Many components can restrict the dimensions of a gaggle, together with exterior ones that members don’t have any management over. Astronomers have discovered that teams of stars in sure environments, nevertheless, can regulate themselves.
A brand new research has revealed stars in a cluster having “self-control,” which means that they permit solely a restricted variety of stars to develop earlier than the most important and brightest members expel many of the gasoline from the system. This course of ought to drastically decelerate the delivery of latest stars, which might higher align with astronomers’ predictions for the way rapidly stars kind in clusters. A paper describing these outcomes appeared within the Aug. 20 subject of The Astrophysical Journal and is obtainable on-line.
This research combines knowledge from a number of telescopes together with NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, NASA’s now-retired Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), the APEX (the Atacama Pathfinder EXperiment) telescope, and ESA’s (European Area Company’s) retired Herschel telescope.
The goal of the observations was RCW 36, a big cloud of gasoline known as an HII (pronounced “H-two”) area primarily composed of hydrogen atoms which have been ionized—that’s, stripped of their electrons. This star-forming advanced is situated within the Milky Way about 2,900 light-years from Earth. Infrared knowledge from Herschel is proven in crimson, orange, and inexperienced, and X-ray knowledge is blue, with level sources in white. North is 32 levels left of vertical.
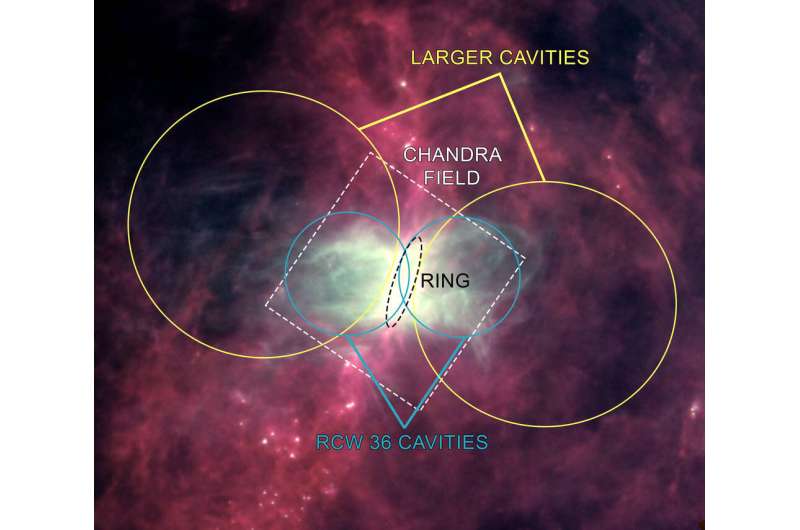
RCW 36 comprises a cluster of young stars and two cavities—or voids—carved out of the ionized hydrogen gasoline, extending in reverse instructions. There may be additionally a hoop of gasoline that wraps across the cluster in between the cavities, forming a waist across the hourglass-shaped cavities. These options are labeled within the picture.
Scorching gasoline with a temperature of about two million Kelvin (3.6 million levels Fahrenheit), radiating in X-rays detected by Chandra, is concentrated close to the middle of RCW 36, near the 2 hottest and most huge stars within the cluster. These stars are a serious supply of the new gasoline. A considerable amount of the remainder of the new gasoline is outdoors the cavities, after having leaked by the borders of the cavities. The SOFIA and APEX knowledge present that the ring comprises cool, dense gasoline (with typical temperatures of 15 to 25 Kelvin, or about -430 to -410 levels Fahrenheit) and is increasing at 2,000 to 4,000 miles per hour.
The SOFIA knowledge present that on the perimeter of each cavities are shells of cool gasoline increasing at about 10,000 miles per hour, possible being pushed outward by strain from the new gasoline noticed with Chandra. The new gasoline, plus radiation from stars within the cluster, has additionally cleared even bigger cavities round RCW 36, forming a Russian doll construction. These options are labeled in a Herschel picture protecting a bigger space, which additionally reveals the Chandra field-of-view and the opposite constructions described right here. The depth ranges on this picture have been adjusted to indicate the bigger cavities as clearly as doable, inflicting a lot of the interior areas close to the RCW 36 cavities to be saturated. North is vertical on this picture.
The researchers additionally see proof from the SOFIA knowledge for some cool gasoline across the ring being ejected from RCW 36 at even increased speeds of about 30,000 miles per hour, with the equal of 170 Earth lots per 12 months being pushed out.
The growth speeds of the totally different constructions described right here, and the mass ejection charge, present that many of the cool gasoline inside about three light-years of the middle of the HII area could be ejected in 1 million to 2 million years. This can filter the uncooked materials wanted to kind stars, suppressing their continued delivery within the area. Astronomers name this course of the place stars can regulate themselves “stellar suggestions.” Outcomes comparable to this assist us perceive the function stellar suggestions performs within the star formation course of.
Extra data:
L. Bonne et al, The SOFIA FEEDBACK Legacy Survey Dynamics and Mass Ejection within the Bipolar H ii Area RCW 36, The Astrophysical Journal (2022). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac8052
Supplied by
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Quotation:
Astronomers see stellar self-control in motion (2022, November 29)
retrieved 29 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-astronomers-stellar-self-control-action.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




