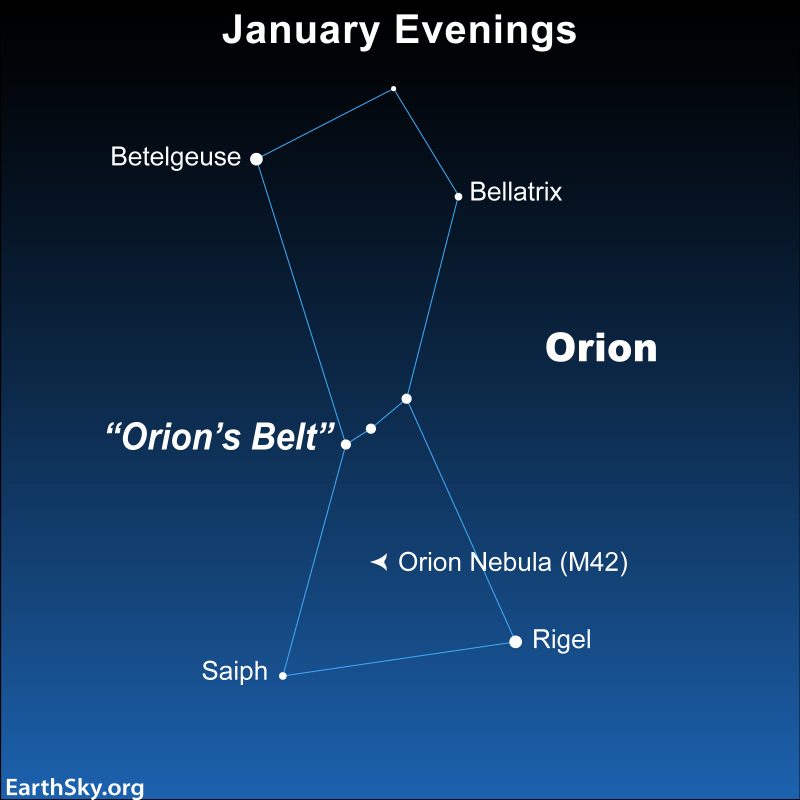
Tonight search for the constellation Orion the Hunter. It’s a relentless companion on winter evenings within the Northern Hemisphere, and on summer time nights within the Southern Hemisphere. Plus, it’s in all probability the best constellation to identify due to its distinctive Belt. Orion’s Belt consists of three medium-bright stars in a brief, straight row on the Hunter’s waistline. So when you see any three equally vivid stars in a row this night, you’re in all probability taking a look at Orion. Do you need to ensure? There are two even brighter stars – one reddish and the opposite blue – on both aspect of the Belt stars.
When to search for Orion
As seen from mid-northern latitudes, you’ll discover Orion within the southeast within the early night and shining excessive within the south by mid-to-late night (round 9 to 10 p.m. native time, the time in your clock wherever you reside). In case you dwell at temperate latitudes south of the equator, you’ll see Orion excessive in your northern sky round that very same hour.

What to search for in Orion the Hunter
First, search for the 2 brightest stars in Orion: Betelgeuse and Rigel. Rigel’s distance is roughly 773 light-years. Nevertheless, the space to Betelgeuse has been more durable for scientists to find out. Its current estimate is about 724 light-years away, however uncertainties stay.
Betelgeuse dimmed for a while in late 2019, producing a good quantity of pleasure, as a result of Betelgeuse is a star on the point of a supernova. Nevertheless, the star has since returned to its normal brightness. So how bright does it look tonight?
