Italian researchers have demonstrated experimentally for the primary time that microorganisms can photosynthesize utilizing the infrared-dominated gentle emitted by the most typical sort of star within the Milky Way. The outcomes from the Star Mild Simulator, offered on the Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC) 2022, recommend that life might develop round stars completely different from our Solar and produce oxygen-rich worlds which are liveable by extra complicated organisms.
Most stars in our Milky Way are the smallest sort of hydrogen-burning star, generally known as pink M-dwarfs. They’re cooler and fewer luminous than our Solar and primarily emit gentle within the infrared and far-infrared, with very low emissions at visible wavelengths. As a result of their abundance, many exoplanets have been discovered round M-dwarfs. Nonetheless, whether or not or not these planets might help life has been the topic of a lot debate lately.
The Star Mild Simulator, constructed by a collaboration of groups from the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), the Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnology (IFN-CNR) and the Division of Biology in Padua, can generate gentle intensities and spectra at completely different ranges to breed the sunshine for any star. For this experimental setup, the crew recreated the emitted gentle from an M-dwarf together with an atmospheric simulator chamber that replicated a synthetic planetary surroundings.
“We initially centered on cyanobacteria since they’ve extraordinary capacities to resist each surroundings on the Earth, in addition to a recognized capacity to outlive in near-infrared gentle,” stated Prof Nicoletta La Rocca of the College of Padua, who led the examine. “When these acclimatized to the simulated surroundings, we prolonged our checks to mosses and numerous sorts of pink and inexperienced microalgae.”
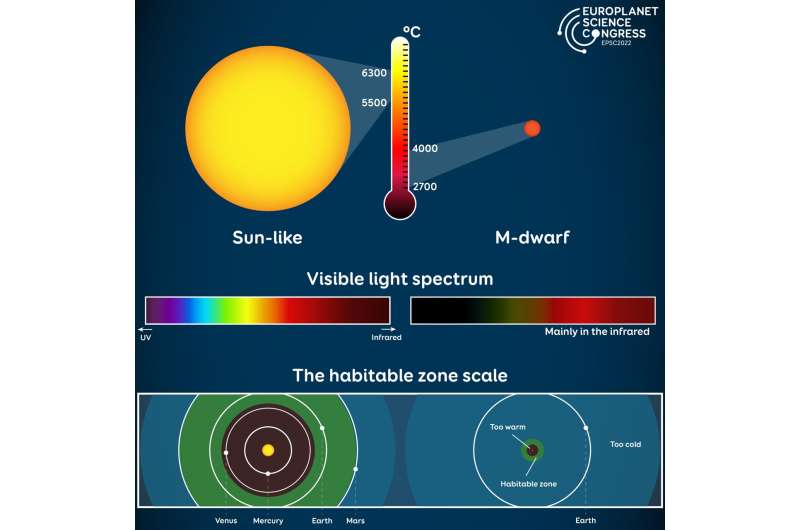
All of the experiments had been profitable, with all of the microorganisms demonstrating that they might develop and photosynthesize below M-dwarf gentle.
Prof La Rocca commented that “life as we all know it is dependent upon liquid water, in order that is likely one of the main standards for an exoplanet to be thought-about to be liveable. Extra complicated terrestrial life varieties additionally depend upon oxygen. On Earth, photosynthesizing cyanobacteria performed an important function in oxidizing our environment. The brand new experimental outcomes lengthen our data of probably liveable environments and therefore, the place we would look forward to finding a planet harboring complicated life.”
Convention: www.epsc2022.eu/
Offered by
Europlanet
Quotation:
Simulator illuminates the seek for life across the Milky Way’s most typical stars (2022, September 21)
retrieved 21 September 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-09-simulator-illuminates-life-milky-common.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




