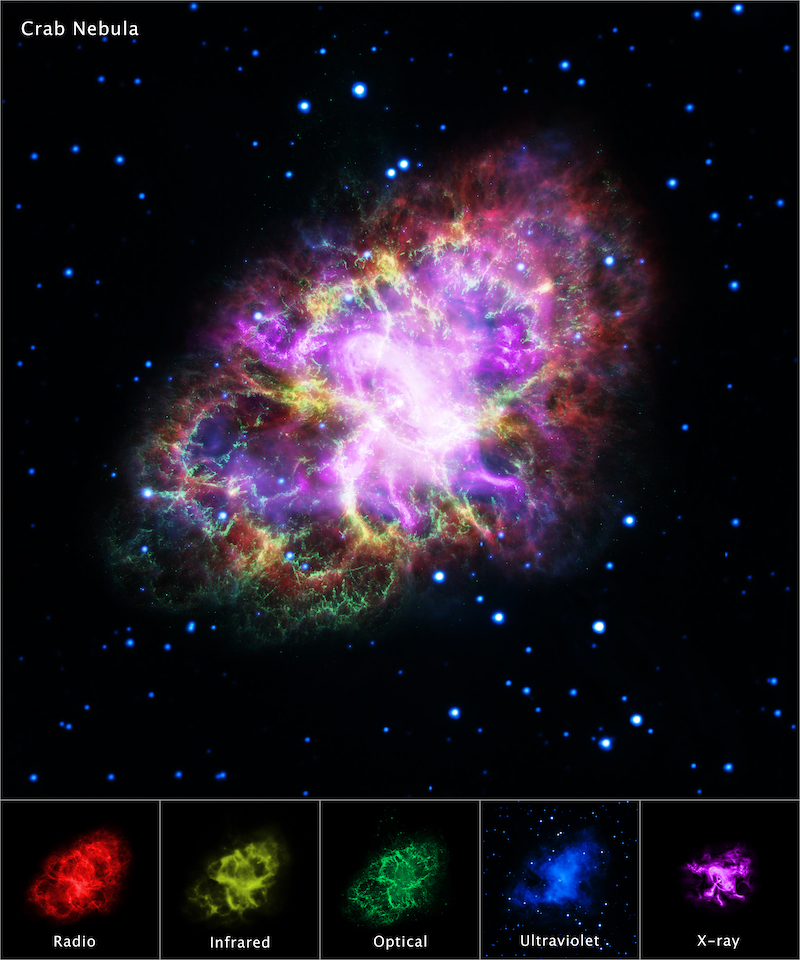
A supernova explodes
The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant. It’s what’s left of an exploded star. So it’s an enormous increasing cloud of fuel and dust surrounding one of many densest objects within the universe, a neutron star.
Chinese language astronomers seen the sudden appearance of a star blazing within the daytime sky on July 4, 1054 CE. It seemingly outshone the brightest planet, Venus, and was quickly the Third-brightest object within the sky, after the sun and moon. This “visitor star” – the exploding supernova – remained seen in daylight for some 23 days. At night time it shone close to Tianguan – a star we now name Zeta Tauri, within the constellation of the Taurus the Bull – for almost two years. Then it light from view.
The supernova erupted – and the Crab Nebula fashioned – about 6,500 light-years away.
The Crab Nebula and supernova in historical past
The ancestral Puebloan folks within the American Southwest could have viewed the brilliant new star in 1054. Additionally, a crescent moon was within the sky close to the brand new star on the morning of July 5, the day following the observations by the Chinese language. So the pictograph beneath, from Chaco Canyon in New Mexico, could depict the occasion. And the multi-spiked star to the left represents the supernova close to the crescent moon. Moreover, the handprint above could signify the significance of the occasion or could be the artist’s “signature.”
After exploding onto the scene in 1054 and shining brightly for 2 years, there aren’t any experiences of something uncommon on this spot within the sky till 1731. Then in that 12 months, English beginner astronomer John Bevis recorded an commentary of a faint nebulosity. In 1758, French comet-hunter Charles Messier noticed the hazy patch. It grew to become the primary entry in his catalog of objects that have been fuzzy however not comets, now generally known as the Messier Catalog. Thus, the Crab Nebula has the title M1.
In 1844, astronomer William Parsons – the third Earl of Rosse – noticed M1 by his massive telescope in Eire. As a result of he described it as having a form resembling a crab, that grew to become its acquainted nickname.
But it wasn’t till 1921 that individuals made the affiliation between the Crab Nebula and Chinese language information of the 1054 “visitor” star.

