Because the discovery in 1995 of a planet in orbit round a star apart from the sun, analysis in exoplanetology has revolutionized our information of planetary programs. The SPIRou instrument, put in on the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope, contributes to those outcomes, specifically by observing the attainable planets recognized by the TESS observatory satellite.
By combining the information from each devices, the planet TOI-1695b has been found, and is among the new sub-Neptune and super-Earth sort planets revealed by SPIRou round stars much less large and cooler than the sun, by a world group wherein the Institut d’astrophysique de Paris performs a serious function. These outcomes promote a greater understanding of most of these planet that don’t exist within the solar system.
For hundreds of years, solely the planets of the solar system have been identified and noticed: 4 large planets removed from the sun, and 4 telluric planets (together with Earth) nearer to our star. In trendy nineteenth and twentieth century thought, it appeared very seemingly that many, if not all different stars additionally hosted planets; being inaccessible to our technique of statement, these remained nonetheless within the area of the imaginary or of science fiction. It was subsequently not identified whether or not these attainable extrasolar planets actually existed, have been just like these of the solar system, or had totally different properties.
The scenario modified in 1995 with the primary detection of an extrasolar planet, carried out on the Haute-Provence Observatory by astronomers Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, later awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. New devices have since been developed; they’ve enabled the detection and characterization of hundreds of exoplanets, revolutionizing our information of planetary programs, and specifically of their formation and evolution.

Amongst these, France and the Institut d’astrophysique de Paris have made a serious contribution to the event of the SPIRou instrument (Determine 1) on the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (Determine 2), put in on the Large Island of Hawaii. It’s a spectropolarimeter working within the infrared vary. It makes it attainable to seek for planets round stars much less large, smaller and cooler than the sun, the red dwarfs (their temperature is between 2500 and 4000°C, whereas the sun is at 5500°C).
It additionally makes it attainable to check the magnetic exercise of those small stars, that are probably the most quite a few stars in our galaxy. The scientific groups use SPIRou specifically to characterize the candidate planets (objects more likely to be planets) which have been recognized round red dwarf stars by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite tv for pc (TESS), a NASA observatory satellite, and which needs to be noticed with SPIRou to determine their nature.
It’s on this context that researchers from the Institut d’astrophysique de Paris, together with Flavien Kiefer (collaborator and former postdoctoral fellow on the IAP), Eder Martioli (IAP affiliate researcher and former postdoctoral fellow on the IAP), Guillaume Hébrard (senior CNRS researcher), Alain Lecavelier des Étangs (senior CNRS researcher) and Pierre-Cécil König (former Ph.D. scholar on the IAP) current the invention and characterization of the brand new planet TOI-1695b, carried out inside a world group. The work is revealed within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
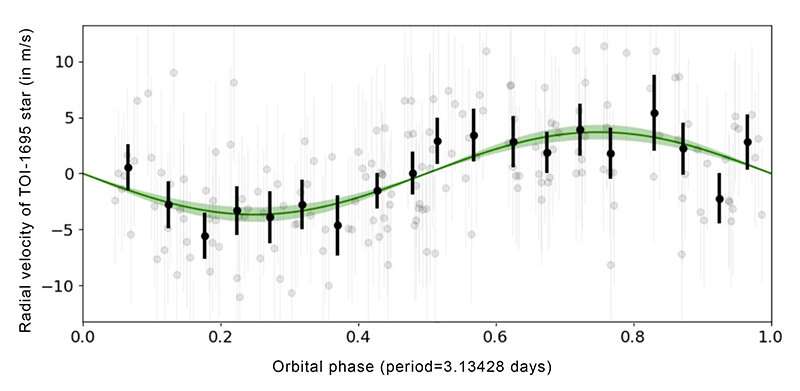
Barely twice as large however six occasions extra large than Earth, this new planet has a density barely decrease than that of Earth. It’s of the sub-Neptune sort (a planet somewhat smaller than Neptune). Its temperature, nonetheless, is a couple of hundred levels increased than that of Neptune, and its ambiance most certainly accommodates massive quantities of hydrogen, helium, and water vapor. Lastly, this planet goes round its crimson dwarf star in three days (Determine 3).
Beforehand, the identical group had already introduced the discoveries of the super-Earth TOI-1452b (revealed in The Astronomical Journal) and the the sub-Neptune TOI-1759b (revealed in Astronomy & Astrophysics). Like TOI-1695b, these two planets orbit a crimson dwarf star. The scale of those three planets is between 1.7 and three.1 occasions that of Earth, and their lots between 5 and 7 occasions that of Earth. They’re subsequently intermediate planets between Earth and Neptune, however they’re nearer to their host stars (from 6 to 18 million km, in comparison with the 150 million km of the Earth-sun distance).
Although these sorts of planets are non-existent within the solar system, statement applications have proven for a number of years that these super-Earths and sub-Neptunes are nonetheless considerable in our galaxy. These new planets detected and characterised with SPIRou will make it attainable to higher perceive this new planetary inhabitants. It raises the query of how, within the historical past of their formation, some might have turn into gaseous planets or rocky planets, regardless of related lots. Answering this query might assist clarify the dichotomy of the planets of the solar system, between small telluric planets and gas giant planets.
Extra info:
F. Kiefer et al, A sub-Neptune planet round TOI-1695 found and characterised with SPIRou and TESS, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2022). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202245129
Charles Cadieux et al, TOI-1452 b: SPIRou and TESS Reveal a Tremendous-Earth in a Temperate Orbit Transiting an M4 Dwarf, The Astronomical Journal (2022). DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ac7cea
E. Martioli et al, TOI-1759 b: A transiting sub-Neptune round a low mass star characterised with SPIRou and TESS, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2022). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202142540
Offered by
Institut d’astrophysique de Paris
Quotation:
Small planets orbiting low-mass stars detected with the SPIRou instrument and the TESS satellite (2023, February 13)
retrieved 13 February 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-02-small-planets-orbiting-low-mass-stars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




