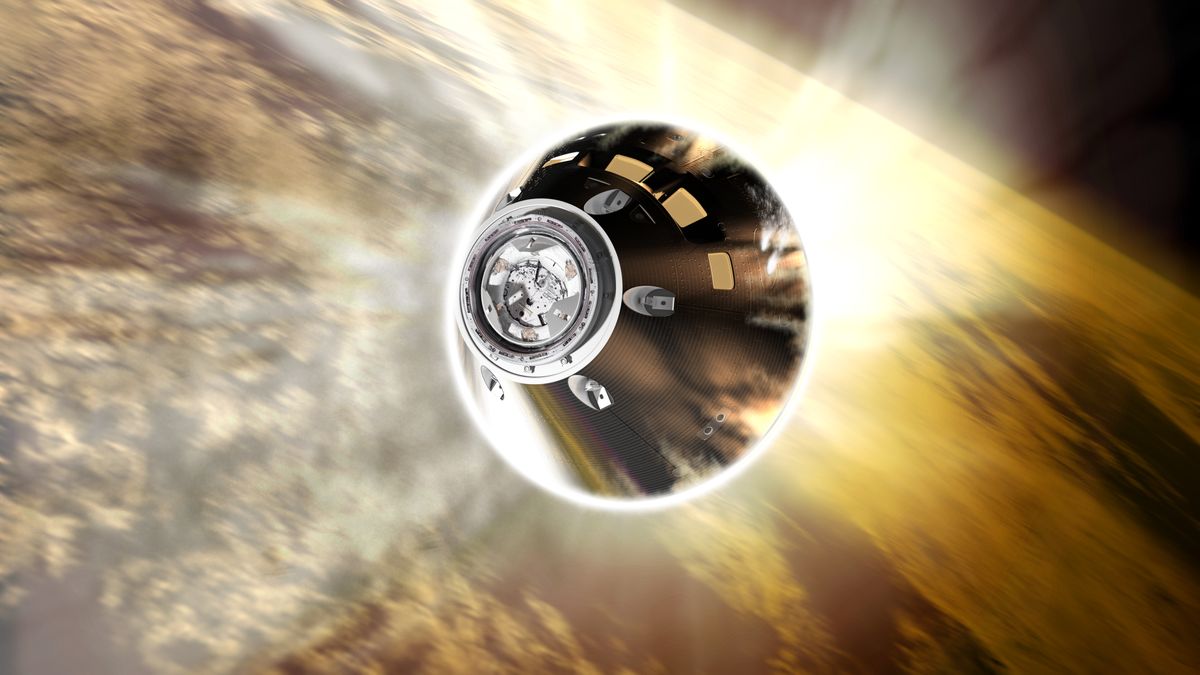
In its previous couple of minutes in space, the Orion spacecraft has a giant job to do.
The Artemis 1 mission launched the NASA Orion capsule safely into deep space on Nov. 16, and after a virtually month that noticed it fly across the moon, it is time for the automobile to come back residence.
Returning on Sunday (Dec. 11) will not be straightforward. Orion will do an unprecedented “skip” off the ambiance of Earth earlier than returning to our planet in earnest. Then it should deploy a collection of parachutes to make a protected ocean splashdown inside attain of U.S. Navy restoration ships.
Artemis 1’s closing moments have to go exceedingly properly for NASA to approve future missions of the Artemis program, that are slated to proceed with Artemis 2 bringing astronauts across the moon in 2024 and Artemis 3 touchdown upon the floor in 2025 or so.
The eight predominant steps of Orion’s epic touchdown sequence are under.
1. Orion capsule separates from service module
The primary main occasion in Orion’s return to Earth is the crew capsule’s separation from its service module, which was constructed by the European Area Company and comprises the thrusters, engine and solar arrays for the spacecraft.
The Orion capsule will separate from its service module at about 12 p.m. EST (1700 GMT), about 40 minutes earlier than splashdown, NASA has mentioned.