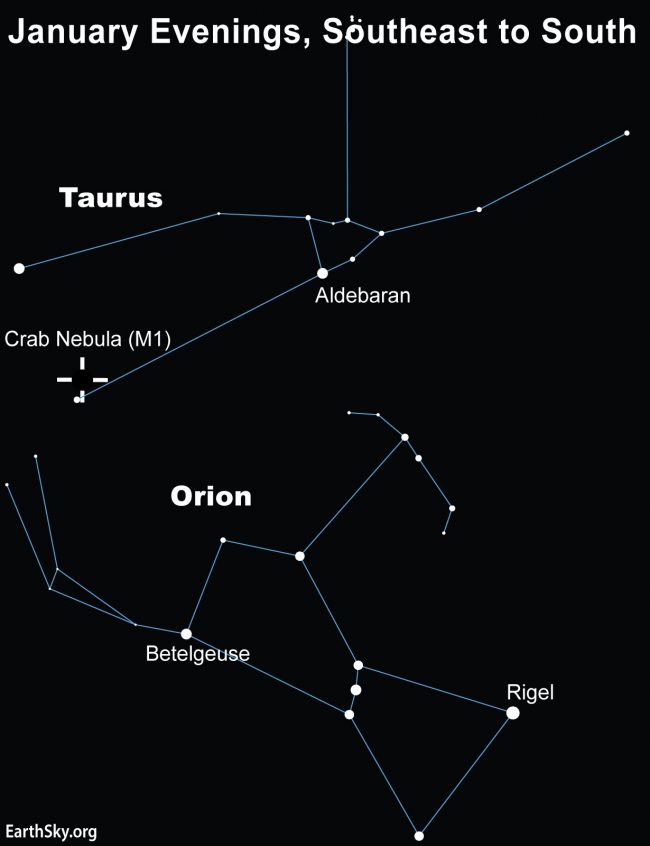
Methods to see the Crab Nebula
Since this stunning nebula, shines at magnitude 8.4, it requires magnification to see. Thankfully, it’s comparatively simple to seek out with binoculars or a telescope as a consequence of its location close to a number of brilliant stars. Plus, it’s close to a number of recognizable constellations. Though you’ll be able to see it at a while of night time all 12 months besides – from roughly Might by July – when it’s too near the sun, the perfect observing is late fall by early spring.
To search out the Crab Nebula, first draw an imaginary line from brilliant Betelgeuse in Orion to Capella in Auriga. About midway alongside that line is the star Beta Tauri (or Elnath) on the Taurus-Auriga border.
Having recognized Beta Tauri, backtrack just a little greater than a 3rd of the best way again to Betelgeuse to seek out the fainter star Zeta Tauri. Scanning the realm round Zeta Tauri ought to reveal a tiny, faint smudge. It’s a couple of degree (twice the width of the full moon) from Zeta Tauri and roughly within the route of Beta Tauri.
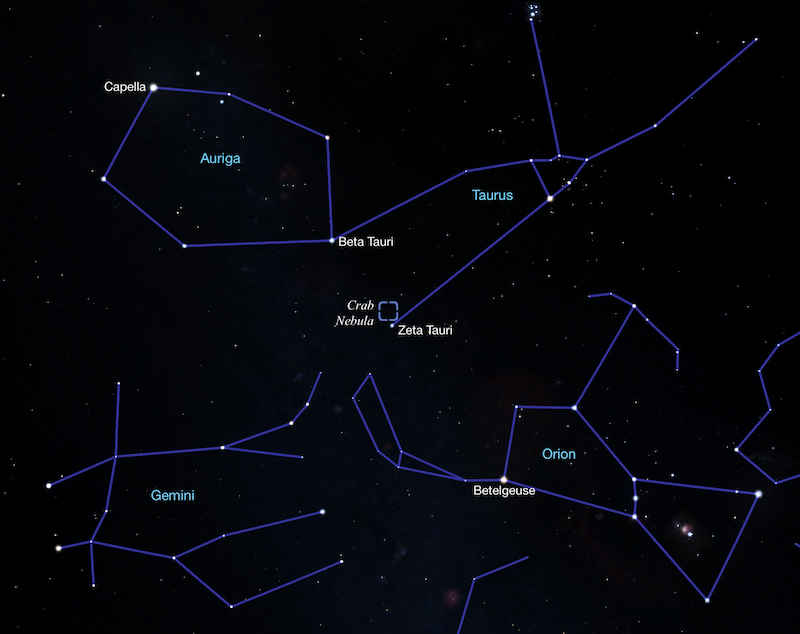
Views by binoculars or a telescope
Binoculars and small telescopes are helpful for locating the article and displaying its roughly rectangular form. Nonetheless, they received’t present the filamentary construction or any of its inside element. Listed below are two examples displaying what to anticipate in binoculars or by a telescope.

First, the eyepiece view, above, simulates a 7-degree area of view centered round Zeta Tauri. That is what you would possibly anticipate from a 7 X 50 pair of binoculars. After all, the precise orientation and visibility will vary broadly relying on time of commentary, sky circumstances and so forth. Scan round Zeta Tauri for the faint nebulosity.
