Graphene Flagship Companions College of Cambridge (U.Okay.) and Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB, Belgium) paired up with the Mohammed bin Rashid House Heart (MBRSC, United Arab Emirates), and the European House Company (ESA) to check graphene on the moon. This joint effort sees the involvement of many worldwide companions, corresponding to Airbus Protection and House, Khalifa College, Massachusetts Institute of Know-how, Technische Universität Dortmund, College of Oslo, and Tohoku College.
The Rashid rover is deliberate to be launched on December 1, 2022 from Cape Canaveral in Florida and can land on a geologically wealthy and, as but, solely remotely explored space on the moon’s nearside—the facet that all the time faces the Earth. Throughout one lunar day, equal to roughly 14 days on Earth, Rashid will transfer on the lunar surface investigating attention-grabbing geological options.
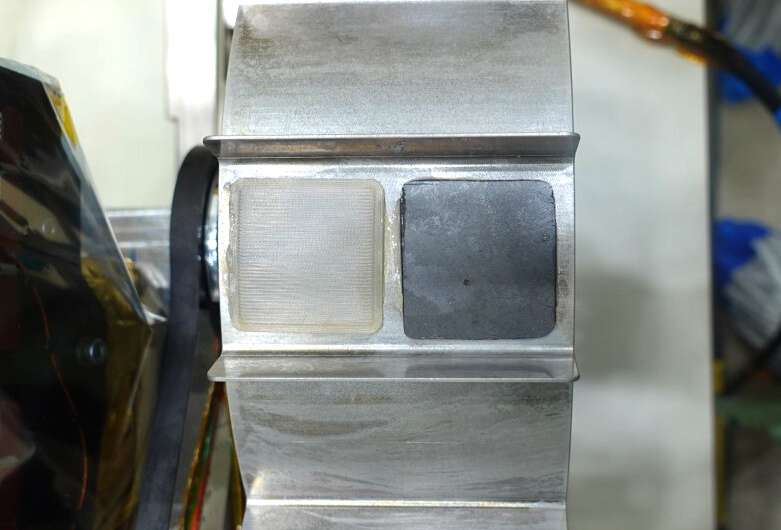
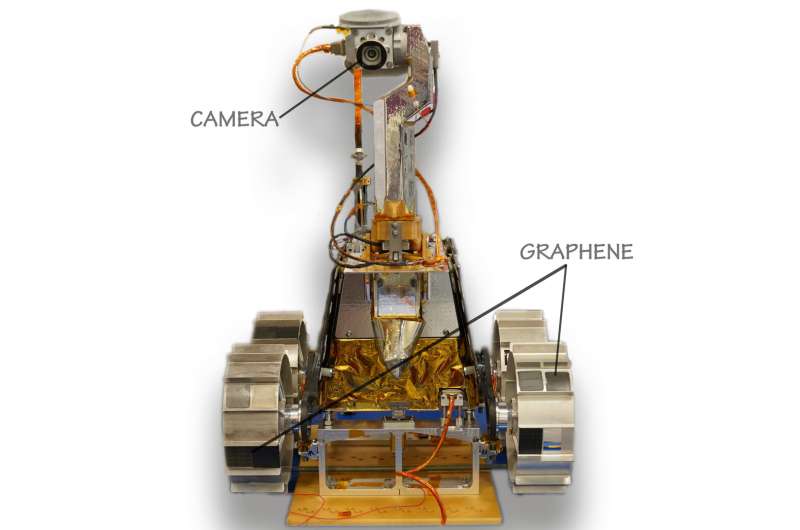
The Rashid rover wheels shall be used for repeated publicity of various supplies to the lunar floor. As a part of this Materials Adhesion and abrasion Detection experiment, graphene-based composites on the rover wheels shall be used to grasp if they’ll shield spacecraft towards the harsh conditions on the moon, and particularly towards regolith (also referred to as “lunar dust”).
Regolith is product of extraordinarily sharp, tiny and sticky grains and, for the reason that Apollo missions, it has been one of many largest challenges lunar missions have needed to overcome. Regolith is answerable for mechanical and electrostatic injury to gear, and is subsequently additionally hazardous for astronauts. It clogs spacesuits’ joints, obscures visors, erodes spacesuits and protecting layers, and is a possible well being hazard.
College of Cambridge researchers from the Cambridge Graphene Heart produced graphene/polyether ether ketone (PEEK) composites. The interplay of those composites with the moon regolith (soil) shall be investigated. The samples shall be monitored by way of an optical digicam, which is able to report footage all through the mission. ULB researchers will collect info throughout the mission and recommend changes to the trail and orientation of the rover. Pictures obtained shall be used to check the consequences of the moon atmosphere and the regolith abrasive stresses on the samples.
This moon mission comes quickly after the ESA announcement of the 2022 class of astronauts, together with the Graphene Flagship’s personal Meganne Christian, a researcher at Graphene Flagship Associate the Institute of Microelectronics and Microsystems (IMM) on the Nationwide Analysis Council of Italy.
