There is a thriller occurring in some satellites going through the sun, and scientists from the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST) and the Laboratory for Atmospheric and House Physics (LASP) are on the case. The crew has been attempting to determine what’s clouding up and compromising the efficiency of tiny, skinny metallic membranes that filter daylight because it enters detectors that monitor the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays.
These detectors can warn us about impending solar storms—bursts of radiation from the floor of the sun—that would attain Earth and quickly disrupt communications or intrude with GPS readings.
Final yr, the crew disproved the prevailing theory: that this clouding was a buildup of carbon on the floor of the filters from natural sources stowing away on the satellite.
Now, in a collection of three new papers, the identical crew from NIST and LASP has made a robust case for what they suppose is the true offender: oxidation brought on by water, which along with UV gentle from the sun is producing a thick layer of aluminum oxide—a lot thicker than beforehand thought doable—that blocks incoming rays.
As a bonus, the researchers imagine they’ve recognized the supply of the water: thermal blankets, that are used to manage the temperature of devices on a spacecraft. This data may assist scientists enhance the efficiency of future satellites that depend on any such filter, maybe by including {hardware} that limits the filters’ publicity to the realm across the thermal blankets, or by utilizing totally different supplies as part of the filters themselves.
The primary of the three papers was revealed at this time in Photo voltaic Physics.
“So far as I do know we’re the one folks filter oxidation as a result of publicity to ultraviolet light,” mentioned NIST’s Charles Tarrio.
Proving that water is liable for the issue “was form of a one-two punch,” mentioned NIST physicist Robert Berg. “Punch one was bodily displaying that this chemical process involving water may trigger one thing akin to what we really see occurring within the satellites. And the quantity two punch is saying when you create a theoretical mannequin that takes all the things under consideration, then the numbers line up quantitatively with what we see within the satellites.
“Placing all the things collectively, I am satisfied,” Berg mentioned. “Water is liable for the filter degradation.”
#NoFilter
Many of the gentle produced by the sun is seen and ranges from crimson gentle, with a wavelength of round 750 nanometers (nm, billionths of a meter), to violet gentle, with a wavelength of about 400 nm. Amongst different wavelengths, the sun additionally emits comparatively small quantities of sunshine within the excessive ultraviolet (EUV) vary, which extends from 100 nm down to only 10 nm—wavelengths too quick for human eyes to see.
Although small, that EUV sign is helpful as a result of it spikes in tandem with the solar flares that may disrupt communications on Earth or trigger GPS to expertise issues. EUV indicators additionally give scientists a heads-up of hours and even days earlier than extra damaging phenomena similar to coronal mass ejections attain Earth. These blasts of charged particles can overload energy traces or enhance radiation publicity for airline crew and passengers.
A crucial piece of kit on the sun-facing space detectors are the aluminum filters, every smaller than a postage stamp, that block all however the EUV gentle between 17 nm and 80 nm wavelength.
Although they start their lives in space transmitting loads of EUV gentle of their vary, inside just some years they’ll lose a major quantity of transmission potential. For instance, a filter would possibly begin by permitting 50% of 30-nm EUV gentle via to the detector. That quantity can go all the way down to 25% inside a yr, and 10% inside 5 years.
Scientists believed some unknown substance should be rising or being deposited on the filters, inflicting them to go darkish over mere months and limiting the quantity of sunshine that makes it into the detectors. The main concept was that carbon was outgassing from the instrument itself and getting deposited on the filters.
When NIST and LASP employees disproved that final yr, they turned their consideration to what they felt was a more likely clarification: the method of oxidation, during which oxygen atoms from water molecules (H2O) mix with aluminum atoms from the filter itself (Al) to kind a hazy layer of aluminum oxide (Al2O3). (By the way, a skinny layer of aluminum oxide naturally coats all aluminum objects on Earth, from soda cans to frying pans.)
Scientists already knew that exposing an aluminum floor to UV gentle within the presence of water can develop further layers of oxide past those that naturally kind. However there was no current concept that would clarify how the aluminum oxide may develop thick sufficient to trigger this clouding downside.
