NASA’s Earth Floor Mineral Mud Supply Investigation (EMIT) mission is mapping the prevalence of key minerals within the planet’s dust-producing deserts—info that can advance our understanding of airborne dust’s results on local weather. However EMIT has demonstrated one other essential functionality: detecting the presence of methane, a potent greenhouse fuel.
Within the knowledge EMIT has collected since being put in on the Worldwide Area Station in July, the science group has recognized greater than 50 “super-emitters” in Central Asia, the Center East, and the southwestern United States. Tremendous-emitters are services, tools, and different infrastructure sometimes throughout the fossil-fuel, waste, or agriculture sectors, that emit methane at excessive charges.
“Reining in methane emissions is essential to limiting global warming. This thrilling new growth is not going to solely assist researchers higher pinpoint the place methane leaks are coming from, but in addition present perception on how they are often addressed—rapidly,” mentioned NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson. “The Worldwide Area Station and NASA’s greater than two dozen satellites and devices in space have lengthy been invaluable in figuring out adjustments to the Earth’s local weather. EMIT is proving to be a vital software in our toolbox to measure this potent greenhouse fuel—and cease it on the supply.”
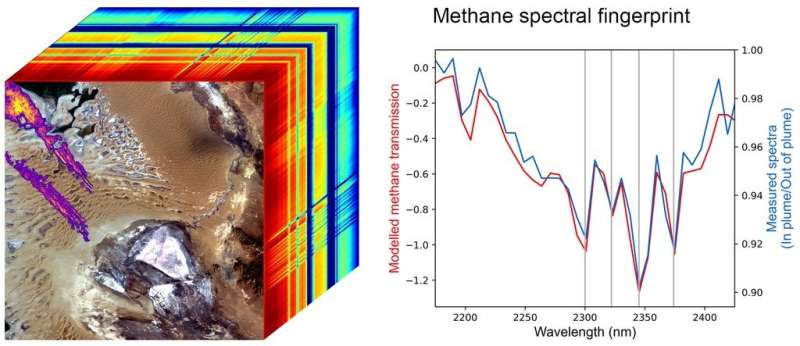
Methane absorbs infrared gentle in a novel sample—known as a spectral fingerprint—that EMIT’s imaging spectrometer can discern with excessive accuracy and precision. The instrument may also measure carbon dioxide.
The brand new observations stem from the broad protection of the planet afforded by the space station’s orbit, in addition to from EMIT’s capability to scan swaths of Earth’s floor dozens of miles broad whereas resolving areas as small as a soccer subject.
“These outcomes are distinctive, they usually reveal the worth of pairing global-scale perspective with the decision required to establish methane level sources, all the way down to the power scale,” mentioned David Thompson, EMIT’s instrument scientist and a senior analysis scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which manages the mission. “It is a distinctive functionality that can elevate the bar on efforts to attribute methane sources and mitigate emissions from human actions.”
Relative to carbon dioxide, methane makes up a fraction of human-caused greenhouse-gas emissions, however it’s estimated to be 80 occasions simpler, ton for ton, at trapping warmth within the ambiance within the 20 years after launch. Furthermore, the place carbon dioxide lingers for hundreds of years, methane persists for a few decade, which means that if emissions are diminished, the ambiance will reply in an identical timeframe, resulting in slower near-term warming.
Figuring out methane level sources is usually a key step within the course of. With data of the places of massive emitters, operators of services, tools, and infrastructure giving off the fuel can rapidly act to restrict emissions.
EMIT’s methane observations got here as scientists verified the accuracy of the imaging spectrometer’s mineral knowledge. Over its mission, EMIT will gather measurements of floor minerals in arid areas of Africa, Asia, North and South America, and Australia. The information will assist researchers higher perceive airborne dust particles’ function in heating and cooling Earth’s ambiance and floor.
