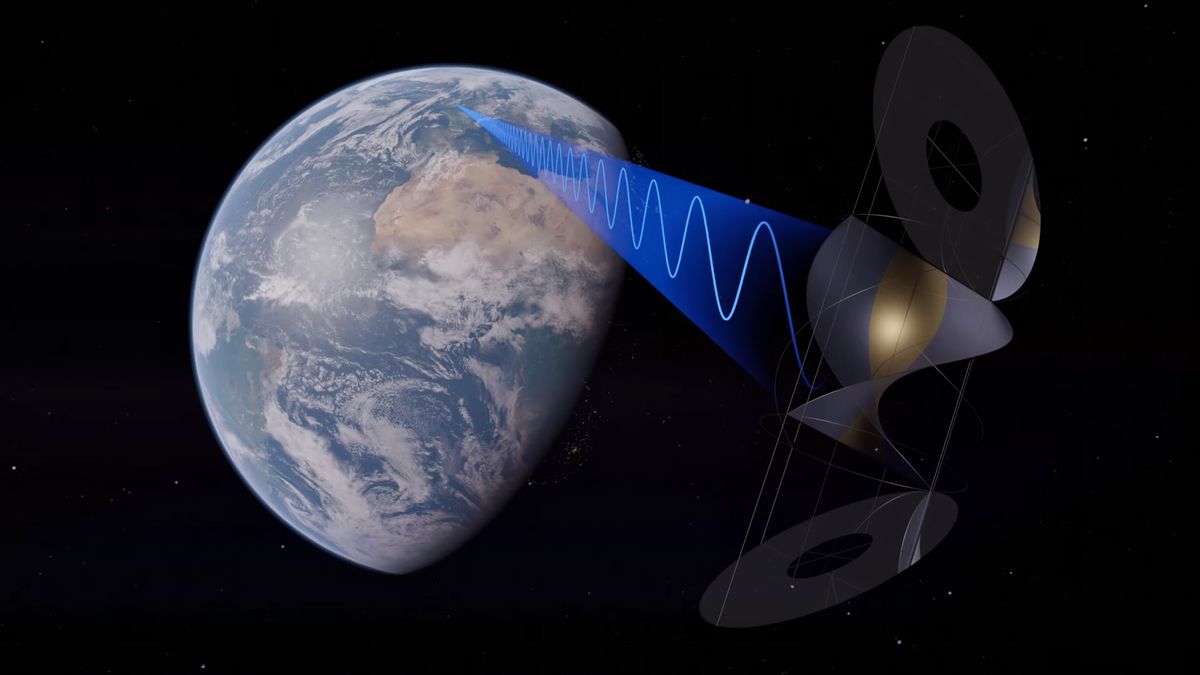
Beaming solar energy from space was once thought-about science fiction. However in recent times, space companies from all around the world have launched research wanting on the feasibility of developing orbiting energy vegetation for actual.
Such initiatives can be difficult to drag off, the stakeholders agree, however because the world’s makes an attempt to curb climate change proceed to fail, such moonshot endeavors could turn out to be obligatory.
Based on the United Nations’ Panel on Climate Change (opens in new tab), the world is at the moment on monitor to heat by 4.5 levels Fahrenheit (2.5 levels Celsius) by the top of the century. That’s 1.8 levels F (1 diploma C) above the brink thought-about secure by the worldwide local weather science group to keep away from disastrous local weather change penalties.
In actual fact, to restrict the warming to anyplace close to that threshold, the world’s economies must lower down their greenhouse gasoline emissions by 45% by 2030. That may imply phasing out numerous fossil-fuel-guzzling know-how in a really brief time period.
For instance, the UK would want at the least 30 to 40 gigawatts of latest on-demand sustainable energy technology to eliminate all fossil gas energy technology (according to a 2019 statement (opens in new tab)). That is the equal of constructing over 30 new nuclear energy plant blocks.