2. Orion briefly skips off Earth’s ambiance
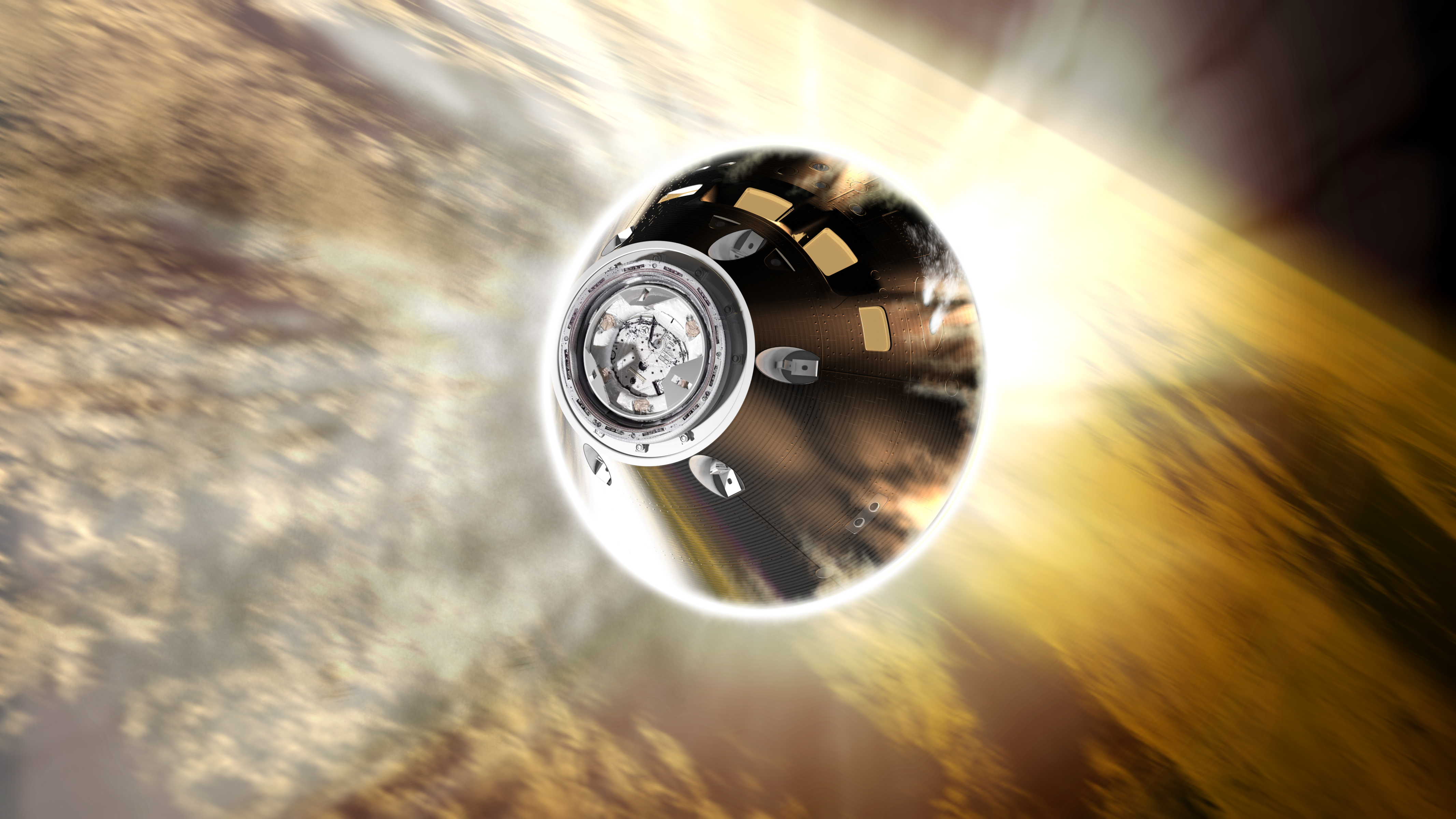

After discarding its unneeded service module, which provided electrical energy and energy for practically a month, Orion will do a daring skip maneuver off the sting of Earth’s ambiance. The capsule will use a little bit of our protecting envelope, together with related carry, to skip similar to a rock throughout the floor of a lake. This maneuver wasn’t potential throughout the Apollo program, however advances in spacecraft navigation make that potential in the present day.
