On January 25, 2023, NASA stated in a blog post that the Webb space telescope has achieved one other milestone. It noticed the thin rings of Chariklo – the primary asteroid identified to have rings – a small icy physique greater than 2 billion miles (3 billion km) from Earth. That’s out previous Saturn.
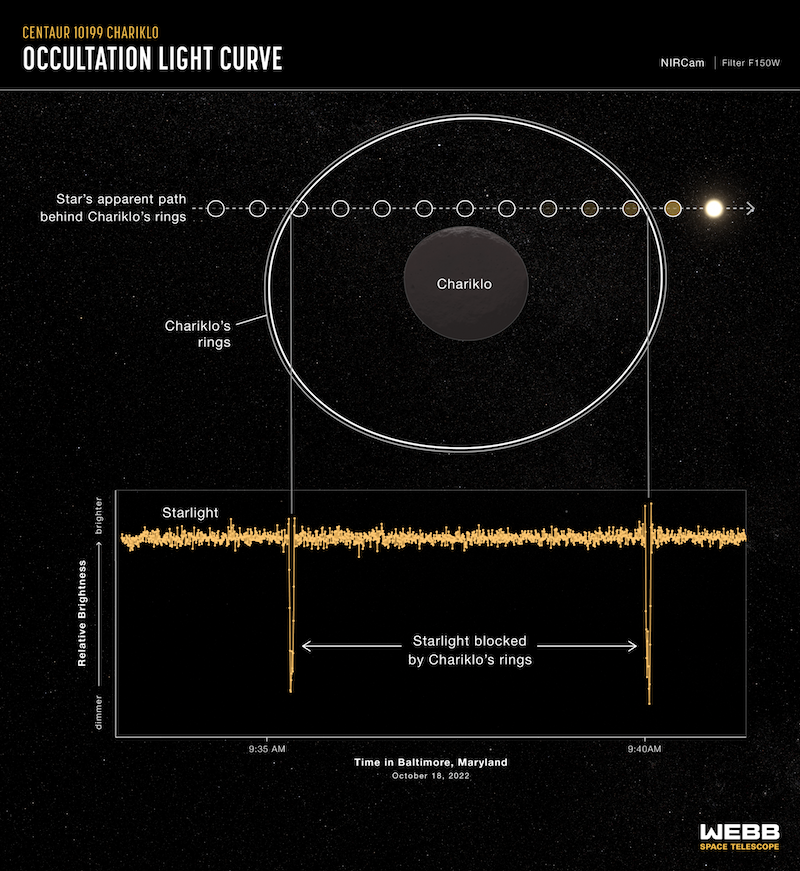
Webb did this by taking a look at Chariklo throughout a stellar occultation, the place it handed in entrance of a distant star from Earth’s viewpoint. Webb noticed the star blink not solely because it handed behind the asteroid, but in addition because it handed behind Chariklo’s rings.
Chariklo is the biggest identified of the Centaur asteroids, which orbit the sun between Saturn and Uranus.
It needs to be famous that the outcomes mentioned listed here are a part of Webb’s “science in progress” and haven’t but been peer-reviewed. However they do present a brand new, tantalizing glimpse of a hoop system that some scientists beforehand doubted even may exist.
Webb observes Chariklo’s rings
The researchers wished to aim to see stellar occultations of Chariklo with Webb. This could be achieved, particularly, as a part of the “Goal of Alternative” program (GTO 1271). Webb’s Assured Time Observations (GTO) for the solar system contains this program. Pablo Santos-Sanz, from Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía in Granada, Spain, is the Principal Investigator for Goal of Alternative. Heidi Hammel from the Affiliation of Universities for Analysis in Astronomy leads GTO.
So, would there be a great stellar occultation occasion throughout which to watch Chariklo? Because it turned on the market was, in October 2022. Furthermore, this was not solely the primary stellar occultation for Chariklo, but in addition Webb’s very first stellar occultation of any form. Because the weblog publish explained:
On October 18, we used Webb’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) instrument to carefully monitor the star Gaia DR3 6873519665992128512, and look ahead to the tell-tale dips in brightness indicating an occultation had taken place. The shadows produced by Chariklo’s rings have been clearly detected, demonstrating a brand new manner of utilizing Webb to discover solar system objects. The star shadow because of Chariklo itself tracked simply out of Webb’s view. This appulse (the technical title for an in depth move with no occultation) was precisely as had been predicted after the final Webb course trajectory maneuver.
Profitable occultation
To make sure, the occultation try was a terrific success. The weblog publish added:
The Webb occultation gentle curve, a graph of an object’s brightness over time, revealed that the observations have been profitable! The rings have been captured precisely as predicted. The occultation gentle curves will yield fascinating new science for Chariklo’s rings.
Even Webb can’t picture the rings as distinct options from Chariklo itself, nevertheless. Usually talking, Chariklo is just too small and too far-off. So on this case, a stellar occultation is the subsequent greatest method to examine them.
Composition of the rings
Astronomer Felipe Braga-Ribas and his colleagues first found the rings in 2013, utilizing ground-based telescopes. Similar to with Webb, they noticed Chariklo move in entrance of, or occult, a background star. However then, the astronomers observed one thing fascinating. The star blinked twice, each simply earlier than Chariklo moved in entrance of it and simply after. Consequently, the astronomers realized that two skinny rings round Chariklo brought on the blinking. Certainly, this was the primary time that astronomers had discovered such rings round a small asteroid-type physique within the solar system.
Scientists estimate the rings to be between two and 4 miles (three and 4 km) large.
That such a small physique, solely about 160 miles (250 km) in diameter, can have a hoop system is fascinating. But in addition, what are the rings manufactured from? Scientists say they’re seemingly darkish materials blended with ice particles. They imagine the darkish materials is leftover particles from an historic collision between Chariklo and one other icy physique.
As well as, water ice within the rings was a key discovery. Webb discovered it by taking a look at Chariklo once more after the occultation. The telescope detected three distinct absorption bands of water ice. Noemí Pinilla-Alonso, who led the observations, stated:
Spectra from ground-based telescopes had hinted at this ice (Duffard et al. 2014), however the beautiful high quality of the Webb spectrum revealed the clear signature of crystalline ice for the primary time.

New insights into Chariklo’s rings
Dean Hines, principal investigator of the GTO program, added:
As a result of high-energy particles remodel ice from crystalline into amorphous states, detection of crystalline ice signifies that the Chariklo system experiences steady micro-collisions that both expose pristine materials or set off crystallization processes.
Santos-Sanz added:
As we delve deeper into the info, we’ll discover whether or not we cleanly resolve the 2 rings. From the shapes of rings’ occultation gentle curves, we additionally will discover the rings’ thickness, the sizes and colours of the ring particles, and extra. We hope to realize perception into why this small physique even has rings in any respect, and maybe detect new fainter rings.
It’s additionally doable that Chariklo might have a tiny moon or two as properly. Scientists say they might assist maintain the rings slender and confined, as we see them. Again in 2014, Braga-Ribas said:
So, in addition to the rings, it’s seemingly that Chariklo has a minimum of one small moon nonetheless ready to be found.
Backside line: NASA’s Webb telescope took its first take a look at tiny asteroid Chariklo’s rings, displaying they include water ice. Webb used a stellar occultation to watch the rings.