Solar energy vegetation in space, uncovered to fixed sunshine with no clouds or air limiting the effectivity of their photovoltaic arrays, might have a spot on this future emissions-free infrastructure. However these buildings, beaming power to Earth within the type of microwaves, can be fairly troublesome to construct and keep.
Listed below are the primary execs and cons of this know-how.
Associated: A solar power plant in space? The UK wants to build one by 2035.
The professionals
The know-how is much less science fiction than you would possibly suppose
Ian Money is a British engineer, whose CASSIOPeiA Photo voltaic Energy Satellite tv for pc idea has been adopted by a U.Okay. government-backed space power initiative as a place to begin for a possible future space-based solar energy plant demonstrator. A staunch advocate of the know-how, Money thinks that creating and constructing a solar farm in space presents fewer challenges than cracking nuclear fusion.
In terms of space-based solar energy, “there isn’t a science to unravel,” Money advised House.com. “We’ve all of it labored out just about because the Nineteen Seventies, when NASA with the U.S. Division of Vitality carried out a really large-scale research. We have confirmed the physics behind this ever since we first launched a communication satellite into geostationary orbit. You have received solar wings, which face the sun. And you’ve got the physique of the satellite, both with a parabolic dish or a phased array antenna, which faces the Earth. All of the ideas are the identical; you are changing solar power to electrical energy, changing it to microwaves and beaming it to Earth. The one factor that is totally different is the size of the apertures.”
Andrew Wilson, a researcher on the Superior House Ideas Lab on the College of Strathclyde in Scotland, who led a research wanting into the feasibility of space-based solar energy, agrees: “I do not suppose there’s know-how that must be developed versus simply advancing by way of the know-how readiness ranges,” Wilson advised House.com. “There’s nothing actually that must be invented.”
Nevertheless, as detailed later on this piece, the required “know-how advancing” is slightly appreciable.
It might present 13 occasions extra power than an an identical ground-based plant
Constructing solar energy vegetation in space definitely is not a straightforward activity, nevertheless it appears to have benefits — at the least for some international locations. The know-how’s proponents declare {that a} solar-power plant in Earth’s orbit would produce 13 occasions extra energy than an equal set up positioned within the notoriously cloudy U.Okay.
House-based solar energy vegetation would simply produce gigawatts of energy, matching the electrical energy output of nuclear energy vegetation. In distinction, the U.Okay.’s largest solar energy plant, Shotwick Solar Park (opens in new tab) in northern Wales, produces a meager 72.2 megawatts throughout peak insolation occasions. Solely the world’s largest solar vegetation, sprawling installations in among the sunniest international locations, attain the gigawatt mark. For instance, the Bhadla solar farm in India generates as much as 2.7 gigawatts and covers 52 sq. miles (160 sq. kilometers) of land, which is greater than double the scale of Manhattan, in keeping with the Ecoexperts.
Constructing a solar energy plant in space would include an infinite price ticket. As soon as constructed, nevertheless, the plant would pay for itself a lot sooner than any Earth-based renewable energy producing know-how, in keeping with Wilson.

Ian Money is a British electronics engineer and director of Worldwide Electrical Firm. His idea of an orbiting solar energy plant referred to as CASSIOPeiA (Fixed Aperture, Stable-State, Built-in, Orbital Phased Array) has been adopted by the U.Okay. House Vitality Initiative as a place to begin for a potential future space-based solar energy plant demonstration. The initiative believes such a demonstrator may very well be in orbit by the mid-2030s.
It gives completely clear electrical energy 24/7
House-based solar energy would not endure from the primary downside plaguing most most important renewable power technology applied sciences. In space, the sun at all times shines. No clouds ever block the sun’s rays from reaching photovoltaic arrays. And in case you select the orbit properly, you may even keep away from the evening. A solar energy plant in space, not like its equal on Earth, or an off-shore wind farm, would supply a continuing quantity of energy 24/7 year-round. This energy would feed Earth-based energy grids at a gradual charge with out having operators fear about pesky blackouts or sudden overloads.
