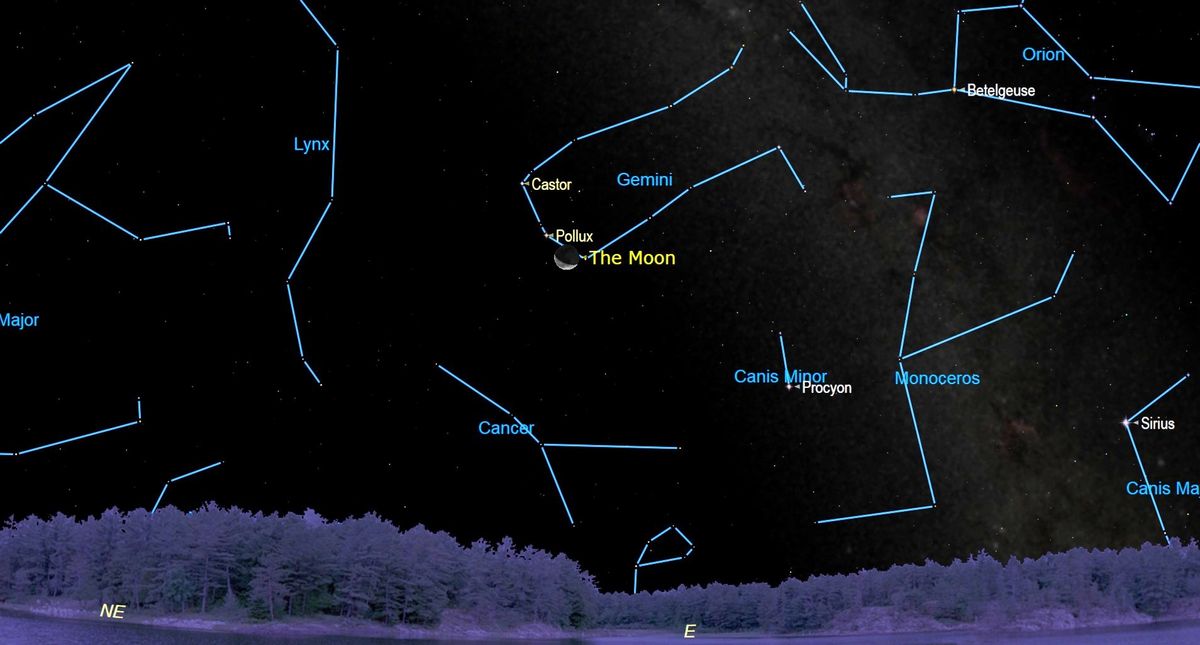
On Tuesday (Sept. 20), skywatchers will get the chance to see the moon subsequent to Pollux, one of many brilliant twin stars of the constellation Gemini.
The waning crescent moon will cross Pollux within the early morning, that means astronomers are going to need to be early risers or severe night time owls to identify the occasion.
Because the moon sits subsequent to Pollux, the star’s stellar twin Castor shall be positioned barely above and to the best of the pair. The moon is at present waning, that means is gentle facet is receding and shall be seen as a tremendous crescent on Tuesday.
Associated: Night sky, September 2022: What you can see tonight [maps]
Learn Extra: What is the moon phase today? Lunar phases 2022
The constellation of Gemini takes its identify from the dual stars of Pollux and Castor, with these stars seen because the heads of the stick figures that make up the constellation.
Pollux and Castor are notable due to their proximity to one another within the night time sky and due to how comparable in brightness they’re.
The marginally brighter star, Pollux is likely one of the 20 brightest stars within the night time sky with a magnitude of 1.16. The star has a golden shade as seen from Earth, whereas its barely dimmer twin Castor has a white/blue shimmer. (The decrease an object’s magnitude, the brighter it seems to the attention.)
Regardless of showing so shut within the night time sky, the dual stars are distant from one another in space. Pollux is positioned roughly 33 light-years away from the solar system, whereas Castor is extra distant at 51 light-years away.
Pollux is a red giant star with a diameter that’s round ten instances that of the sun regardless of solely having round twice the mass of our star. Stars attain the crimson large phase of their lives once they have exhausted their provide of hydrogen of their cores.
(opens in new tab)
As hydrogen is the gas for nuclear fusion and this course of offers the power for the outward push that balances the inward pull of gravity, the stellar core can not shield itself in opposition to gravitational collapse. Because the core crushes inwards, the outer layers of the star ‘puff out’ leading to a red giant star.
The sun will exhaust its hydrogen in round 5 billion years and can endure the transformation right into a crimson large like Pollux. The sun’s diameter will swell out to across the orbit of Mars, consuming the inside rocky worlds — together with Earth.
Regardless of having undergone this harmful course of, we all know that Pollux has managed to hold on to a minimum of one in all its planets. The exoplanet now we have found orbiting Pollux — generally known as Pollux b or Thestias — is a gas giant with a mass twice that of Jupiter.
Thestias orbits Pollux at a distance of about 153 million miles, just a bit additional out from the star than Mars is from the sun.
As winter approaches within the Northern Hemisphere, so does the optimum time to watch each Pollux and Castor. Each are pretty simple to identify through the evenings of the Winter months, positioned above the constellation of Orion within the southern sky.
Do not miss our guides for the best binoculars and the best telescopes to identify the moon, the dual stars of Gemini, or some other celestial wonders. For capturing the very best moon photos you may, take a look at our information for photographing the moon, together with our suggestions for the very best cameras for astrophotography and best lenses for astrophotography.
Editor’s Observe: Should you snap a photograph of the moon close to Pollux and wish to share it with Area.com’s readers, ship your picture(s), feedback, and your identify and placement to spacephotos@space.com.
Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or on Facebook (opens in new tab).