What does Earth appear to be from outer space? And … how distant from Earth can we be and see it nonetheless with our personal eyes?
To search out the answer to those questions, let’s take an imaginary journey by the solar system. Certainly, spacecraft exploring our solar system have given us marvelous views of Earth. Preserve studying, and take a look at the photographs on this web page, to see how Earth seems to be from numerous different locations in our personal neighborhood of space.
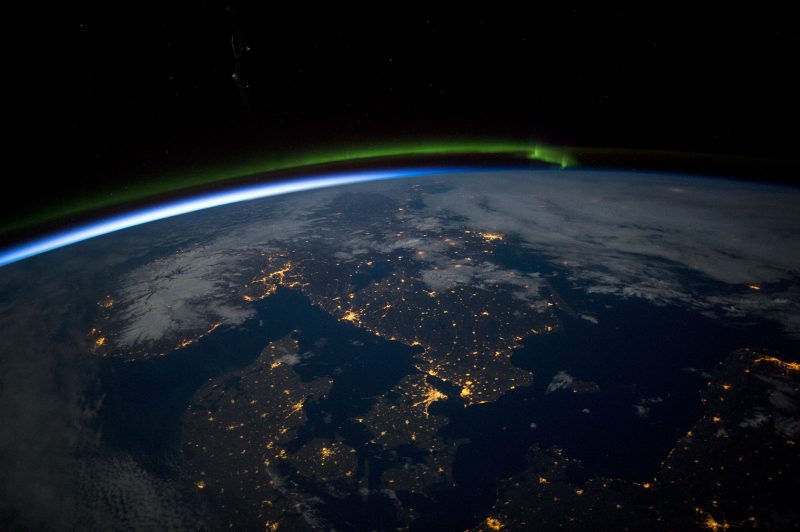
The view from orbiting the Earth
First, think about blasting off and being about 200 miles (300 km) above Earth’s floor. That’s in regards to the top of the orbit of the Worldwide Area Station (ISS). From the window of the ISS, the floor of the Earth looms giant. Certainly, within the daytime, you may clearly see main landforms. Subsequently, at evening, from Earth orbit, you see the lights of Earth’s cities.


From the moon
Now, let’s get farther away, say, the space of the orbit of the moon.
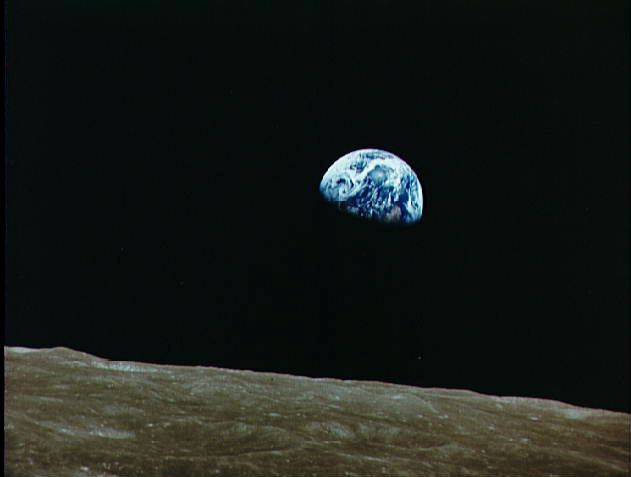
As we go the moon – some quarter million miles (about 380,000 km) away – Earth seems to be like a shiny ball in space. In truth, it’s not terribly totally different from the way in which the moon seems to be to us.
Considerably, the primary photos of the Earth from the moon got here from the Apollo mission. Apollo 8 in 1968 was the primary human spaceflight to depart Earth orbit. Likewise, it was the primary earthly spacecraft to be captured by and escape from the gravitational subject of one other celestial physique, on this case the moon.
It was, subsequently, the primary voyage during which people visited one other world and returned to Earth.