House-based solar energy proponents, nevertheless, do not anticipate the heavenly electrical energy to push out extra humble ground-based renewables. They suppose space-based solar energy ought to change energy vegetation which can be at the moment getting used to cowl power wants when the sun would not shine and the wind would not blow. Within the U.Okay., this so-called dispatchable energy comes principally from oil and gas-fired energy vegetation, the kind of carbon-producing amenities which can be including to the world’s rising climate-change downside..
“The factor with space primarily based solar energy is that very excessive ranges of energy will be delivered, just like nuclear energy vegetation,” Wilson stated. “Most different renewable power choices cannot present such portions directly. With out space-based solar energy, we’d in all probability be seeking to construct many extra nuclear energy stations, for certain.”
After all, renewable energy may very well be fed into large batteries in occasions of surplus technology for use at occasions of want. However power storage know-how of this scale is barely barely extra solved then nuclear fusion.
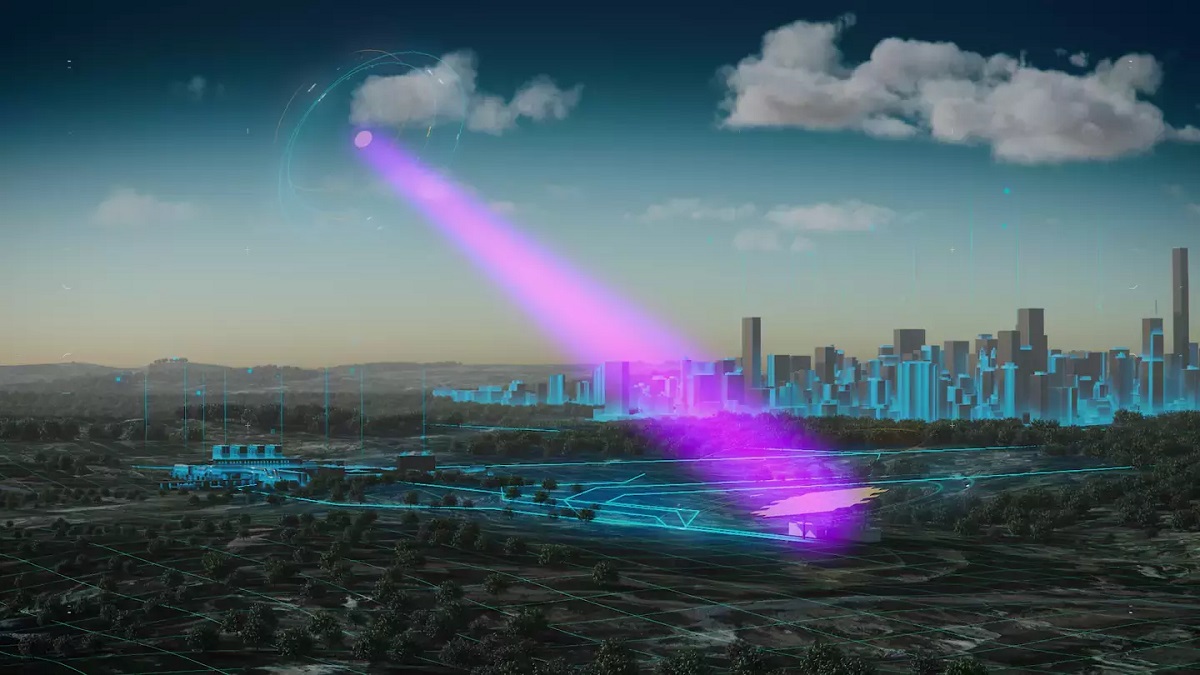

It may very well be beamed anyplace with out wires and energy strains
House-based solar energy would not endure from the primary downside plaguing most most important renewable power technology applied sciences. In space, the sun at all times shines. No clouds ever block the sun’s rays from reaching photovoltaic arrays. And in case you select the orbit properly, you may even keep away from the evening. A solar energy plant in space, not like its equal on Earth, or an off-shore wind farm, would supply a continuing quantity of energy 24/7 year-round. This energy would feed Earth-based energy grids at a gradual charge with out having operators fear about pesky blackouts or sudden overloads.
