Regardless of having radically completely different atmospheres, Mars and Earth appear to have comparable cloud patterns, hinting that the options might kind in a lot the identical method.
The observations, obtained by the European House Company’s (ESA) Mars Express spacecraft and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, have been sudden. Maybe most shocking to scientists was that the clouds noticed over the dry and arid ambiance of Mars resembled these present in very completely different environments on Earth.
“When considering of a Mars-like ambiance on Earth, one may simply consider a dry desert or polar area,” Mars Categorical venture scientist Colin Wilson stated in a statement (opens in new tab). “It’s fairly sudden then, that by way of monitoring the chaotic motion of dust storms, parallels might be drawn with the processes that happen in Earth’s moist, scorching and decidedly very un-Mars-like tropical areas.”
Associated: NASA’s Curiosity rover spots strange, colorful clouds on Mars
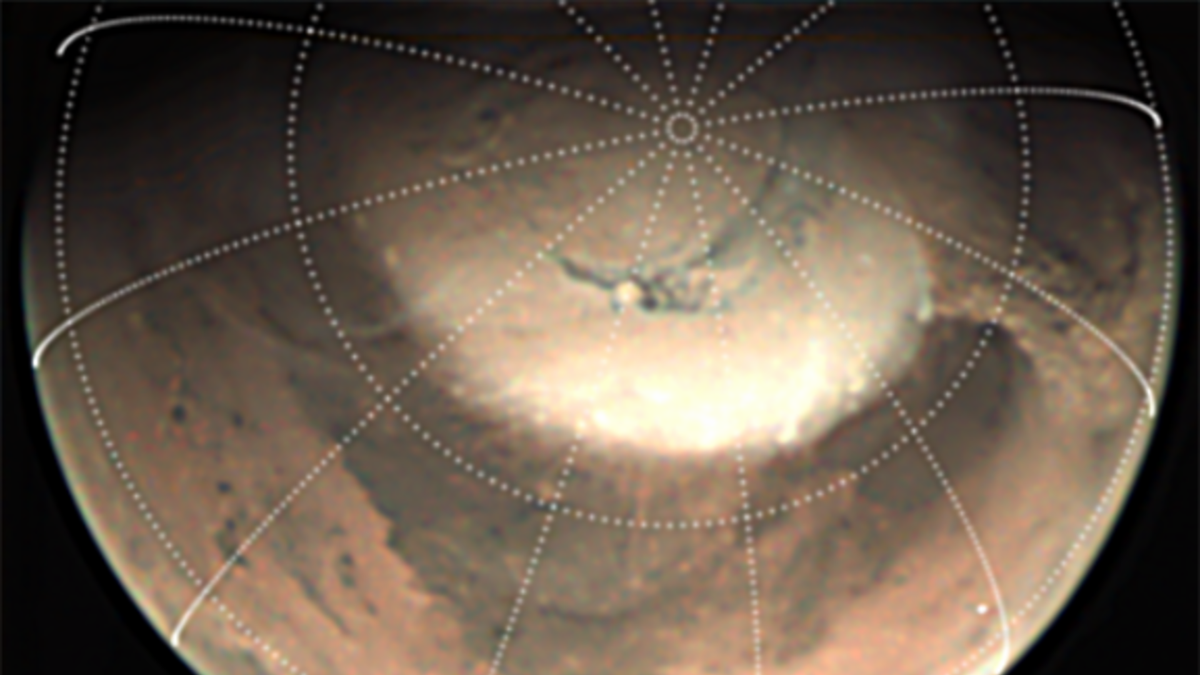
For the analysis, the scientists checked out two dust storms that occurred close to the Martian north pole within the spring of 2019. To look at the storms from orbit across the Crimson Planet, they considered photographs taken by Mars Categorical’ Visible Monitoring Digicam (VMC) and Excessive-Decision Stereo Digicam (HRSC) and MRO’s Mars Coloration Imager.
The VMC photographs present the storms rising after which disappearing in a cycle that displays widespread options and shapes as it’s repeated over intervals of days. Seen within the wider-view HRSC photographs are spiral shapes with lengths between round 1,600 and three,200 miles (1,000 to 2,000 kilometers). These spirals appear to kind in the identical methods as extratropical cyclones seen at midlatitudes and polar latitudes on Earth.
