Utilizing the Very Giant Telescope and the radio telescope ALMA in Chile, a workforce of astronomers together with researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute has found a swarm of galaxies orbiting the environment of a hyper-luminous and vigorously star-forming galaxy within the early universe. The remark gives vital clues to how exceptionally brilliant galaxies develop, and to how they evolve into energetic quasars, beaming gentle throughout many of the observable universe.
A basic challenge in astronomy is the query of how galaxies type, develop, and evolve.
As part of their evolution, most galaxies appear to foster a supermassive black hole of their heart. These gravitational monsters often swallow close by fuel and stars, spewing out excess energy as highly effective jets, a phenomenon generally known as a quasar.
From galaxy to quasar
Many particulars in regards to the transition from “regular” galaxies to quasars are nonetheless unknown. However in a brand new examine printed in Nature Communications, a workforce of astronomers led by Michele Ginolfi at ESO, Garching, might have come a step nearer to understanding this evolution.
“Earlier than evolving right into a full-blown quasar, some galaxies are thought to undergo a phase of being very dusty, and really ‘lively’ when it comes to star formation and accretion of fuel onto their central, supermassive black holes,” Ginolfi explains. “We got down to design an experiment to be taught extra about this transition phase.”
Ginolfi and his collaborators targeted on an already recognized galaxy, W0410-0913, one of many brightest, most large and gas-rich galaxies within the distant universe, seen 12 billion years again in time.
The dust is heated by the vitality from starlight and the central black hole, making it glow and divulging the galaxy by means of its infrared gentle. This has led to one of these galaxies being known as scorching dust-obscured galaxies (additionally recognized colloquially as “scorching DOGs”).

Galaxies in 3D
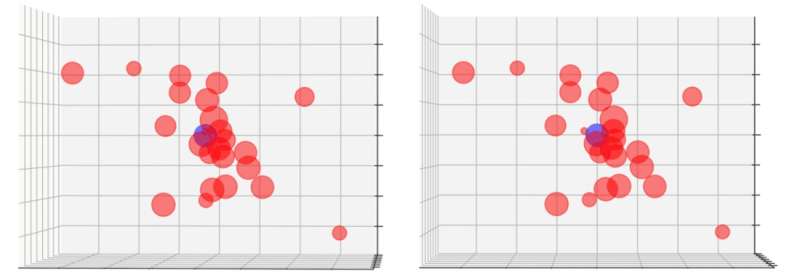
As a result of the evolution of galaxies is inherently related with their environment, Ginolfi and his workforce—whose core considerably atypically consisted principally of early profession researchers—determined to watch W0410-0913 with the “MUSE” instrument on the Very Giant Telescope (VLT) in Chile. This superior instrument allowed them to check a area 40 instances wider than the galaxy itself.
Peter Laursen from the Cosmic Daybreak Heart in Copenhagen participated within the examine. He explains: “The observations revealed that W0410-0913 is surrounded by a swarm of no fewer than 24 smaller galaxies. The cool factor in regards to the MUSE instrument is that we are able to measure not solely their place on the sky, but additionally their distance alongside our line of sight. In different phrases, we are able to measure their 3D positions.”
Though this suggests that W0410-0913 resides in a area no less than ten instances extra dense than the typical universe, this isn’t completely sudden, since scorching DOGs are certainly thought to reside in dense environments.
A galactic automotive crash
Furthermore, whereas W0410-0913 is seen at a time when the universe was 1/8 its present age, it’s already ten instances as large as our personal galaxy, the Milky Way. Rising such an enormous galaxy in such brief time, and feeding a supermassive black hole, does require a considerable provide of recent materials. This all suits properly with the standard image that large galaxies develop by accreting fuel and satellite galaxies, attracted from intergalactic space by their immense gravity.
Actually, in such a dense atmosphere, the speed of galaxy interactions and merging is anticipated to be very excessive. Uncovered to such a bombardment, the astronomers anticipated W0410-0913 to be a automotive wreck of chaotically whirling clumps of fuel and stars.
Nevertheless, digging into previous observations obtained by the ALMA radio antennae positioned solely 300 km north-east of the VLT, Ginolfi and his colleagues have been capable of measure the inner movement of the fuel inside W0410-0913.
And right here a totally totally different image emerged.
Throwing pebbles at a glass pane
Surprisingly, the ALMA observations revealed that W0410-0913 appears to not have been disturbed by interactions with companion galaxies in any respect. Based on the observations, is fuel rotates properly and orderly across the central black hole. Orderly, however amazingly quick, with speeds reaching 500 km/s.
“Coupling the outcomes from the 2 very totally different telescopes, we see an image of how essentially the most large and dusty galaxies might evolve. Such a galaxies, an important stage within the transition from a dusty and star-forming galaxy to a quasar, tends to develop in very dense environments,” Ginolfi says. “However, regardless of the anticipated frequent merging with different galaxies, these gravitational interactions usually are not essentially harmful—they feed the central galaxy and whirl up the fuel a bit, however go away it virtually intact. A bit like throwing small pebbles in opposition to a pane of strong glass: chances are you’ll scratch it, however will not break it…”
Michele Ginolfi’s observations provide first clues on the multi-scale course of that drive the evolution of the uncommon and excessive inhabitants of scorching dust-obscured galaxies. They develop in dense, particular habitats, however the interplay with their companions could be light.
As a parable to this galactic automotive crash, the examine got here near not being performed in any respect, when Michele Ginolfi received caught in a visitors jam in Rome’s visitors, having to submit the proposal utilizing his cellphone from his automotive, minutes earlier than the deadline.
M. Ginolfi et al, Detection of companion galaxies round scorching dust-obscured hyper-luminous galaxy W0410-0913, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32297-x
Quotation:
Astronomers uncover a swarm of galaxies orbiting a hyper-luminous galaxy (2022, September 12)
retrieved 12 September 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-09-astronomers-swarm-galaxies-orbiting-hyper-luminous.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