House-based solar energy proponents, nevertheless, do not anticipate the heavenly electrical energy to push out extra humble ground-based renewables. They suppose space-based solar energy ought to change energy vegetation which can be at the moment getting used to cowl power wants when the sun would not shine and the wind would not blow. Within the U.Okay., this so-called dispatchable energy comes principally from oil and gas-fired energy vegetation, the kind of carbon-producing amenities which can be including to the world’s rising climate-change downside..
“The factor with space primarily based solar energy is that very excessive ranges of energy will be delivered, just like nuclear energy vegetation,” Wilson stated. “Most different renewable power choices cannot present such portions directly. With out space-based solar energy, we’d in all probability be seeking to construct many extra nuclear energy stations, for certain.”
After all, renewable energy may very well be fed into large batteries in occasions of surplus technology for use at occasions of want. However power storage know-how of this scale is barely barely extra solved then nuclear fusion.
It’s theoretically secure from Earth-based battle
The obvious sabotage of the Nord Stream gas pipelines within the Baltic Sea that shocked the world in September 2022 confirmed that, within the politically unstable world that we dwell in, counting on power from overseas is slightly unsafe.
House-based solar energy, proponents say, is safer from worldwide battle than gasoline provides from Russia — and safer than conventional solar vegetation right here on Earth as effectively.
“Some folks say that in case you strategically place solar panels in sure unpopulated areas in, for instance, the Sahara desert, you can energy all humanity’s power wants,” stated Wilson. “However the identical factor that we have now seen occur with Russia might then occur to our power safety if a conflict erupted within the Sahara area.”
Some opponents argue {that a} space-based solar energy plant may very well be simply attacked by anti-satellite missiles. Money, nevertheless, disagrees. Taking pictures down a platform in geostationary orbit, he says, is exterior of the present capabilities of most states. On high of that, whereas disrupting undersea pipelines in a stealth means utilizing submarines permits for believable deniability, an adversary launching a missile to destroy a space-based solar plant of a rival can be simply recognized.
“There definitely is a threat, nevertheless it’s no higher than hostile gamers desirous to assault nuclear energy stations, gasoline pipelines or excessive voltage energy line cables working between continents,” Money stated. “A lot of these items will be attacked covertly, and the attacking nation can simply deny duty. However in space, any assault includes a launch that can certainly be detected.”
Wilson added that, as any space-based solar energy plant venture will most certainly be a world endeavor, the worldwide nature gives an additional layer of safety in opposition to political upheavals.

The infrastructure on the bottom will likely be allegedly much less obtrusive than that of different renewables
Photovoltaic vegetation on the bottom devour big areas of land to reap any cheap quantity of energy. Wind farms within the panorama, too, are unmissable. The rectifying antennas (or rectennas) wanted to obtain microwave beams carrying solar energy generated in space would too require an enormous footprint. These rectennas will, nevertheless be far much less obtrusive, claimed Money, and permit for different makes use of of the land or sea on which they are going to be constructed.
“The rectennas will likely be a skinny mesh building; they will let daylight by way of and will likely be nearly invisible when seen from a distance,” Money stated. “We envisage a future the place we might have a rectenna raised up a couple of meters above floor through poles, and repurpose the land beneath for, say, robotic farming and even human farming, because the land will likely be beneath a microwave defend, so there will likely be no publicity to microwave radiation.”

Andrew Wilson is a analysis affiliate on the Superior House Ideas Lab on the College of Strathclyde, Scotland. His most important analysis curiosity is in life cycle evaluation, carbon accounting, price evaluation and power methods, with specific deal with the space sector.
It might energy flying airplanes
In Airbus’ concept of the long run, solar energy produced in space might contribute to cleansing up the hard-to-deal-with carbon footprint of aviation. Not that it might wean plane off fossil fuels completely, nevertheless it might make a bit dent within the quantity of greenhouse gas the world’s plane discharge into Earth’s atmosphere.
