Antarctic ice is melting
We bought a double whammy of stories this week, about Antarctic ice. First, on February 27, 2023, the Nationwide Snow and Ice Knowledge Middle in Boulder, Colorado, said Antarctic sea ice has hit a document low, at its possible minimal extent for the yr. These scientists stated the ocean ice surrounding Earth’s southernmost continent is now the bottom within the 45-year satellite document.
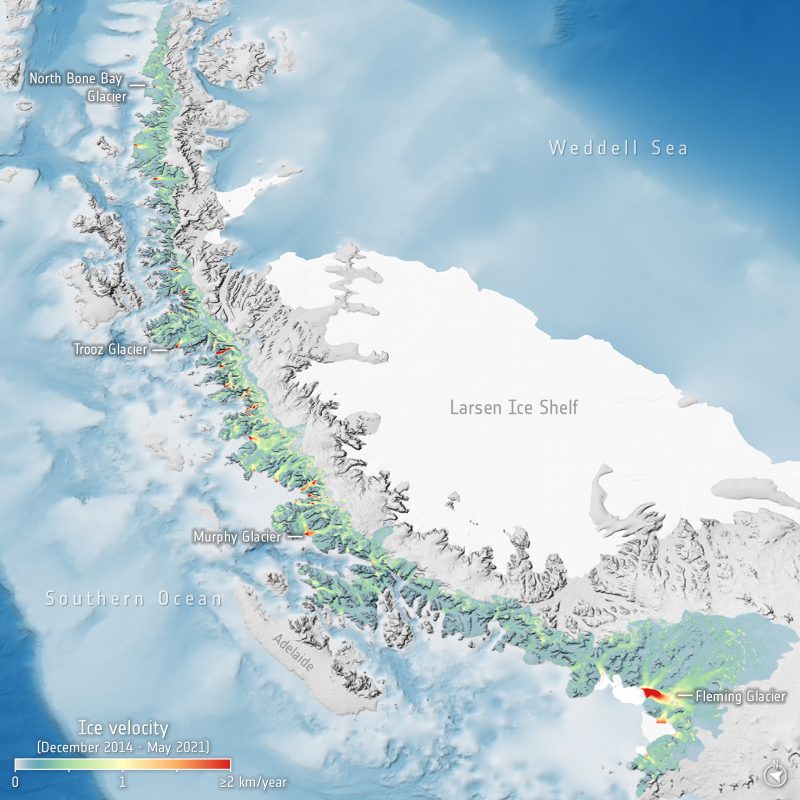
On the identical time, the European House Company reported this week (additionally February 27) that scientists reviewing satellite photos from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission – acquired between 2014 and 2021 – have been “shocked” to find simply how briskly 105 glaciers on the west coast of Antarctica are flowing in the summertime months.
The summer time months … that’s now, in Antarctica. And the ESA scientists said:
The Antarctic Peninsula is probably the most northern and warmest area of Antarctica. And with a 1000-km-long [600-mile-long] mountainous backbone, it’s residence to a wealthy marine ecosystem. The peninsula holds sufficient ice to lift international sea ranges by round 7 cm [2.8 inches]. It’s quickly altering in response to the local weather disaster.
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
A document low in Antarctic ice, in 2023
Scientists on the Nationwide Snow and Ice Knowledge Middle (NSIDC) harassed that the Antarctic sea ice outcomes are preliminary. And, they stated:
… Continued soften situations might nonetheless push the ice extent decrease.
On February 21, 2023, they stated, Antarctic sea ice coated 1.79 million sq. kilometers (691,000 million sq. miles). In reality, this yr’s minimal extent was decrease by 136,000 sq. kilometers (52,500 sq. miles) than the earlier document low, set in 2022.
Ted Scambos at Cires in Boulder has traveled to Antarctica many occasions and revealed extensively on local weather change in Antarctica. As well as, he additionally contributes to NSIDC’s Arctic Sea Ice News and Analysis web page. He commented in a statement:
Antarctica’s response to local weather change has been totally different from the Arctic’s. The downward development in sea ice could also be a sign that international warming is lastly affecting the floating ice round Antarctica. However it’s going to take a number of extra years to be assured of it. Decrease sea ice extent signifies that ocean waves will pound the coast of the enormous ice sheet, additional lowering ice cabinets round Antarctica.
Julienne Stroeve, of each NSIDC and College of Manitoba, added:
The ocean ice helps to buffer massive floating ice cabinets and main outlet glaciers equivalent to Pine Island and Thwaites.
And if these glaciers start a extra fast runaway lack of land ice, it might set off a dramatic enhance in sea degree rise charges earlier than the tip of this century.
For extra particulars and pictures, see NSIDC’s Arctic Sea Ice News & Analysis page.
A stunning ice-melt speed-up
In the meantime, ESA was pointing this week particularly to the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. That is the place over 100 massive glaciers drain ice from the ice sheet immediately into the Southern Ocean. With this in thoughts, a crew of scientists from the College of Leeds in the UK and the Utrecht College within the Netherlands processed over 10,000 Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar images, to be able to measure the velocity of of those glaciers on the Peninsula’s west coast. They studied a six-year interval, general, from 2014 to 2021.
This work resulted in a paper, which the peer-reviewed journal Nature Geoscience published on February 27. Within the paper, ESA stated, scientists:
… describe how they discovered that the glaciers experiencing probably the most seasonal change really stream over 22% sooner in summer time than winter, with all glaciers on this area rushing up by 12% on common.
Satellite tv for pc knowledge exhibits related conduct to Greenland
This new discovery stunned them. That’s as a result of, though scientists have recognized for a very long time that glaciers in Greenland have a seasonal conduct, it’s solely now that satellite knowledge has proven related conduct in Antarctica. In different phrases, sooner summer time ice speeds weren’t seen previous to this research, on this area of Antarctica. Anna Hogg from the College of Leeds commented in a statement:
The Antarctic Peninsula has seen among the most fast warming of any area on Earth. Persevering with work like it will assist glaciologists monitor how rapidly change is going on, enabling correct assessments of how Earth’s ice will reply to local weather change.
Video exhibits ice stream in Antarctica
The video beneath exhibits ice stream from the Trooz Glacier, on the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula, within the yr 2021.
Backside line: Antarctic ice is melting. In late February 2023, it’s at its lowest extent within the 45-year satellite document. Additionally, a long-term soften research is suggesting a stunning speed-up.
Source: Widespread seasonal speed-up of west Antarctic Peninsula glaciers from 2014 to 2021