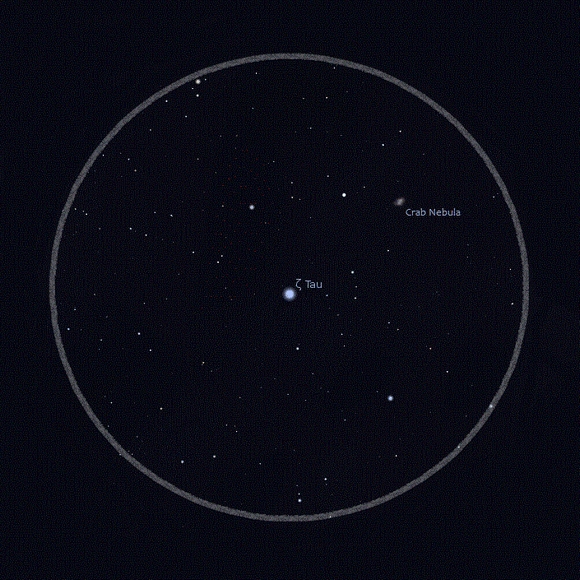
Then the second picture, above, simulates an roughly 3.5-degree view that you just would possibly see by a small telescope or finder scope. To provide you a transparent thought of scale, two full moons would match with room to spare within the space between Zeta Tauri and the Crab Nebula on this chart.
Though remember that actual circumstances will differ.
Science of the Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula is an oval gaseous nebula with tremendous filamentary (thread-like) constructions, increasing at round 930 miles (1,500 km) per second. What’s extra, in its coronary heart is a neutron star concerning the mass of the sun however solely about 12 miles (19 km) in diameter. What’s extra, this neutron star can be a pulsar that spins about 30 occasions per second. Plus, the neutron star’s highly effective magnetic area concentrates radiation emitted by the star as two beams that seem to flash periodically because the beams sweep into view.
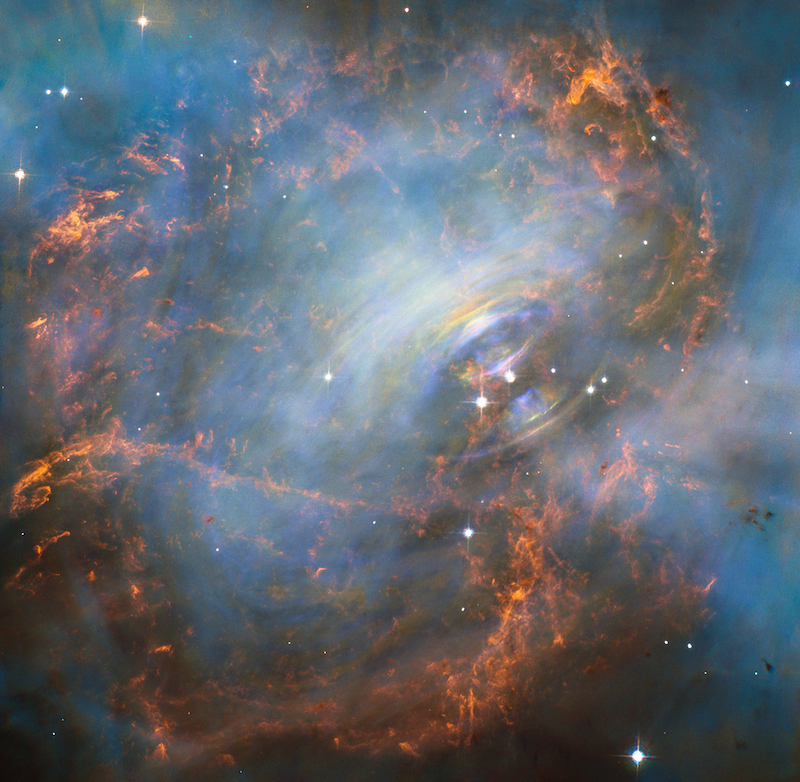


The Crab Nebula could also be from a brand new sort of supernova
For a very long time scientists thought the Crab Nebula was the remnant of a type II supernova. However in June 2021, scientists introduced they’d lastly discovered proof for a brand new sort of supernova, an electron-capture supernova. Consequently, they now imagine the Crab Nebula could also be this sort of supernova. Read more about this exciting discovery.
The middle of the Crab Nebula is roughly RA: 5h 34m 32s; Dec: +22° 0′ 52″
Backside line: The Crab Nebula is seen with binoculars and small telescopes, and comparatively simple to seek out because it’s close to brilliant stars in distinguished constellations. Though astronomers lengthy thought that it was the remnant of a kind II supernova, there’s growing proof that it might have been a brand new sort of supernova referred to as an electron seize supernova.




