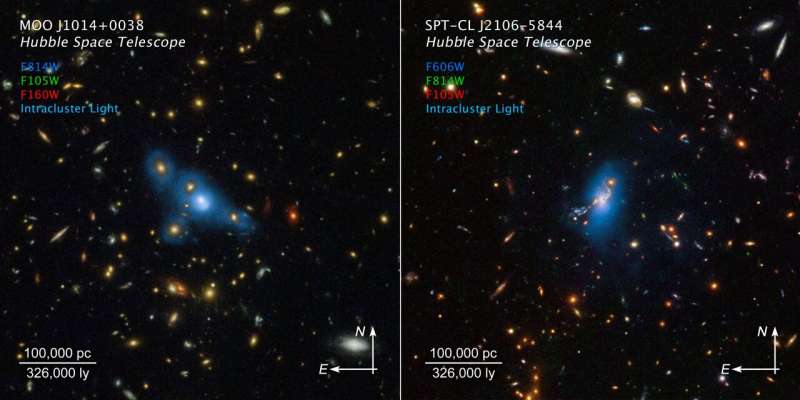
In big clusters of lots of or hundreds of galaxies, innumerable stars wander among the many galaxies like misplaced souls, emitting a ghostly haze of sunshine. These stars are usually not gravitationally tied to anyone galaxy in a cluster.
The nagging query for astronomers has been: how did the celebs get so scattered all through the cluster within the first place? A number of competing theories embrace the likelihood that the celebs have been stripped out of a cluster’s galaxies, or they have been tossed round after mergers of galaxies, or they have been current early in a cluster’s childhood many billions of years in the past.
A latest infrared survey from NASA’s Hubble House Telescope, which seemed for this so-called “intracluster mild” sheds new mild on the thriller. The brand new Hubble observations counsel that these stars have been wandering round for billions of years, and are usually not a product of newer dynamical exercise inside a galaxy cluster that will strip them out of regular galaxies.
The survey included 10 galaxy clusters as distant as practically 10 billion light-years. These measurements should be created from space as a result of the faint intracluster mild is 10,000 instances dimmer than the night time sky as seen from the bottom.
The survey reveals that the fraction of the intracluster mild relative to the total mild within the cluster stays fixed, trying over billions of years again into time. “Which means these stars have been already homeless within the early levels of the cluster’s formation,” mentioned James Jee of Yonsei College in Seoul, South Korea. His outcomes are being revealed within the January 5 subject of Nature journal.
Stars could be scattered exterior of their galactic birthplace when a galaxy strikes by way of gaseous materials within the space between galaxies, because it orbits the middle of the cluster. Within the course of, drag pushes fuel and dust out of the galaxy. Nevertheless, based mostly on the brand new Hubble survey, Jee guidelines out this mechanism as the first trigger for the intracluster star manufacturing. That is as a result of the intracluster mild fraction would enhance over time to the current if stripping is the primary participant. However that’s not the case within the new Hubble information, which present a relentless fraction over billions of years.
“We do not precisely know what made them homeless. Present theories can’t clarify our outcomes, however by some means they have been produced in giant portions within the early universe,” mentioned Jee. “Of their early childhood, galaxies may need been fairly small they usually bled stars fairly simply due to a weaker gravitational grasp.”
“If we work out the origin of intracluster stars, it would assist us perceive the meeting historical past of a whole galaxy cluster, they usually can function seen tracers of dark matter enveloping the cluster,” mentioned Hyungjin Joo of Yonsei College, the primary creator of the paper. Darkish matter is the invisible scaffolding of the universe, which holds galaxies, and clusters of galaxies, collectively.
If the wandering stars have been produced by way of a relatively latest pinball sport amongst galaxies, they don’t have sufficient time to scatter all through your entire gravitational subject of the cluster and due to this fact wouldn’t hint the distribution of the cluster’s dark matter. But when the celebs have been born within the cluster’s early years, they’ll have absolutely dispersed all through the cluster. This may permit astronomers to make use of the wayward stars to map out the dark matter distribution throughout the cluster.
This method is new and complementary to the standard technique of dark matter mapping by measuring how your entire cluster warps mild from background objects as a result of a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing.
Intracluster mild was first detected within the Coma cluster of galaxies in 1951 by Fritz Zwicky, who reported that certainly one of his most attention-grabbing discoveries was observing luminous, faint intergalactic matter within the cluster. As a result of the Coma cluster, containing at the least 1,000 galaxies, is among the nearest clusters to Earth (330 million light-years), Zwicky was capable of detect the ghost light even with a modest 18-inch telescope.
NASA’s James Webb House Telescope’s near-infrared functionality and sensitivity will vastly prolong the seek for intracluster stars deeper into the universe, and due to this fact ought to assist clear up the thriller.
Extra data:
Myungkook Jee, Intracluster mild is already ample at redshift past unity, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05396-4. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05396-4
Offered by
ESA/Hubble Information Centre
Quotation:
Hubble finds that ghost mild amongst galaxies stretches far again in time (2023, January 4)
retrieved 4 January 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-01-hubble-ghost-galaxies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