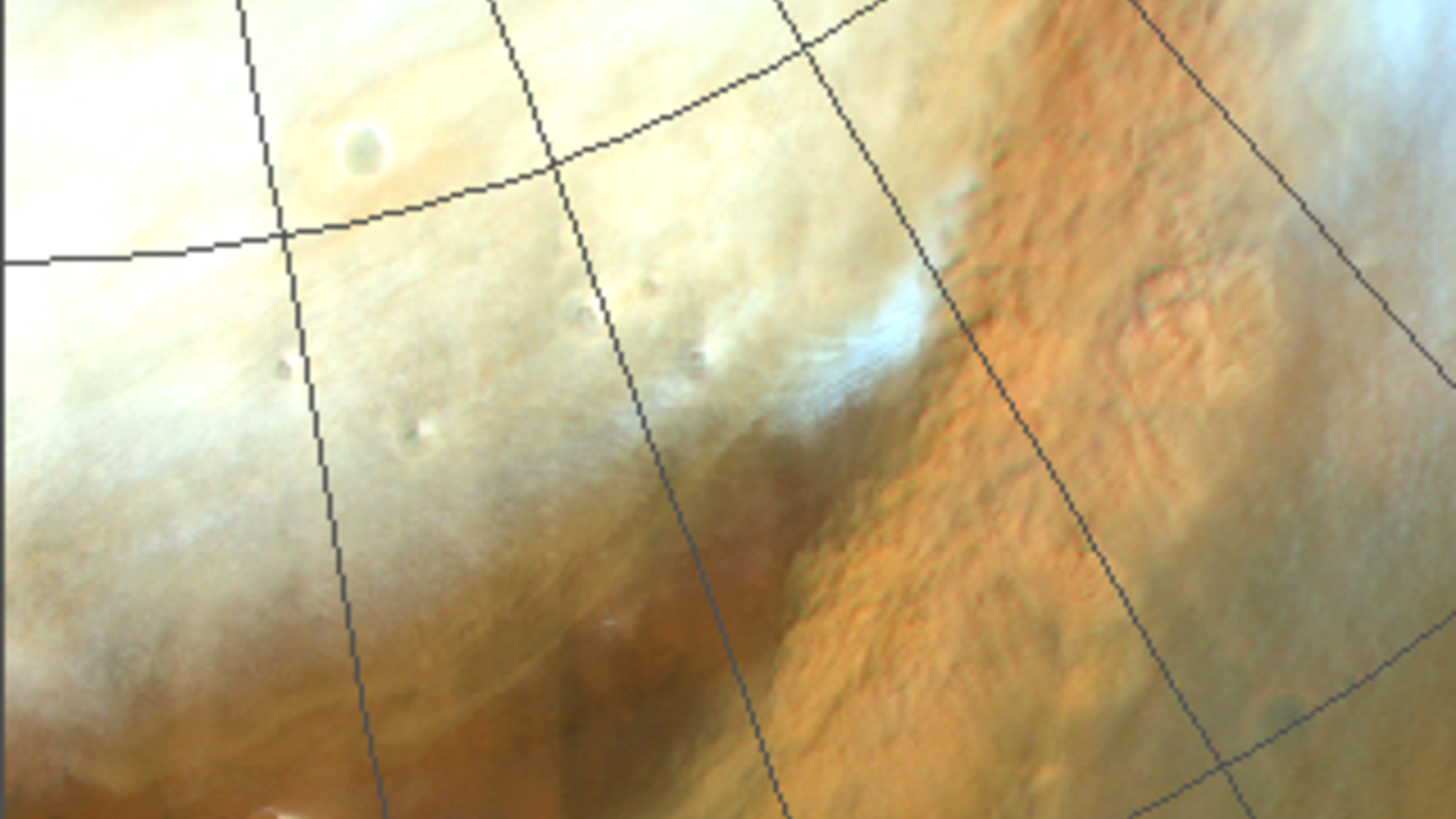
The photographs additionally reveal that dust storms on Mars are composed of repeatedly spaced, smaller cloud cells which are organized like pebbles, forming a garden-path-like texture that can be seen in clouds over Earth.
These patterns are created when scorching air rises and denser, cool air falls in cell-like models — a phenomenon known as closed-cell convection. As scorching air rises by way of the middle of those cells, cool air falls by way of “pathways” that kind in gaps between the person cells, the researchers defined.
On Earth, this convection causes clouds to kind as a result of rising scorching air comprises water, which then condenses and falls as rain. Within the dry and arid setting of Mars, nevertheless, these rising hot-air columns carry dust. Because the air cools and sinks, it carries much less dust. In consequence, cells kind over Mars with a well-recognized granular sample seen within the clouds over Earth, albeit with a dusty, somewhat than watery, composition.
The dust cells seen over Mars are helpful as a measurement instrument, as their motion in sequences of photographs permits scientists to measure Martian wind speeds. This course of has revealed winds blowing at as much as 87 mph (140 kph); these high-speed winds trigger the convection cells to be elongated within the route the winds blow.
The lengths of the shadows in photographs taken with VMC, when measured and in contrast with the recognized place of the sun, additionally revealed the altitude of the Martian dust clouds — round 4 to 7 miles (6 to 11 km — and confirmed that the conference cells are round 12 to 25 miles (20 to 40 km) large.
“Regardless of the unpredictable conduct of dust storms on Mars and the robust wind gusts that accompany them, we’ve got seen that inside their complexity, organized constructions reminiscent of fronts and mobile convection patterns can emerge,” Agustín Sánchez-Levaga, VMC science staff chief and lead creator of the research, stated within the assertion.
Earth and Mars aren’t the one locations within the solar system the place such mobile convection is seen; ESA’s Venus Express spacecraft noticed comparable patterns in Venusian clouds.
“Our work on Mars dry convection is an additional instance of the worth of comparative research of comparable phenomena occurring in planetary atmospheres with a purpose to higher perceive the mechanisms underlying them underneath completely different situations and environments,” Sánchez-Levaga stated.
This perception into the clouds of Mars offers planetary scientists a greater understanding of the dynamics of the Martian ambiance. Furthermore, the data of Martian dust storms might assist inform future missions to the Crimson Planet.
Mud storms can block gentle from the sun that’s wanted to energy the solar cells of robotic rovers that discover the Martian floor. The doubtless damaging results of dust storms on Mars have been demonstrated in 2018, when a planet-wide occasion blocked out daylight and coated the solar panels of the Alternative rover with dust, ending its mission.
Predicting the evolution of such dust storms might shield solar-powered missions in opposition to these highly effective pure occasions and even assist future Mars astronauts take care of dust storms.
The staff’s analysis was printed Tuesday (Nov. 15) within the journal Icarus.
Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or on Facebook.