“The skip entry will assist Orion land nearer to the coast of the USA, the place restoration crews can be ready to deliver the spacecraft again to land,” Chris Madsen, Orion steering, navigation and management subsystem supervisor, mentioned in a NASA statement (opens in new tab).
“After we fly crew in Orion starting with Artemis 2, touchdown accuracy will actually assist be certain that we will retrieve the crew rapidly and reduces the variety of sources we might want to have stationed within the Pacific Ocean to help in restoration.”
The maneuver will even scale back the g-forces future Artemis program astronauts will expertise as soon as the Orion capsule is crewed. “As a substitute of a single occasion of excessive acceleration, there can be two occasions of a decrease acceleration of about 4 g’s every,” NASA wrote in the identical assertion. “The skip entry will scale back the acceleration load for the astronauts in order that they have a safer, smoother experience.”
3. Orion enters Earth’s ambiance
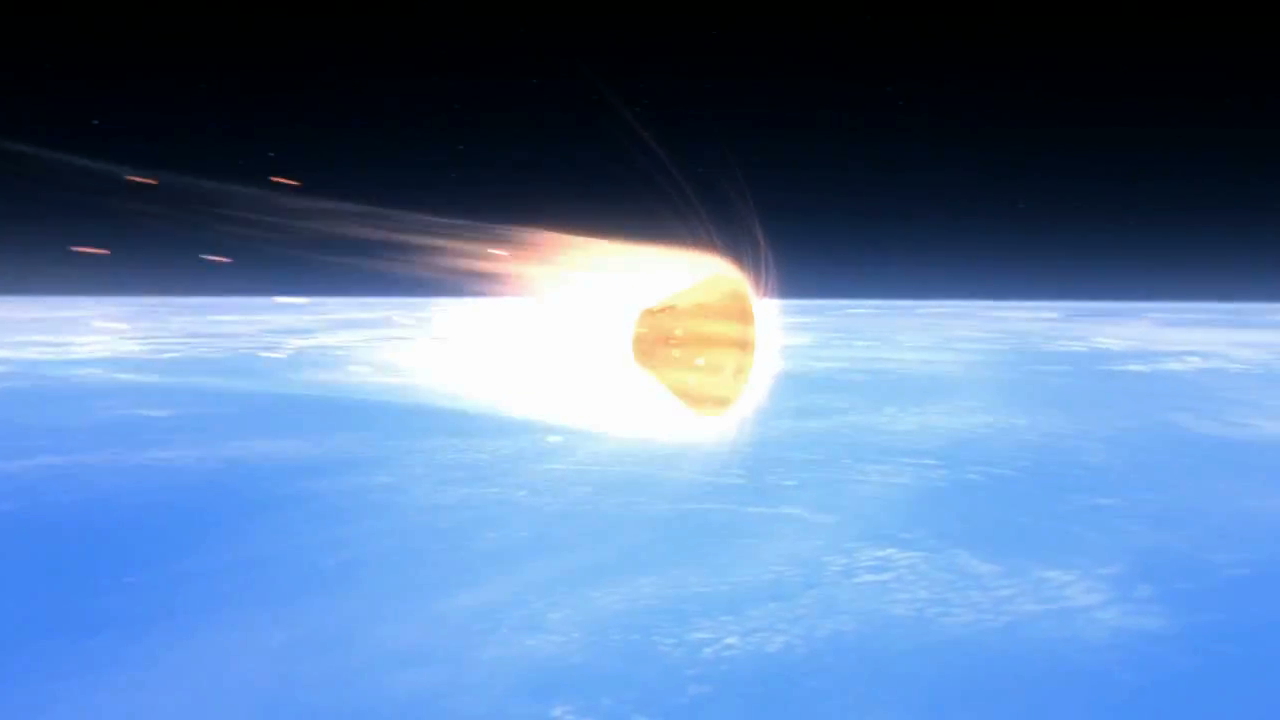

After the skipping maneuver, Orion will enter Earth’s ambiance at a blazing pace of 25,000 mph (40,000 km/h). At peak, its temperatures will soar to half of the sun’s temperature, at 5,000 levels Fahrenheit (2,800 levels Celsius), and actually take a look at out the Orion warmth protect’s capacity to guard the spacecraft and any future passengers.
