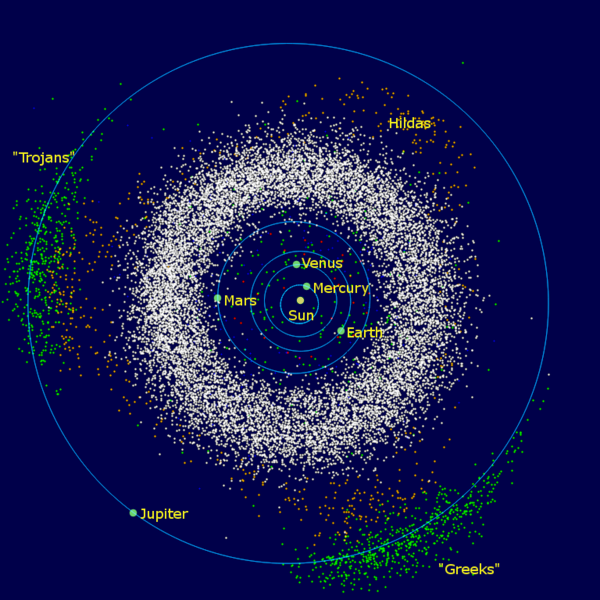
Meet the asteroid belt, a spot in our solar system the place small our bodies – largely rocky and a few metallic – orbit the sun. Generally scientists name these little worlds minor planets. One (Ceres) is technically a dwarf planet. These objects transfer largely between the orbits of our solar system’s 4th planet, Mars, and fifth planet, Jupiter. Astronomers as soon as thought they had been leftovers of a rocky planet that Jupiter’s gravity tore aside way back. Now they assume in a different way. They assume the asteroids are probably merely remnants from the formation of our solar system 4.6 billion years in the past.
The phrase asteroid means starlike. Asteroids received this title as a result of, when astronomers first found them within the early 1800s, they thought they appeared like stars. And but their motion was separate from stars. As a result of they’re nearer to us, they transfer towards the starry backdrop. This confirmed asteroids to be one thing apart from stars.
Asteroids by the thousands and thousands
Whereas the graphic might make it appear to be the asteroid belt is teeming with particles, when you lumped all the fabric collectively it will solely create a physique smaller than Earth’s moon.
The asteroid belt comprises objects that modify wildly in dimension. It has 1 to 2 million asteroids greater than half a mile (a couple of km) throughout. Plus, the asteroid belt comprises untold thousands and thousands of smaller ones, some most likely no greater than pebbles. In 1801, the astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi found the primary asteroid, which can be the largest object within the asteroid belt. It’s 1 Ceres, which measures some 587 miles (945 km) throughout. The Worldwide Astronomical Union has reclassified Ceres from an asteroid to a dwarf planet.
Distances within the asteroid belt
Outer space is huge. And thus, regardless of there being many thousands and thousands (probably billions) of objects within the asteroid belt, the typical distance between them is 600,000 miles (about 1 million km). Which means spacecraft can fly via the asteroid belt with out colliding with any asteroids. (Though, clearly, an opportunity collision is rarely fully out of the realm of risk and dangerous luck.) The asteroid belt is actually nothing just like the densely packed fields depicted in fantasies reminiscent of “Star Wars.”
Standing on any asteroid within the belt, you’ll probably be unable to see another asteroids, due to their distance.
The asteroid belt lies between 2.2 and three.2 astronomical items (AU) from our sun. One AU is the gap between the Earth and sun. So the width of the asteroid belt is roughly 1 AU, or 92 million miles (150 million km).
Its thickness is equally about 1 AU.
Asteroids out and in of the primary belt
We frequently name the asteroid belt the fundamental belt to differentiate it from different, smaller teams of asteroids within the solar system such because the Lagrangians and Centaurs within the outer solar system.
What scientists as soon as thought was a homogeneous belt they now know to be barely extra difficult. There are totally different and distinct zones inside the main-belt asteroids. That is very true at its edges, the place astronomers now acknowledge the Hungaria group on the internal edge and the Cybele asteroids on the outer. Towards the center of the belt there’s the extremely inclined Phocaea family.
As well as, astronomers have established that the age of asteroids in the primary belt additionally varies. They’ve now categorised a number of asteroid groupings by their age, together with the Karin family, a bunch of about 90 main-belt asteroids that share an orbit and should have come from a single object some 5.7 million years in the past. And there’s the Veritas family, from about 8.3 million years in the past. A really current group is the Datura family, relationship from a collision simply 530,000 years in the past.
Backside line: The asteroid belt is a area of our solar system – between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter – the place many small our bodies orbit our sun.