“Now we have been wanting to see how EMIT’s mineral knowledge will enhance local weather modeling,” mentioned Kate Calvin, NASA’s chief scientist and senior local weather advisor. “This extra methane-detecting functionality gives a outstanding alternative to measure and monitor greenhouse gases that contribute to local weather change.”
Detecting methane plumes
The mission’s research space coincides with identified methane hotspots around the globe, enabling researchers to search for the fuel in these areas to check the potential of the imaging spectrometer.
“Among the plumes EMIT detected are among the many largest ever seen—not like something that has ever been noticed from space,” mentioned Andrew Thorpe, a analysis technologist at JPL main the EMIT methane effort. “What we have present in a simply a short while already exceeds our expectations.”
For instance, the instrument detected a plume about 2 miles (3.3 kilometers) lengthy southeast of Carlsbad, New Mexico, within the Permian Basin. One of many largest oilfields on the planet, the Permian spans elements of southeastern New Mexico and western Texas.
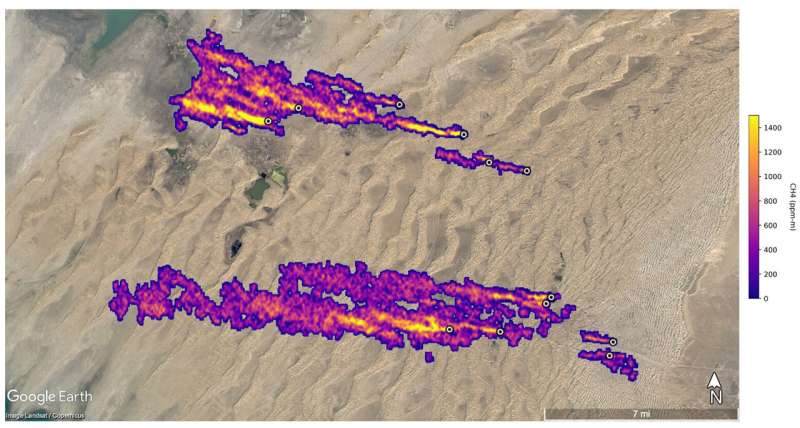
In Turkmenistan, EMIT recognized 12 plumes from oil and fuel infrastructure east of the Caspian Sea port metropolis of Hazar. Blowing to the west, some plumes stretch greater than 20 miles (32 kilometers).
The group additionally recognized a methane plume south of Tehran, Iran, not less than 3 miles (4.8 kilometers) lengthy, from a serious waste-processing advanced. Methane is a byproduct of decomposition, and landfills is usually a main supply.
Scientists estimate move charges of about 40,300 kilos (18,300 kilograms) per hour on the Permian website, 111,000 kilos (50,400 kilograms) per hour in total for the Turkmenistan sources, and 18,700 kilos (8,500 kilograms) per hour on the Iran website.
The Turkmenistan sources collectively have an identical move price to the 2015 Aliso Canyon fuel leak, which exceeded 110,000 kilos (50,000 kilograms) per hour at occasions. The Los Angeles-area catastrophe was among the many largest methane releases in U.S. historical past.
With broad, repeated protection from its vantage level on the space station, EMIT will probably discover a whole lot of super-emitters—a few of them beforehand noticed by way of air-, space-, or ground-based measurement, and others that have been unknown.
“Because it continues to survey the planet, EMIT will observe locations during which nobody thought to search for greenhouse-gas emitters earlier than, and it’ll discover plumes that nobody expects,” mentioned Robert Inexperienced, EMIT’s principal investigator at JPL.
EMIT is the primary of a brand new class of spaceborne imaging spectrometers to check Earth. One instance is Carbon Plume Mapper (CPM), an instrument in growth at JPL that is designed to detect methane and carbon dioxide. JPL is working with a nonprofit, Carbon Mapper, together with different companions, to launch two satellites geared up with CPM in late 2023.
Quotation:
Methane ‘super-emitters’ mapped by NASA’s new Earth space mission (2022, October 25)
retrieved 25 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-methane-super-emitters-nasa-earth-space.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




