ESA initially revealed this text on February 17, 2023. Learn the original article here. Edits by EarthSky.
Recognizing asteroids close to the sun
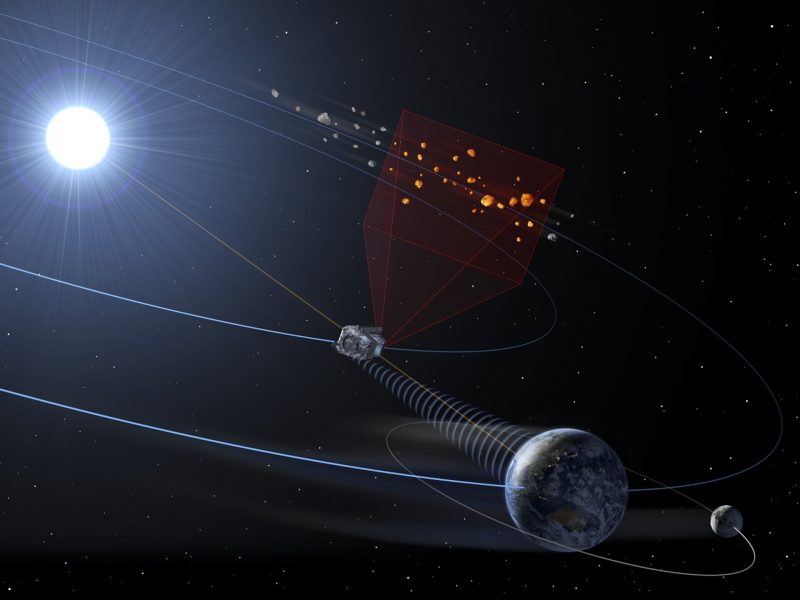
Astronomers have gotten good at detecting even small asteroids that is likely to be headed towards Earth. However an unknown variety of asteroids have paths which may carry them towards us from the sun’s route. And it’s powerful – or unimaginable – to identify these asteroids coming towards us. ESA’s deliberate NEOMIR mission will orbit between Earth and the sun on the first Lagrange level (L1). It’ll act as an early warning system for asteroids – 65 ft (20 meters) and bigger – that devices on Earth’s floor can not see.
NEOMIR stands for Close to-Earth Object Mission within the Infrared.
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
No warning for Chelyabinsk
Nobody noticed the Chelyabinsk meteor approaching February 15, 2013. Simply after dawn on a peaceful and sunny winter’s day, a 65-foot (20-meter) asteroid struck the ambiance over the Ural Mountains in Russia at a velocity of greater than 11 miles per second (18 km/s).
This comparatively small rock approached Earth from very close to the route of the sun. It exploded within the ambiance and created a shockwave that broken 1000’s of buildings, breaking home windows and injuring roughly 1,500 individuals from flying shards of glass. Furthermore, it was the biggest asteroid to strike Earth in over a century.
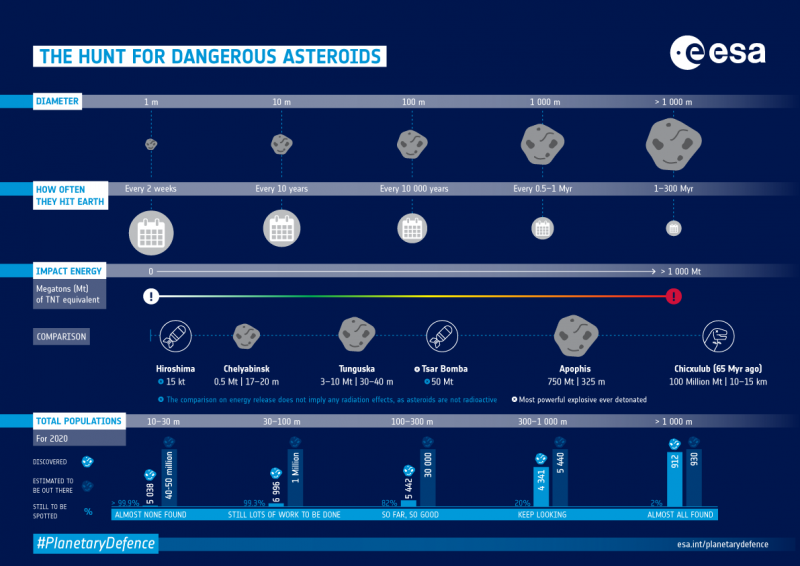
Statistically, asteroids this measurement strike Earth about as soon as each 50-100 years. Bigger asteroids are far much less frequent, however do a terrific deal extra harm. Thankfully, the bigger asteroids are a lot simpler to detect.
Actually, we’ve got found nearly all asteroids bigger than 1/2 mile (1 km) in measurement. Nonetheless, small and medium-sized asteroids are extra frequent and may nonetheless do nice harm. Fortunately, warning instances of some days could be sufficient for native authorities to inform the general public to stay away from home windows and even to evacuate a neighborhood space.
Early warning for asteroids close to the sun
NEOMIR offers us a possibility to deflect a big asteroid possibly years prematurely. And, it could possibly present information for native authorities to maintain communities knowledgeable of doable air bursts weeks forward. NEOMIR will fill a niche in our present asteroid-detection capabilities.
The NEOMIR mission will orbit on the first Lagrange level (L1) between the sun and Earth. Thus, it can have a continuing view of asteroids that will come towards Earth from the route of the sun. Located exterior of Earth’s distorting ambiance, NEOMIR will observe in infrared gentle. It’ll monitor an in depth ring across the sun that’s unimaginable to watch from the bottom.
By making observations within the infrared a part of the sunshine spectrum, NEOMIR will detect the warmth emitted by asteroids themselves. This warmth isn’t drowned out by daylight. Earth’s ambiance absorbs this thermal emission, however from space NEOMIR will be capable of see nearer to the sun than we at the moment can from Earth.
So, asteroids 65 ft (20 meters) and bigger heading towards Earth needs to be detected by NEOMIR no less than three weeks prematurely. Within the worst-case situation, wherein the asteroid is noticed passing close to the spacecraft, we’d get a minimal of three days’ warning. That’s the quickest an asteroid may transfer from L1 to Earth.
Mission standing
NEOMIR is at the moment within the early mission examine phase. Finally, a NEOMIR mission deliberate launch date could be round 2030. NEOMIR would complement NASA’s NEO Surveyor mission. The U.S.-funded mission ought to fulfill the U.S. Congress mandate to find 90% of near-Earth objects bigger than 460 ft (140 meters) in diameter. NEOMIR is designed to give attention to imminent impactors of any measurement.
Backside line: NEOMIR – an early asteroid warning system – will goal asteroids close to the sun. It’ll search for and monitor asteroids 65 ft (20 m) and bigger.