In November 2022, EarthSky reported on new proof for magma nonetheless present beneath the floor of Mars. And, on December 5, 2022, researchers on the College of Arizona said they’ve now discovered much more clues that the crimson planet continues to be volcanically lively. A brand new evaluation of orbital pictures of the Elysium Planitia area suggests an enormous mantle plume of sizzling molten rock (magma) pushing upward from the mantle deep beneath. Such mantle plumes, additionally discovered on Earth, could cause earthquakes, faulting and volcanic eruptions. On Mars, this mantle plume possible drives a lot of the seismic exercise – 1000’s of marsquakes – NASA’s InSight lander has detected in the region since 2018.
The researchers published the brand new peer-reviewed proof in Nature Astronomy on December 5, 2022.
Large blob of sizzling rock beneath the floor of Mars
Previous to newer new discoveries, most planetary scientists thought that Mars was geologically lifeless. The proof for present marsquakes and subsurface magma has upended that view, nonetheless. Now, the proof for an enormous and lively mantle plume additional challenges the previous assumptions.
Scientists mentioned the mantle plume, like ones on Earth, is an enormous blob of sizzling magma. The researchers mentioned it’s pushing upward from deep contained in the planet. This motion causes the marsquakes and subsurface volcanic exercise. We should always be aware that even on Earth, scientists nonetheless regard mantle plumes as a speculation. Albeit, nonetheless, one for which there’s now substantial proof.
As lead creator Adrien Broquet, a postdoctoral analysis affiliate within the College of Arizona’s Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, said:
Our research presents a number of strains of proof that reveal the presence of an enormous lively mantle plume on present-day Mars.
Co-author Jeffrey Andrews-Hanna additionally famous that:
Now we have sturdy proof for mantle plumes being lively on Earth and Venus, however this isn’t anticipated on a small and supposedly chilly world like Mars. Mars was most lively 3 to 4 billion years in the past, and the prevailing view is that the planet is actually lifeless at this time.
Broquet added:
An incredible quantity of volcanic exercise early within the planet’s historical past constructed the tallest volcanoes within the solar system and blanketed many of the northern hemisphere in volcanic deposits. What little exercise has occurred in current historical past is usually attributed to passive processes on a cooling planet.
The Hawaiian Islands are a superb instance of this course of on Earth. They shaped because the Pacific tectonic plate, the Pacific Plate, drifted over high of a giant mantle plume.
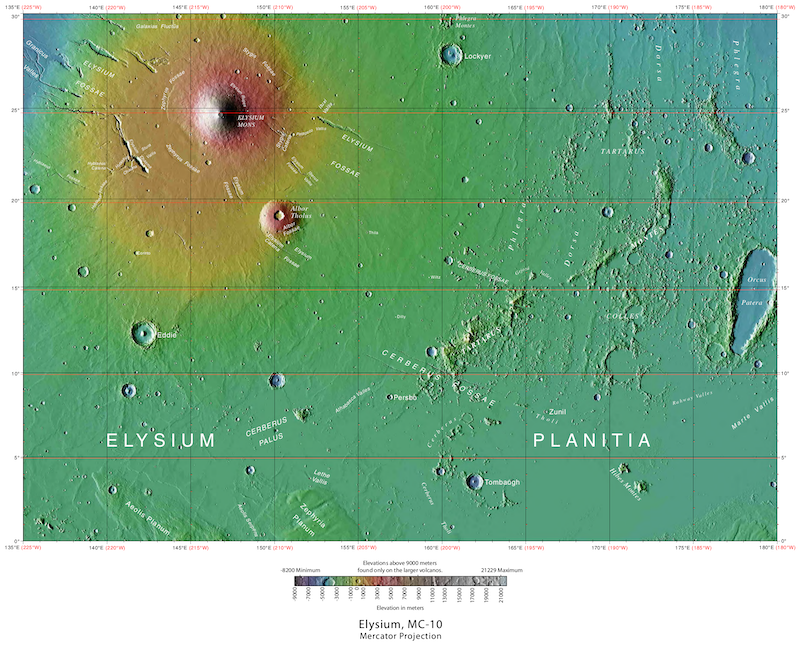
Elysium Planitia as a volcanic hotspot
One area of Mars specifically stands out for its volcanic exercise: an enormous, flat plain referred to as Elysium Planitia. Though another areas, like Tharsis, even have big volcanoes, scientists mentioned these volcanoes have been lifeless or dormant for billions of years (no less than on the floor). In Elysium Planitia, nonetheless, scientists have discovered proof for volcanic eruptions occurring inside the previous 200 million years. And even some eruptions far more not too long ago, geologically talking. Andrews-Hanna said:
Earlier work by our group discovered proof in Elysium Planitia for the youngest volcanic eruption recognized on Mars. It created a small explosion of volcanic ash round 53,000 years in the past, which in geologic time is actually yesterday.