The warmth protect is the biggest of its sort for astronaut missions, spanning 16.5 ft (5 meters) in diameter, according to NASA (opens in new tab). The warmth protect features a sturdy titanium truss with a composite “pores and skin” fabricated from versatile carbon fiber, together with an ablative materials to intentionally shed a few of the protect off into the ambiance to take stress off the remainder of the system and carry warmth away from the spacecraft.
4. Orion opens protecting bay cowl for parachutes
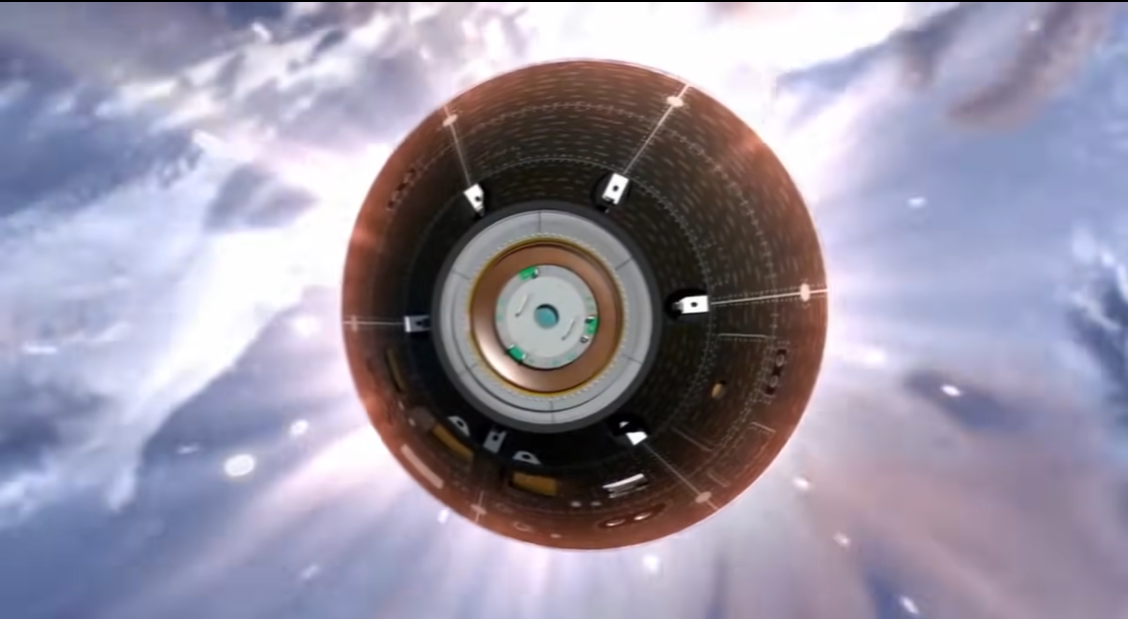
The capsule’s parachutes should keep protected as Orion rides via the worst of re-entry, however because it will get nearer to the bottom they need to come out effectively.
To take action, the spacecraft deploys a ahead bay cowl made out of titanium, which is each light-weight and very sturdy. Three 8-pound (4-kg) ahead bay cowl parachutes will guarantee the quilt’s separation from the spacecraft.
“It is good for spaceflight, the place each further pound is extra pricey,” Orion spacecraft maker Lockheed Martin notes of the cover technology (opens in new tab).