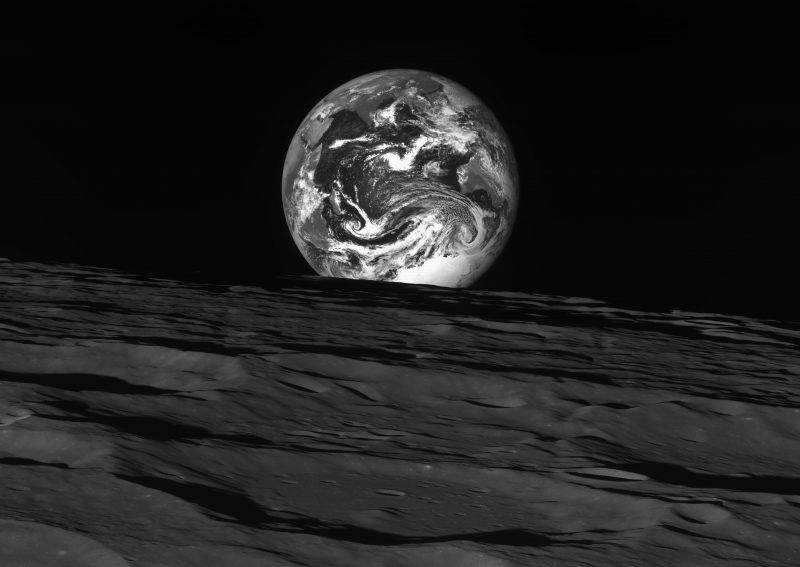
Within the a long time since Voyager first started touring outward, moon exploration has turn out to be extra frequent. For instance, the Korea Aerospace Analysis Institute (KARI) only in the near past launched a set of black-and-white photos of the Earth and moon. The Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter – also called KPLO or Danuri (moon take pleasure in) – captured the picture under someday after it entered lunar orbit on December 26, 2022.

Earth and moon collectively
Now, let’s maintain transferring outward till we are able to see each the Earth and moon collectively in space.
Since 1977, many robotic spacecraft have ventured outward into our solar system. The picture under of Earth and the moon was acquired by the multispectral imager on the Close to Earth Asteroid Rendezvous Spacecraft (NEAR) on January 23, 1998. It was recorded 19 hours after the spacecraft swung by Earth on its approach to the asteroid 433 Eros. The pictures of each had been taken from a spread of 250,000 miles (400,000 km), roughly the identical as the space between the 2 our bodies.
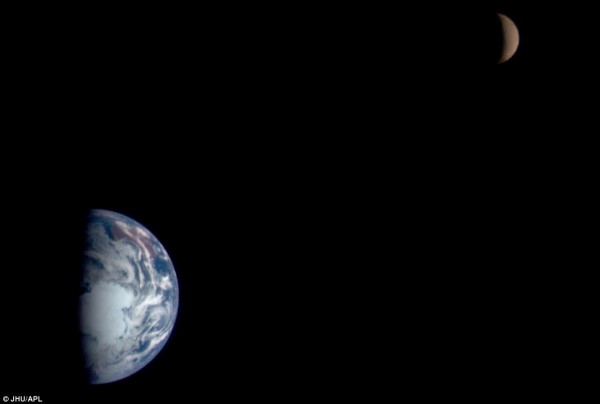

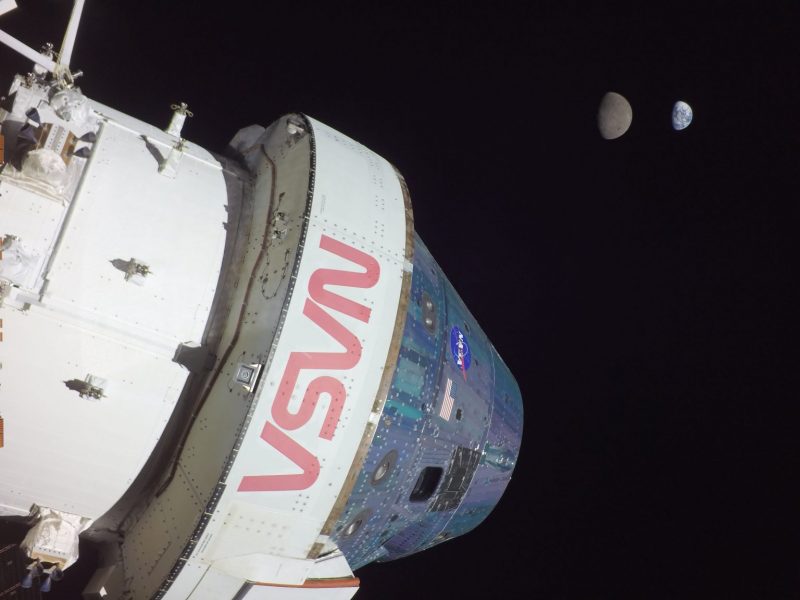
Under is a latest view of the Earth and the moon captured by the Orion spacecraft on November 28, 2022.