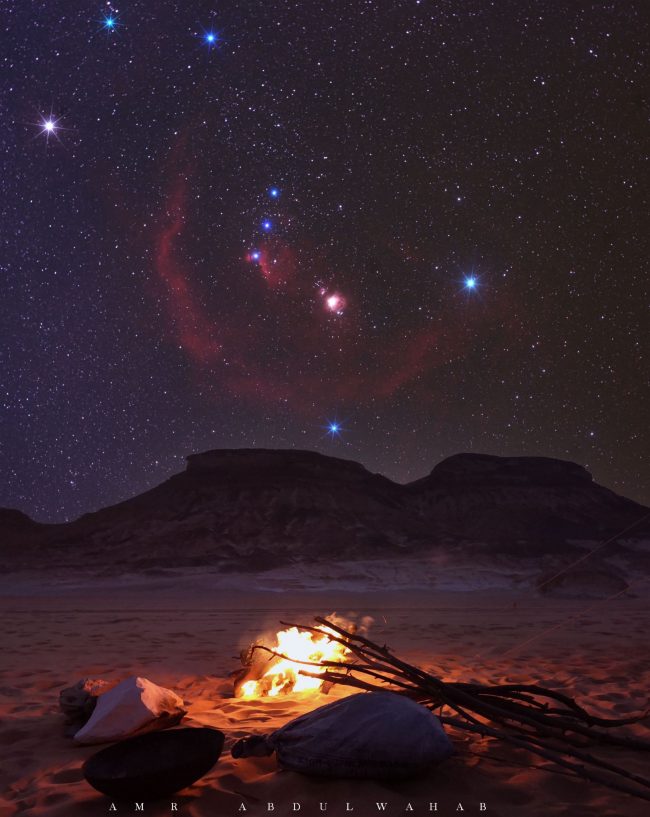
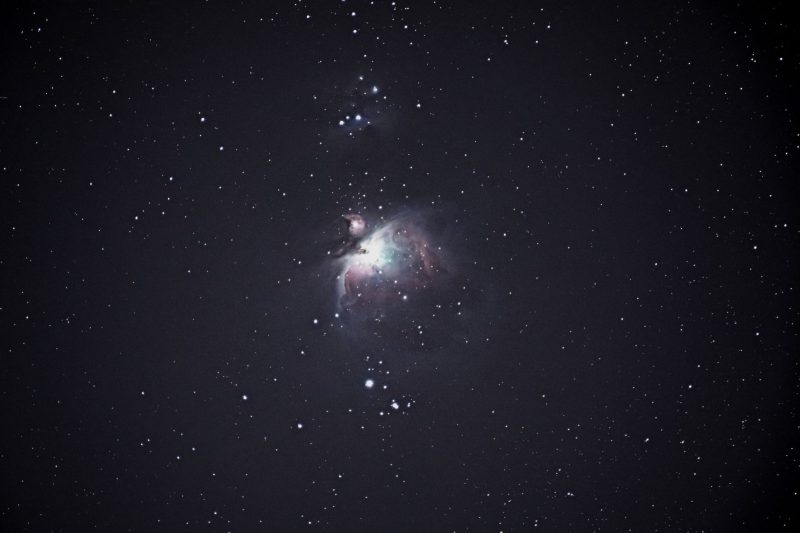
Additionally, take a second to hint the Belt of Orion and the Sword that hangs from his belt. If one of many stars within the Sword seems blurry to you, that’s since you’re really seeing the Orion Nebula. And when you use binoculars or a telescope to take a look at the Orion Nebula, you’ll begin to see some form within the fuel and dust cloud.

Connections between the celebrities
Whereas the celebrities of constellations typically appear like they need to be bodily associated and gravitationally certain, they normally usually are not.
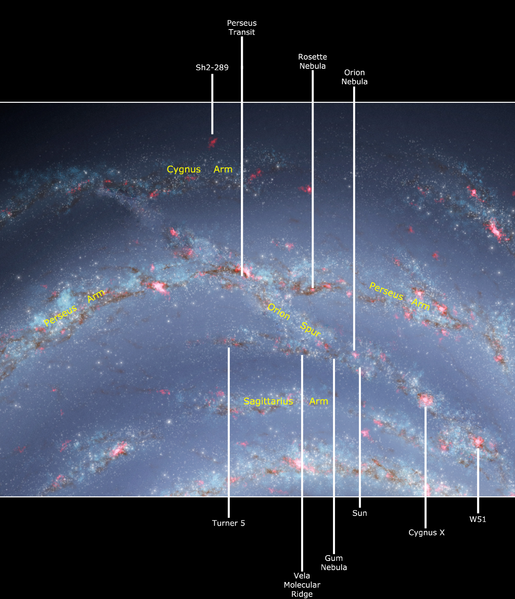
Nevertheless, a few of Orion’s most well-known stars do have a connection. A number of of the brightest stars in Orion are members of our local spiral arm, typically known as the Orion Arm or typically the Orion Spur of the Milky Way. Our native spiral arm lies between the Sagittarius and Perseus Arms of the Milky Way.
Now take into account these three distinguished Belt stars. They seem fainter than Rigel or Betelgeuse, and, not surprisingly, they’re farther away. As a matter of truth, they’re all big stars positioned within the Orion Arm. These stars’ names and approximate distances are Mintaka (900 light-years), Alnilam (1,300 light-years), and Alnitak (800 light-years). If you take a look at these three stars, know that you simply’re trying throughout huge space, and into our local arm of the Milky Way galaxy.
Backside line: Orion the Hunter is likely one of the best constellations to establish due to its Belt, the three medium-bright stars in a brief, straight row at his waist.