“With the ability to comply with the moon rover’s progress in actual time will allow us to trace how the lunar atmosphere impacts numerous forms of graphene-polymer composites, thereby permitting us to deduce which ones is most resilient underneath such situations. It will improve our understanding of how graphene-based composites could possibly be used within the building of future lunar floor vessels,” says Sara Almaeeni, MBRSC science crew lead, who designed Rashid’s communication system.

“New supplies corresponding to graphene have the potential to be sport changers in space exploration. Together with the assets accessible on the moon, superior supplies will allow radiation safety, electronics shielding and mechanical resistance to the harshness of the moon’s atmosphere. The Rashid rover would be the first alternative to collect information on the conduct of graphene composites inside a lunar atmosphere,” says Carlo Iorio, Graphene Flagship House Champion, from ULB.
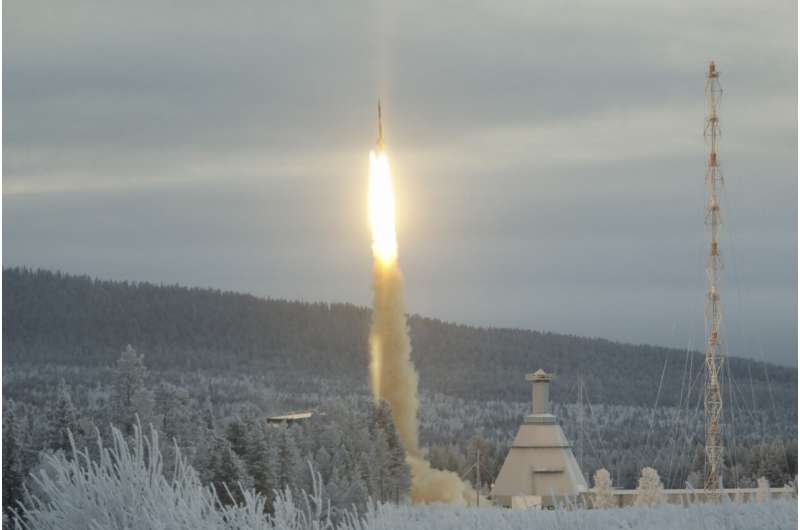
Main as much as the moon mission, quite a lot of inks containing graphene and associated supplies, corresponding to conducting graphene, insulating hexagonal boron nitride and graphene oxide, semiconducting molybdenum disulfide, ready by the College of Cambridge and ULB had been additionally examined on the MAterials Science Experiment Rocket 15 (MASER 15) mission, efficiently launched on the twenty third of November 2022 from the Esrange House Heart in Sweden.
This experiment, named ARLES-2 (Superior Analysis on Liquid Evaporation in House) and supported by European and UK space businesses (ESA, UKSA) included contributions from Graphene Flagship Companions College of Cambridge (UK), College of Pisa (Italy) and Trinity Faculty Dublin (Eire), with many worldwide collaborators, together with Aix-Marseille College (France), Technische Universität Darmstadt (Germany), York College (Canada), Université de Liège (Belgium), College of Edinburgh and Loughborough.
This experiment will present new details about the printing of GMR inks in weightless situations, contributing to the event of latest addictive manufacturing procedures in space corresponding to 3d printing. Such procedures are key for space exploration, throughout which substitute elements are sometimes wanted, and could possibly be manufactured from purposeful inks.
“Our experiments on graphene and associated supplies deposition in microgravity pave the way in which addictive manufacturing in space. The research of the interplay of moon regolith with graphene composites will handle some key challenges led to by the cruel lunar atmosphere,” says Yarjan Abdul Samad, from the Universities of Cambridge and Khalifa, who ready the samples and coordinated the interactions with the United Arab Emirates.
“The Graphene Flagship is spearheading the investigation of graphene and associated supplies (GRMs) for space purposes. In November 2022, we had the primary member of the Graphene Flagship appointed to the ESA astronaut class. We noticed the launch of a sounding rocket to check printing of quite a lot of GRMs in zero gravity situations, and the launch of a lunar rover that may check the interplay of graphene—based mostly composites with the moon floor.

“Composites, coatings and foams based mostly on GRMs have been on the core of the Graphene Flagship investigations since its starting. It’s thus fairly telling that, main as much as the Flagship’s tenth anniversary, these progressive supplies at the moment are to be examined on the lunar floor. That is well timed, given the continuing effort to convey astronauts again to the moon, with the goal of constructing lunar settlements.
“When mixed with polymers, GRMs can tailor the mechanical, thermal, electrical properties of then host matrices. These pioneering experiments might pave the way in which for widespread adoption of GRM-enhanced supplies for space exploration,” says Andrea Ferrari, Science and Know-how Officer and Chair of the Administration Panel of the Graphene Flagship.
Supplied by
University of Cambridge
Quotation:
Graphene heading to space and to the moon (2022, November 30)
retrieved 30 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-graphene-space-moon.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