“Sooner or later, as we transfer towards hydrogen and battery-powered plane, we might use space-based solar energy to increase the vary of plane,” Coste stated. “We might use it in takeoff help, as a result of the takeoff is the second the place you utilize many of the gas. You can have a beam that gives power throughout takeoff and later to additionally recharge the plane as they fly.”
Cons
A space solar energy plant must be a lot bigger than something flown in space earlier than
The orbiting solar energy plant should be monumental, and never simply to gather sufficient daylight to make itself worthwhile. The primary driver for the big measurement just isn’t the quantity of energy however the necessity to focus the microwaves that can carry the power by way of Earth’s environment into a fairly sized beam that may very well be acquired on the bottom by a fairly sized rectenna. These focusing antennas, Money stated, must be 1 mile (1.6 kilometers) or extra large, merely due to the “physics you might be coping with.”
Examine this with the International Space Station, at 357 toes (108 meters) lengthy the most important space construction constructed in orbit up to now. House primarily based solar energy proponents all agree that how precisely such vegetation may very well be put collectively continues to be a query.
Money says that his CASSIOPeiA idea would work additionally with a number of smaller vegetation in some forms of decrease Earth orbits. Having a plant nearer to Earth would permit for the antenna to have a smaller measurement, presumably lowering the size to one-tenth of what can be wanted in geostationary orbit. Then again, a plant nearer to Earth can be a better goal for anti-satellite missiles and may also annoy astronomers, as it might be too seen from the bottom.
In each case, constructing a space-based solar energy plant would require tons of of rocket launches (which might pollute the atmosphere depending on what type of rocket can be used), and superior robotics methods able to placing all of the constituent modules collectively in space.
This robotic building might be the largest stumbling block to creating this science fiction imaginative and prescient a actuality, Money stated.
“If we will exhibit that we will assemble smaller CASSIOPeiA satellites, 12 meters [40 feet] in diameter, utilizing robots, then we will step by step broaden to 100-meter [330 feet], 1 kilometer [0.6 miles] or 2 kilometer [1.2 miles] scales,” Money stated. “We might simply want to use extra robots working in parallel. However definitely, it is one of many key challenges.”