Researchers determined to completely discover how the presence of water is likely to be affecting the filters, to find out what was actually occurring.
SURF’s up
NIST researchers needed to check their water concept in a managed setting: a machine that successfully lets them create space climate. Known as NIST’s Synchrotron Ultraviolet Radiation Facility (SURF), the gadget is a room-sized particle accelerator that makes use of highly effective magnets to maneuver electrons in a hoop. The movement generates EUV gentle, which will be diverted via specialised mirrors to impression targets such because the satellite filters being examined.
Regardless of exposing their pattern filters to lab-made UV gentle for so long as 20 days, they weren’t capable of develop oxide layers as thick as had been wanted to clarify the cloudiness of actual space filters. However the oxide layers had been nonetheless a lot thicker than predicted by the accepted concept.
The researchers imagine with additional publicity they’d have reached the required thickness. Additionally they projected that the pattern filters would have needed to be uncovered to the SURF beam for about 10 months to realize the identical oxide thickness because the filters in precise space.
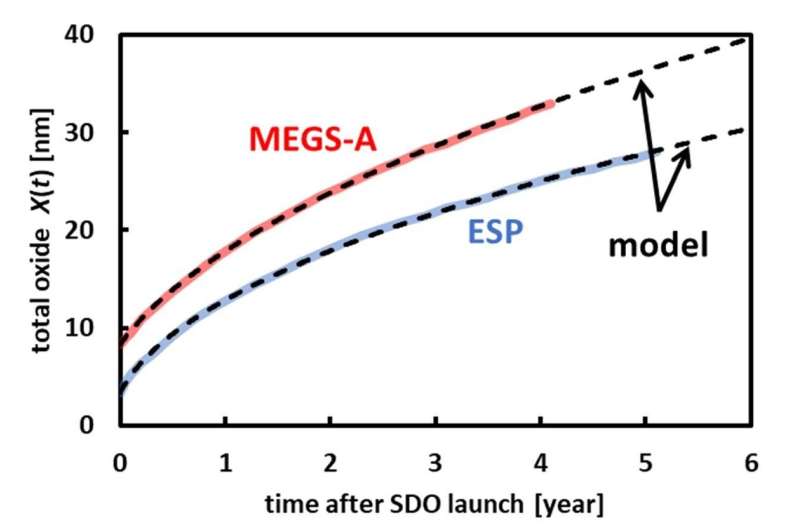
Taking a special tack, the crew additionally carried out modeling research. The completed fashions match virtually precisely what astronomers are seeing in actual aluminum filters in space.
One key piece of the brand new mannequin’s success is that it accounts for the truth that electrons scatter whereas touring throughout the aluminum filters. This scattering slows their progress, which impacts the dynamics of the oxide development.
“That is the primary mannequin that takes scattering electrons under consideration, and it makes use of parameters that agree with what’s anticipated within the literature for every of the steps within the chemical response,” Berg mentioned.
Simply add water
For the fashions to work, although, one key piece of knowledge was lacking: a major supply of water that may very well be feeding this response.
“It needed to be one thing that may emit water for 5 years constantly at moderately fixed charges,” Tarrio mentioned. “That set Bobby [Berg] off on this quest to search out, what the heck may this be? What may very well be a supply that matches? And he discovered it.”
The most definitely supply, Berg concludes, is thermal blankets. These are made with a kind of plastic known as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), recognized to seize water on Earth. This water simply is not normally an issue for many tools.
“It was exhausting to consider the rest that may maintain that form of water,” Berg mentioned.
Future work, the researchers hope, will maybe embrace testing totally different supplies for the filters that may nonetheless be clear on the related wavelengths however would not be inclined to oxidation.
Extra data:
Charles Tarrio et al, The Hazard of UV-Induced Oxidation to Photo voltaic-Viewing Spacecraft Optics, Photo voltaic Physics (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11207-023-02112-x
Supplied by
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Quotation:
Scientists uncover reply to the thriller of cloudy filters on satellites (2023, March 3)
retrieved 3 March 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-03-scientists-mystery-cloudy-filters-satellites.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




