A Northwestern College-led workforce of astronomers has developed essentially the most in depth stock so far of the galaxies the place brief gamma-ray bursts (SGRBs) originate.
Utilizing a number of extremely delicate devices and complex galaxy modeling, the researchers pinpointed the galactic houses of 84 SGRBs and probed the traits of 69 of the recognized host galaxies. Amongst their findings, they found that about 85% of the studied SGRBs come from younger, actively star-forming galaxies.
The astronomers additionally discovered that extra SGRBs occurred at earlier occasions, when the universe was a lot youthful—and with better distances from their host galaxies’ facilities—than beforehand identified. Surprisingly, a number of SGRBs had been noticed far exterior their host galaxies—as in the event that they had been “kicked out,” a discovering that raises questions as to how they had been capable of journey so distant.
“That is the most important catalog of SGRB host galaxies to ever exist, so weexpect it to be the gold normal for a few years to come back,” mentioned Anya Nugent, a Northwestern graduate pupil who led the research centered on modeling host galaxies. “Constructing this catalog and at last having sufficient host galaxies to see patterns and draw vital conclusions is precisely what the sector wanted to push our understanding of those improbable occasions and what occurs to stars after they die.”
The workforce will publish two papers, detailing the brand new catalog. Each papers will publish on Monday, Nov. 21 in The Astrophysical Journal. As a result of SGRBs are among the many brightest explosions within the universe, the workforce calls its catalog BRIGHT (Broadband Repository for Investigating Gamma-ray burst Host Traits). All of BRIGHT’s knowledge and modeling merchandise are publicly accessible on-line for neighborhood use.
Nugent is a graduate pupil in physics and astronomy at Northwestern’s Weinberg School of Arts and Sciences and a member of the Middle for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Analysis in Astrophysics (CIERA). She is suggested by Wen-fai Fong, an assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Weinberg and a key member of CIERA, who led a second research centered on SGRB host observations.
Benchmark for future comparisons
When two neutron stars collide, they generate momentary flashes of intense gamma-ray mild, often called SGRBs. Whereas the gamma rays final mere seconds, the optical mild can proceed for hours earlier than fading under detection ranges (an occasion known as an afterglow). SGRBs are a number of the most luminous explosions within the universe with, at most, a dozen detected and pinpointed every year. They at present symbolize the one technique to research and perceive a big inhabitants of merging neutron star techniques.
Since NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory first found an SGRB afterglow in 2005, astronomers have spent the final 17 years attempting to know which galaxies produce these highly effective bursts. Stars inside a galaxy can provide perception into the environmental circumstances wanted to supply SGRBs and might join the mysterious bursts to their neutron-star merger origins. Thus far, just one SGRB (GRB 170817A) has a confirmed neutron-star merger origin—because it was detected simply seconds after gravitational wave detectors noticed the binary neutron-star merger (GW170817).
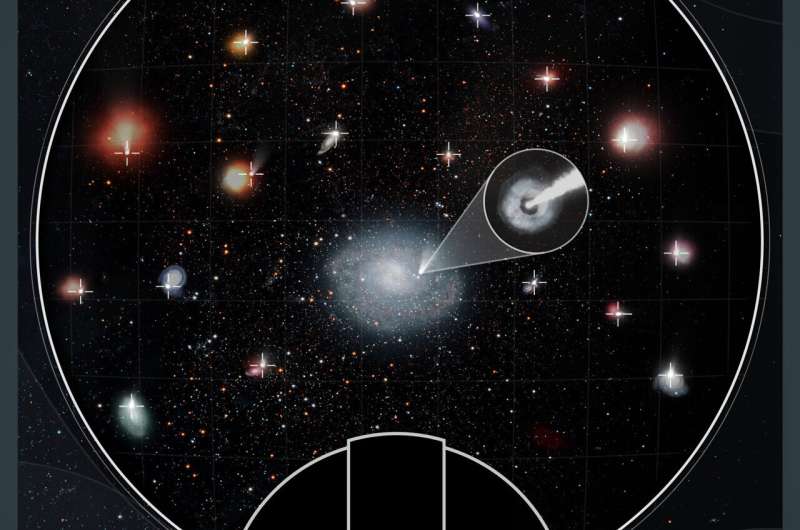
“In a decade, the following era of gravitational wave observatories will have the ability to detect neutron star mergers out to the identical distances as we do SGRBs right this moment,” Fong mentioned. “Thus, our catalog will function a benchmark for comparability to future detections of neutron star mergers.”