“Parachutes aren’t constructed to resist the 5,000-degree Fahrenheit [2,600 degree-Celsius] temperatures upon re-entry — they’d be too heavy and unable to generate sufficient drag to sluggish the spacecraft down — so the ahead bay cowl protects them till simply the precise second.”
5. Orion opens drogue parachutes
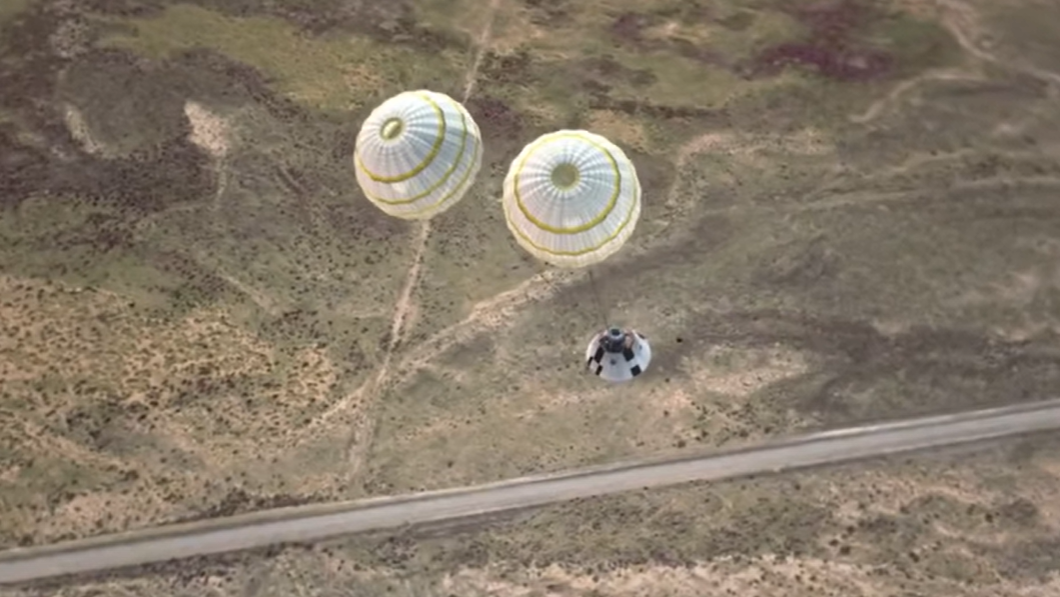

Orion has a number of levels of parachutes to sluggish the spacecraft down. Following the three ahead bay cowl parachutes, at 25,000 ft (7,600 meters) would be the two drogue parachutes, which purpose to sluggish Orion’s pace to roughly 100 mph (160 km/h).
“Drogue parachutes are used to sluggish and stabilize the crew module throughout descent and set up correct situations for predominant parachute deployment to comply with,” NASA writes (opens in new tab) of the expertise.
The drogues are fabricated from Kevlar/Nylon hybrid materials and have a mass of about 80 kilos (36 kg) every. When inflated, every of the parachutes can be 100 ft (30 meters) lengthy, between their attachment to the crew module and the highest or crown.