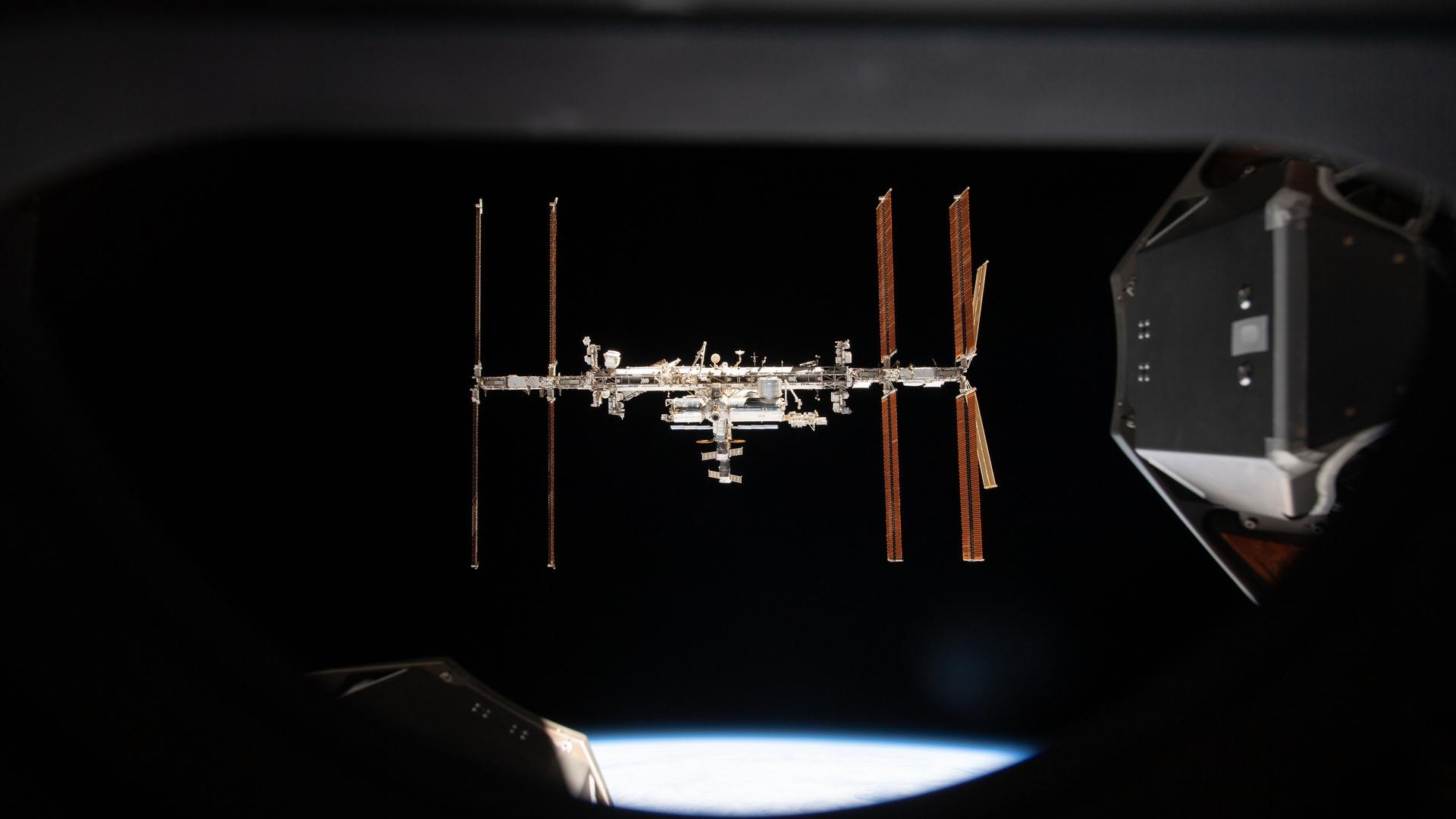
Changing electrical energy into microwaves and again is at the moment awfully inefficient
Airbus, which lately carried out a small-scale demonstration changing electrical energy generated by photovoltaic panels into microwaves and beaming it wirelessly to a receiving station throughout a 118-foot (36 m) distance, says that one of many largest obstacles for possible space-based solar energy is the effectivity of the conversion course of.
Microwaves slide by way of Earth’s environment nearly undisturbed, shedding barely 5% of their power throughout their journey from geostationary orbit, in keeping with Airbus’ calculations. Big quantities of power, nevertheless, are misplaced already on the plant after which on the rectenna when the electrical energy produced by the photovoltaic panels is become microwaves after which again to electrical energy.
“The system we utilized in our demonstration had end-to-end effectivity of about 5%,” stated Coste. “That is not one thing that may be operationally viable, though the daylight is free. For a space-based solar plant to make sense, the effectivity must be round at the least 20%.”

Jean-Dominique Coste is a senior supervisor at Airbus Blue Sky, a division of the European aerospace firm that researches progressive ideas. Airbus Blue SKy focuses on breakthrough applied sciences with the potential to push boundaries and large societal impression.
It could be become a weapon of mass destruction
Some fear that microwave beams in space may very well be become weapons of mass destruction and utilized by evil actors to fry people on the bottom with invisible radiation.
Coste admitted that if somebody wished to develop such a weapon, they presumably might. The microwave beams carrying space-based solar energy, nevertheless, can be engineered from the onset to be secure.
How harmful the beam is to human well being, he stated, will depend on the density of the ability it carries, and that may very well be restricted by design.
“You can design the beam to be so secure that you can take a nap in it together with your little one and never be affected,” stated Coste. “That may be at an influence density degree of about 10 watts per sq. meter. However that can require a particularly giant space to gather [the energy], so we’d wish to have a narrower beam with greater density and a few security system round it.”