Just like the others, these volcanoes are not erupting on the floor. However the brand new findings recommend there may be nonetheless no less than residual volcanic exercise taking place beneath floor.
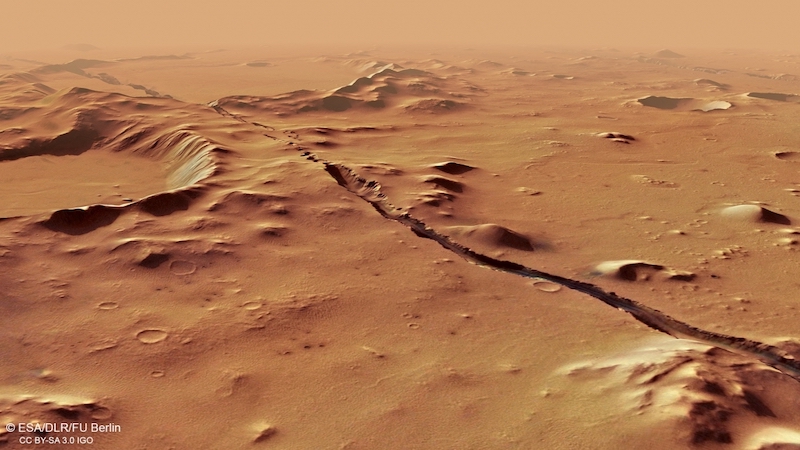
Marsquakes in Cerberus Fossae
There’s additionally a volcanic connection between Elysium Planitia and a area inside it referred to as Cerberus Fossae. Fissures and faults in Cerberus Fossae stretch for greater than 800 miles (1,287 km). Nearly all of the marsquakes detected by NASA’s InSight lander have originated on this area.
However why are there so many marsquakes on this one space? Earthquakes on our personal planet present a clue. They’re related to both plate tectonics or mantle plumes. Since Mars doesn’t have plate tectonics, the researchers investigated whether or not there could possibly be a mantle plume beneath the floor in Cerberus Fossae. They seemed nearer at floor options in Elysium Planitia and located similarities with options on Earth. This included uplifting and stretching of the crust and molten rock from the subsurface plume. The plume erupts as molten basalts that create the volcanic plains. The paper stated:
The inferred plume head traits are corresponding to terrestrial plumes which are linked to the formation of enormous igneous provinces.
The researchers discovered that though Elysium Planitia is a flat plain, one thing from beneath had uplifted its floor by greater than a mile (1.6 km). Evaluation of variations within the gravity of this area additionally confirmed that this upwelling is supported from deep beneath the floor. That is all in step with a mantle plume. Even the flooring of impression craters within the space tilt within the route of the plume. This reveals that the floor was pushed upward and stretched after the craters shaped.
Mantle plume confirmed on Mars
The ultimate piece of the puzzle fell in place when the researchers utilized a tectonic mannequin to the Elysium Planitia area. It revealed the presence of a mantle plume 2,500 miles (4,023 km) extensive. Because the paper noted:
Right here we current observational proof and geophysical fashions demonstrating that Elysium Planitia is underlain by an ~4,000-km-diameter lively mantle plume head.
Broquet said:
When it comes to what you anticipate to see with an lively mantle plume, Elysium Planitia is checking all the fitting packing containers. This mantle plume has affected an space of Mars roughly equal to that of the continental United States. Future research must discover a approach to account for a really massive mantle plume that wasn’t anticipated to be there.
We used to assume that InSight landed in some of the geologically boring areas on Mars, a pleasant flat floor that must be roughly consultant of the planet’s lowlands. As an alternative, our research demonstrates that InSight landed proper on high of an lively plume head.
Life on Mars?
It’s attainable that the warmth from the plume might additionally soften ice deep beneath the bottom. If that’s the case, which may create a liveable atmosphere for microbes. As Andrews-Hanna noted:
Microbes on Earth flourish in environments like this, and that could possibly be true on Mars, as nicely. Realizing that there’s an lively large mantle plume beneath the Martian floor raises essential questions relating to how the planet has advanced over time. We’re satisfied that the long run has extra surprises in retailer.
We might not see big eruptions of ash and lava on Mars, however that doesn’t imply the planet is lifeless. Certainly, evidently deep down, Mars’ geological coronary heart continues to be beating, even when you must pay attention intently to listen to it.
Backside line: Researchers on the College of Arizona have discovered an enormous plume of sizzling rock beneath the floor of Mars, exhibiting that the planet continues to be volcanically lively.
Source: Geophysical evidence for an active mantle plume underneath Elysium Planitia on Mars