6. Orion deploys pilot parachutes
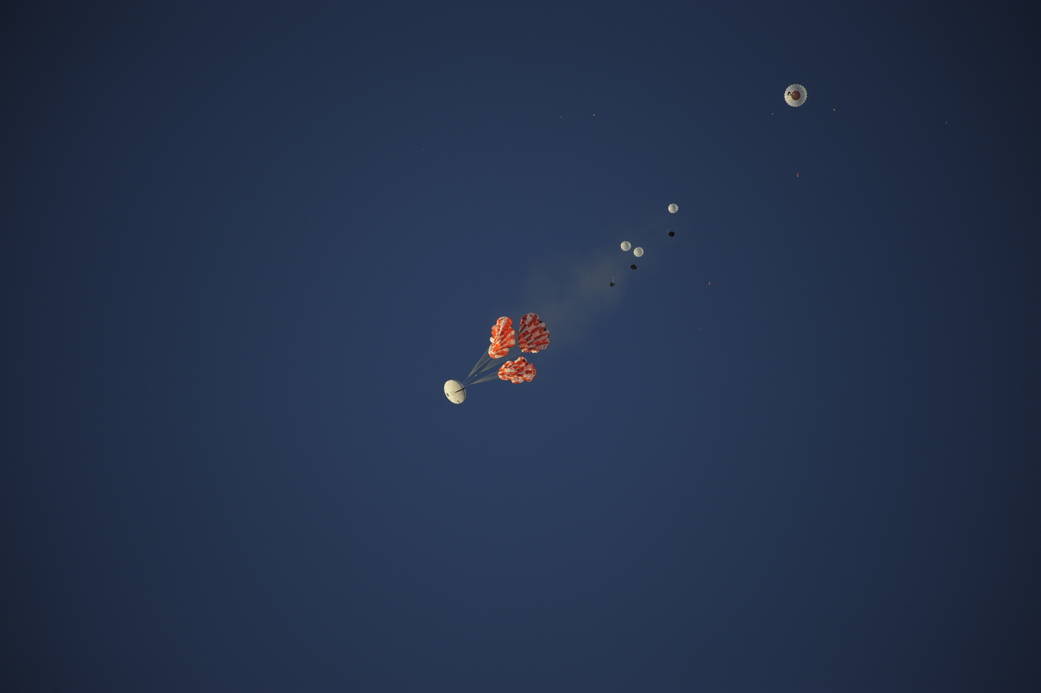

Orion’s drogue parachutes will then lower away, permitting for the three pilot parachutes to deploy. These parachutes are roughly 11 kilos (5 kg) in mass every and are additionally fabricated from Kevlar/Nylon hybrid materials.
The pilot parachutes will deploy when the Orion is roughly 9,500 ft (2,900 m) above the bottom and touring at 190 ft (130 m) per second.
This difficult parachute deployment illustrates a number of expertise, NASA says (opens in new tab), together with the material of the chutes, “cannon-like mortars” to fireplace the assorted rounds of parachutes on the proper time, and fuses to unfurl the parachutes rigorously and swiftly.
7. Orion opens predominant parachutes

The final set of Orion’s 11 parachutes are the three predominant parachutes. The pilot parachutes will pull the mains out, which ought to deploy and sluggish Orion right down to solely 20 mph (32 km/h). Every predominant parachute is roughly 265 ft lengthy (80 meters) from high to attachment.
“Orion’s parachute system was designed with crew security in thoughts: it may well stand up to the failure of both one drogue or one predominant parachute, and it may well guarantee a safe touchdown in an emergency,” NASA says (opens in new tab) of the expertise, noting the greater than decade of floor and air exams to validate the system.
8. Orion splashes down within the Pacific Ocean
7. Orion splashes down

Assuming all of the parachutes work in response to plan, Orion will then splash down off the coast of San Diego at 12:40 p.m. EST (1740 GMT). The U.S. Navy and an exploration floor programs restoration workforce from NASA’s Kennedy Area Heart will work collectively to retrieve the spacecraft. The prime ship assigned to restoration operations is the united statesPortland.
“Earlier than splashdown, the workforce will head out to sea in a Navy ship. On the course of the NASA restoration director, Navy divers and different workforce members in a number of inflatable boats can be cleared to method Orion,” NASA says (opens in new tab) of the restoration operations.
“Divers will then connect a cable to the spacecraft and pull it by winch right into a specifically designed cradle contained in the ship’s properly deck … open water personnel will even work to get better Orion’s ahead bay cowl and three predominant parachutes.”
Elizabeth Howell is the co-author of “Why Am I Taller (opens in new tab)?” (ECW Press, 2022; with Canadian astronaut Dave Williams), a ebook about space drugs. Observe her on Twitter @howellspace (opens in new tab). Observe us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or Facebook (opens in new tab).