The subsequent image was mind-blowing when first launched. It reveals a crescent-shaped Earth and moon – the primary of its form ever taken by a spacecraft – on September 18, 1977.

The view from the outer planets
Lastly, rushing outward from the Earth and moon system, you go the orbits of the planets Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Certainly, from all of those worlds, Earth seems to be like a star, which will get fainter as you get farther away.
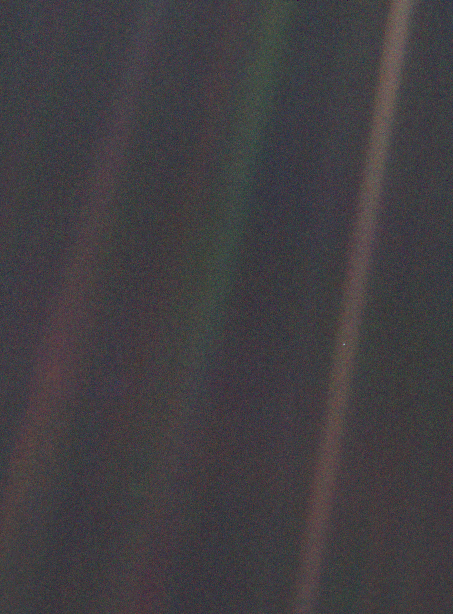

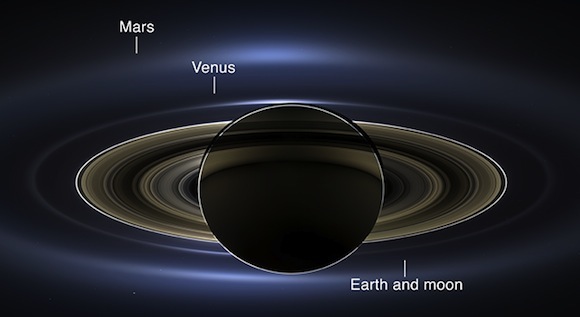

I’ve by no means seen any picture of Earth from Uranus or Neptune or some other physique past Saturn’s orbit. To make sure, solely 5 spacecraft from Earth – the 2 Voyager spacecraft, the 2 Pioneers, and the New Horizons spacecraft, which handed Pluto in 2015 – have ever ventured that far. These craft weren’t designed to look again at Earth, and, to my data, they didn’t seize photos of Earth from distances past Saturn.
And from farther nonetheless?
However, talking theoretically now, might Earth be seen from distances past Saturn?
Particularly, talking solely when it comes to Earth’s brightness, the reply is sure. Our world doesn’t turn out to be too faint to see with the attention alone till far past Neptune’s orbit, at round 9 billion miles (14 billion km) from house. Now, contemplate Pluto’s orbit. It’s extremely elliptical, stretching from simply 2.7 billion miles (4.4 billion km) to over 4.5 billion miles (7.3 billion km) from the sun. Total, Pluto is throughout the limiting distance at which – if we simply contemplate brightness alone, no different elements – we should always have the ability to see Earth with the attention alone.
However there is one other issue. As you go outward from Earth, our world seems nearer and nearer to the blazing sun. As you get farther away, the sun’s glare begins to overwhelm the view of Earth. From Pluto – regardless that Earth could be shiny sufficient to see – you most likely couldn’t see it within the sun’s glare.
So how distant might you see Earth?
What’s the reply to the query of how far you might be from Earth, and nonetheless see it with your individual eyes? Though nobody is aware of for certain as a result of nobody has tried it (and since human eyesight varies from individual to individual), the Earth would turn out to be unimaginable to see with the attention someplace past Saturn’s orbit.
However now, let’s change the sport. Let’s say we might use devices, and never simply the attention alone. And, suppose intrepid astronaut-astronomers went to Pluto. Suppose they took all of the devices they wanted to view Earth within the sun’s glare. May they use telescopes, obscuring disks and different strategies to get a glimpse of Earth? Perhaps!
Nevertheless it nonetheless wouldn’t be simple, nonetheless.
Read more: Wikipedia has a long write-up on extraterrestrial skies
Backside line: How does Earth look from space? How distant in space might you view Earth with the attention alone? Contemplating solely brightness, the reply is about 9 billion miles (14 billion km) away, in regards to the distance of Neptune or Pluto. In apply, although, seeing it from that distance could be a problem as a result of the sun’s glare would overwhelm the view of Earth.