The corporate, he says, is wanting into strategies of “site visitors administration across the beam,” utilizing radars and lasers to search for objects within the beam’s neighborhood to cease the power move in case of a security threat.
“We are able to engineer a system that’s designed to solely be pointed at a receiver and wouldn’t ever work if it pointed anyplace else,” stated Coste. “We work on this idea with some massive power corporations in Europe, and so they do not see it as an excessive amount of of a difficulty, as they’re used to coping with security issues round high-voltage energy strains or gasoline pipelines.”
It might get broken by micrometeorites
The huge orbiting construction of flat interweaving photovoltaic panels can be continuously battered by micrometeorites, working a threat of not solely sustaining substantial injury throughout operations, but additionally of producing big quantities of space particles within the course of.
The James Webb Space Telescope, with its 21.6-foot-wide (6.5 m) mirror, received quite a few significant hits early in its operations, prompting its floor management group to adjust observing plans to keep away from gazing within the route the place many of the rocks come from.
The engineers designing a potential future space-based solar energy plant will surely must construct their construction with this fixed micrometeoroid inflow in thoughts.
“For the lifecycle of the station, it’s a must to design it in a means that it may be maintained and repaired repeatedly,” stated Coste. “As a result of it is such a big construction, you’ll have some defects in some panels. The best design of the antenna will likely be modular in order that you can change tiles and panels.”
Money added that, by making the panels from the thinnest potential materials, engineers can nearly remove the technology of particles from the stricken panels.
“If we make it from some kind of polymer supplies, then issues like micrometeorites would simply punch a gap straight by way of,” Money stated. “We might hope that we will scale back the danger of producing particles but additionally the results on the plant. If we construct every of the modules to be impartial of different modules, then all that occurs is {that a} strike takes out a couple of parts.”
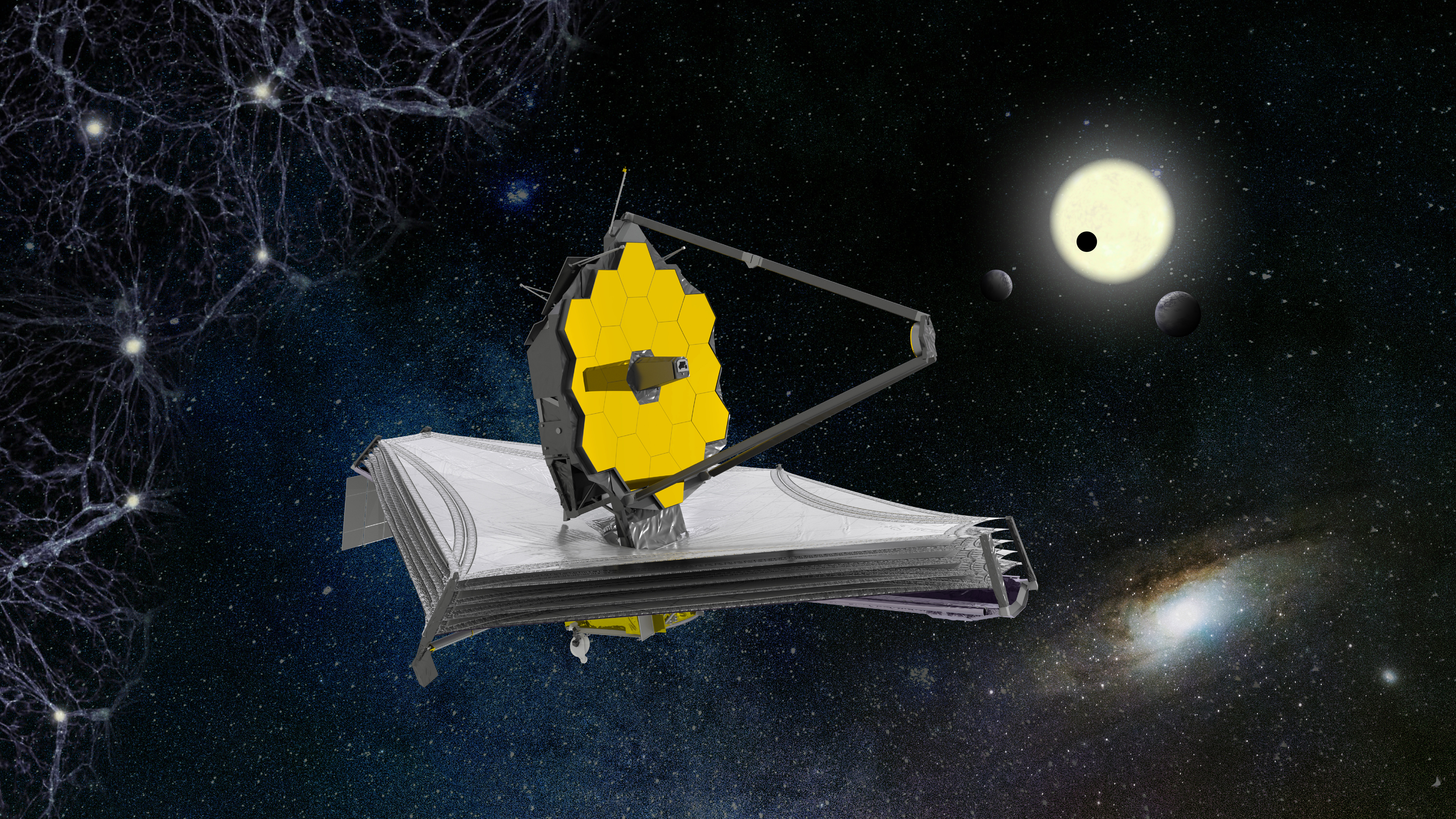
It might create an enormous quantity of particles at finish of life
However what in regards to the finish of life? What would occur with defective modules that had to get replaced? And what about the entire thing as soon as it reaches the top of its life, maybe after a couple of many years of energy technology? Will an object 1 mile (1.6 km) throughout be left in geostationary orbit to slowly decay?
