James Webb House Telescope retains shocking us.
A key benefit of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is its capability to see deep into the previous. By wanting within the infrared a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, it is in a position to see gentle that has taken billions of years to succeed in us, stretched out by the expanding universe alongside its journey.
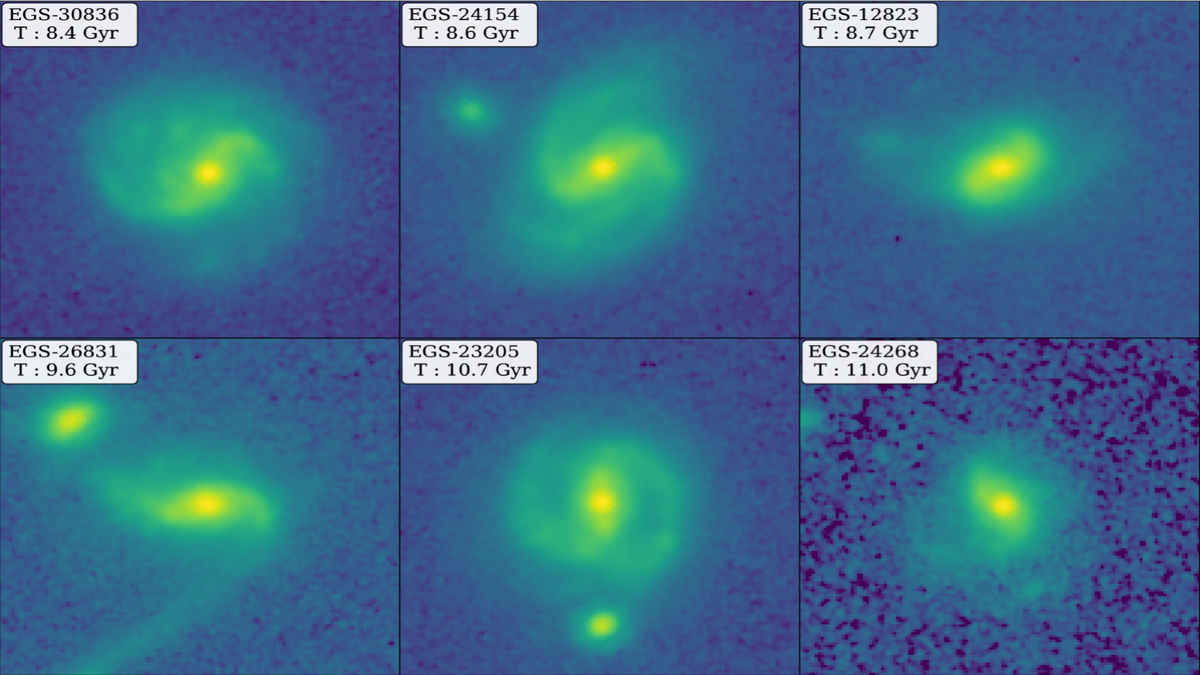
JWST’s specialised eyes on the universe just lately revealed yet one more shock —a number of galaxies that seem like our Milky Way, however from between 8 and 11 billion years previously when the universe was a lot youthful.
New analysis described in a statement from UT Austin (opens in new tab) presents observations from the JWST Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science Survey (opens in new tab) displaying galaxies with stellar bars, straight traces of stars stretching from galactic facilities to their outer disks, presently within the younger universe. The invention might “require scientists to refine their theories of galaxy evolution,” based on the assertion.
Associated: 12 amazing James Webb Space Telescope discoveries of 2022
“I took one take a look at these information, and I stated, ‘We’re dropping the whole lot else!'” Shardha Jogee, an astronomer at UT Austin, stated within the assertion.
That is the primary time stellar bars have been noticed in such younger galaxies, difficult current fashions of how galaxies kind and develop. They could additionally assist astronomers reply current questions on galaxies, similar to how supermassive black holes in galactic facilities develop and the way galaxies get sufficient materials to make stars of their facilities, generally known as the provision chain downside.
“For this examine, we’re a brand new regime the place nobody had used this type of information or accomplished this type of quantitative evaluation earlier than,” added lead writer Yuchen Guo. “So the whole lot is new. It is like going right into a forest that no person has ever gone into.”
Jogee added that these stellar bars might “remedy the provision chain downside in galaxies.”
“Identical to we have to deliver uncooked materials from the harbor to inland factories that make new merchandise, a bar powerfully transports gasoline into the central area the place the gasoline is quickly transformed into new stars at a price usually 10 to 100 occasions quicker than in the remainder of the galaxy,” Jogee defined.
This discovery is yet one more testomony to the extraordinary capabilities of NASA’s new workhorse space telescope, and a step in the direction of understanding how galaxies like our Milky Way got here to be.
The analysis is printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters (opens in new tab).
Comply with Briley Lewis on Twitter at @briles_34 (opens in new tab). Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) and on Facebook (opens in new tab).