“The catalog can actually make impacts past only a single class of transients like SGRBs,” mentioned Yuxin “Vic” Dong, research co-author and astrophysics Ph.D. pupil at Northwestern. “With the wealth of knowledge and outcomes introduced within the catalog, I imagine a wide range of analysis initiatives will make use of it, perhaps even in methods we now have but not considered.”
Perception into neutron-star techniques
To create the catalog, the researchers used a number of extremely delicate devices at W.M. Keck Observatory, the Gemini Observatories, the MMT Observatory, the Massive Binocular Telescope Observatory and the Magellan Telescopes at Las Campanas Observatory to seize deep imaging and spectroscopy of a number of the faintest galaxies recognized within the survey of SGRB hosts. The workforce additionally used knowledge from two of NASA’s Nice Observatories, the Hubble House Telescope and Spitzer House Telescope.
Prior to those new research, astronomers characterised host galaxies from solely a pair dozen SGRBs. The brand new catalog is quadruple the variety of present samples. With the benefit of a a lot bigger dataset, the catalog exhibits that SGRB host galaxies might be both younger and star-forming or outdated and approaching loss of life. This implies neutron-star techniques kind in a broad vary of environments and lots of of them have fast formation-to-merger timescales. As a result of neutron-star mergers create heavy components like gold and platinum, the catalog’s knowledge additionally will deepen scientists’ understanding of when valuable metals had been first created within the universe.
“We suspect that the youthful SGRBs we present in youthful host galaxies come from binary stellar techniques that fashioned in a star formation ‘burst’ and are so tightly sure that they will merge very quick,” Nugent mentioned. “Lengthy-standing theories have recommended there should be methods to merge neutron stars rapidly, however, till now, we now have not been capable of witness them. We discover proof for older SGRBs within the galaxies which might be a lot older and imagine the celebrities in these galaxies both took an extended time to kind a binary or had been a binary system that was additional separated. Therefore, these took longer to merge.”
Potential of JWST
With the power to detect the faintest host galaxies from very early occasions within the universe, NASA’s new infrared flagship observatory, the James Webb House Telescope (JWST), is poised to additional advance the understanding of neutron star mergers and the way far again in time they started.
“I am most enthusiastic about the opportunity of utilizing JWST to probe deeper into the houses of those uncommon, explosive occasions,” Nugent mentioned. “JWST’s capability to look at faint galaxies within the universe may uncover extra SGRB host galaxies which might be at present evading detection, maybe even revealing a lacking inhabitants and a hyperlink to the early universe.”
“I began observations for this venture 10 years in the past, and it was so gratifying to have the ability to go the torch onto the following era of researchers,” Fong mentioned. “It’s one in every of my profession’s best joys to see years of labor come to life on this catalog, due to the younger researchers who actually took this research to the following stage.”
Extra info:
Brief GRB Host Galaxies I: Photometric and Spectroscopic Catalogs, Host Associations, and Galactocentric Offsets, Astrophysical Journal (2022). iopscience.iop.org/article/10. … 847/1538-4357/ac91d0
Brief GRB Host Galaxies II: A Legacy Pattern of Redshifts, Stellar Inhabitants Properties, and Implications for his or her Neutron Star Merger Origins, Astrophysical Journal (2022). iopscience.iop.org/article/10. … 847/1538-4357/ac91d1
Supplied by
Northwestern University
Quotation:
Brief gamma-ray bursts traced farther into distant universe (2022, November 21)
retrieved 22 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-short-gamma-ray-distant-universe.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