Wilson envisions a extra refined disposal process, which assumes that, by the point we could have space-based solar energy vegetation, we’re most certainly going to see fairly a little bit of everlasting infrastructure on the moon. House tugs that do not exist but might then transfer the aged plant to the moon, the place its supplies may very well be recycled and repurposed for one more use.
“One of many concepts for the long run utilization of the moon is to make use of it for space launches into deeper space,” stated Wilson. “We might even have some type of recycling heart there to course of among the materials.”
It might contribute to mild air pollution
Some astronomers are involved in regards to the impression of such large orbiting buildings on the evening sky. SpaceX’s Starlink constellation has been scary backlash from the astronomy group ever because the firm’s first satellite batches unfold throughout the sky within the type of luminous trains.
The Worldwide Astronomical Union decried Starlink as a worse threat to astronomy than urban light pollution, with large-scale survey telescopes scanning huge swaths of the sky particularly affected.
However Coste thinks {that a} plant in geostationary orbit, 22,000 miles away from Earth, can be barely noticable.
“From Earth, you’ll understand it like a single star,” he stated. “The one a part of the plant that will likely be going through Earth is the antenna, and that does not must be light-reflecting. We might in all probability do one thing to the system to cut back the quantity of sunshine that’s coming [to Earth]. I do not suppose it’s as massive an issue because the megaconstellations.”
Money agrees: “The entire idea [of a space-based solar power plant] is to collect and take up as a lot daylight as potential. We keep this fixed perspective, at all times sun-facing. And any components which are not absorbing that daylight, we will prepare them in precept to deflect the daylight away from Earth.”
So what do you suppose? Ought to space-based solar energy turn out to be a factor? Airbus seems critical about its plans, anticipating to launch a small-scale demonstrator with an aerial platform within the subsequent two years. A small-scale energy-beaming satellite could be in orbit by the top of this decade.
“We see no showstopper,” concluded Coste.
Observe Tereza Pultarova on Twitter @TerezaPultarova. Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.