Astrobiology is the sector of science involved with the research of life within the universe and making an attempt to resolve the thriller of how life emerged on Earth. This consists of the seek for life past Earth, finding out environments that might help life in addition to investigating interactions between planets and their stars and exploring how this might affect life.
As such astrobiology may be very a lot an interdisciplinary endeavor encompassing a variety of scientific fields reminiscent of, however not restricted to; biology, astronomy, chemistry, geology, atmospheric science, oceanography, and even aeronautical engineering.
A comparatively younger scientific subject astrobiology is already had a significant impression on how space businesses like NASA and the European Area Company (ESA) conduct and plan their off-world missions.
Associated: The 10 most Earth-like exoplanets
What does an astrobiologist do?
For so long as humanity has understood that the stars within the night sky over Earth are our bodies just like the sun and thus probably possess planets of their very own now we have speculated concerning the risk that these worlds additionally host life. Lastly, our strategies of scientific investigation are catching as much as our aspirations and scientists are starting to seek for clues of life away from Earth.
Astrobiologists research the potential for life past Earth, they could be consultants in biology however may be certified in a wealth of different scientific fields reminiscent of astronomy and chemistry.
According to the University of Washington (opens in new tab), a number of the questions astrobiologists are starting to deal with concerning life elsewhere in the universe embody:
- What sort of setting do residing organisms have to survive?
- What are the boundaries of those environments and what sort of “extremes” might life nonetheless exist in?
- What form would life tackle one other world?
- Would the completely different traits of an alien world trigger life to comply with a radically completely different evolutionary path?
- What clues would point out a world is liveable?
- What indicators might astronomers search for that point out a planet or moon is at the moment inhabited by life or has been sooner or later in its historical past?
These questions apply to planets and moons in our solar system and worlds additional afield, planets orbiting different stars known as ‘extrasolar planets’ or ‘exoplanets.’ Astrobiologists might not actively seek for life however fairly for places the place life might exist.
Different astrobiologists reminiscent of these on the SETI (search for extraterrestrial intelligence) institute are concerned with the seek for radio alerts that might point out the existence of life elsewhere within the universe.
In fact, to this day there is just one planet we all know for positive to host life, and that’s our personal. Thus the work of astrobiologists additionally consists of investigations of how life arose on Earth and the way it has advanced.
Astrobiologists might take a look at the best types of life on Earth or those who dwell in excessive circumstances like temperature extremes and beneath excessive pressures. This enables them to ask if such organisms would be capable of survive in space or within the excessive circumstances of an alien world.
Exobiology and early astrobiology
(opens in new tab)
Arguably one of many foundational experiments in astrobiology was 1853’s now notorious “Miller and Urey Experiment.” Scientists from the College of Chicago Stanley Miller and Harold Urey simulated circumstances on the primeval Earth and confirmed the chemical compounds which might be thought of the foundational constructing blocks of life arose naturally from easy chemical processes. Their experiment discovered that with simply water, ammonia, hydrogen and methane in addition to {an electrical} spark to imitate lightning, a number of protein precursors (crucial for all times) together with amino acids have been fashioned.
NASA would carry out its first astrobiology mission in 1959, initially referring to the sector of research as “exobiology,” by designing an instrument to scour extraterrestrial environments for the indicators of microbial life. This might result in the muse of NASA’s life sciences program which turned the accountability of the Ames Analysis Middle (ARC) the place exobiology would ultimately broaden its horizons and develop into the sector of astrobiology because it exists in the present day.
“NASA’s present astrobiology program addresses three basic questions: How does life start and evolve? Is there life past Earth and, if that’s the case, how can we detect it? What’s the way forward for life on Earth and within the universe?” former director of NASA’s Ames Analysis Middle, G. Scott Hubbard wrote (opens in new tab) in 2008 for NASA’s fiftieth anniversary.
Hubbard defined that the seek for life elsewhere within the universe is so interwoven with what it means to be human, that astrobiology extends past the sciences, nevertheless. “Politics, science, personalities, and serendipity all contributed to the creation and success of what’s now known as astrobiology as a subject of inquiry,” he wrote.
Amongst a wealth of astrobiology missions and initiatives the space company has pioneered and supported within the mid-Seventies, NASA would launch the Viking mission to Mars.
Comprised of two landers and three biology experiments designed to search for doable indicators of life, Viking might have discovered no clear proof of life however this system started what would develop into arguably probably the most distinguished investigation of life elsewhere within the solar system; the seek for the traces of life on Mars.
Astrobiology within the solar system and past

(opens in new tab)
Since Viking turned the primary mission to efficiently contact down on Mars, there have been a wealth of missions on the Crimson Planet’s floor and in its orbit offering essential data for astrobiologists. These missions embody the now-retired rovers Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity rover and the at the moment lively Perseverance rover which touched down on the Martian floor in 2021.
The Perseverance rover, a part of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission, is at the moment offering essential information related to astrobiology analysis from its stomping floor on the Crimson Planet the Jezero crater.
This 28-mile (45-kilometer) vast crater is believed to have flooded with water round 3.5 billion years in the past. With water thought of a key ingredient for all times, Perseverance is in search of biosignatures that point out life as soon as existed on this area of Mars. The rover has not too long ago begun dropping sample tubes on the floor of the Crimson Planet which can be picked up by the joint NASA/ESA Mars Pattern Return Mission within the close to future.
Earlier than this mission goes into operation the Perseverance and Curiosity rovers carry out in-situ chemical evaluation of Martian rock to offer data for astrobiologists.
There’s one other manner astrobiologists can get their fingers on samples from Mars with out ready for a pattern return mission, nevertheless. Meteorites from the Crimson Planet are incessantly deposited on the floor of our planet with scientists discovering a wealth of natural compounds inside these rocks launched into space by violent occasions on Mars.
Although these natural compounds comprised of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and some different components, are related to organic processes they are not direct proof of life as they may also be created by non-biological or “abiotic” processes.
Additional afield within the solar system than Earth’s neighbor Mars, astrobiologists have an interest within the moons of Jupiter that are at the moment being studied in depth by the Juno spacecraft. Amongst Jupiter‘s 4 largest moons, known as the Galilean moon as a result of they have been found by Galileo Galilei within the 1600s, Europa is without doubt one of the most promising prospects for locating life elsewhere within the solar system.
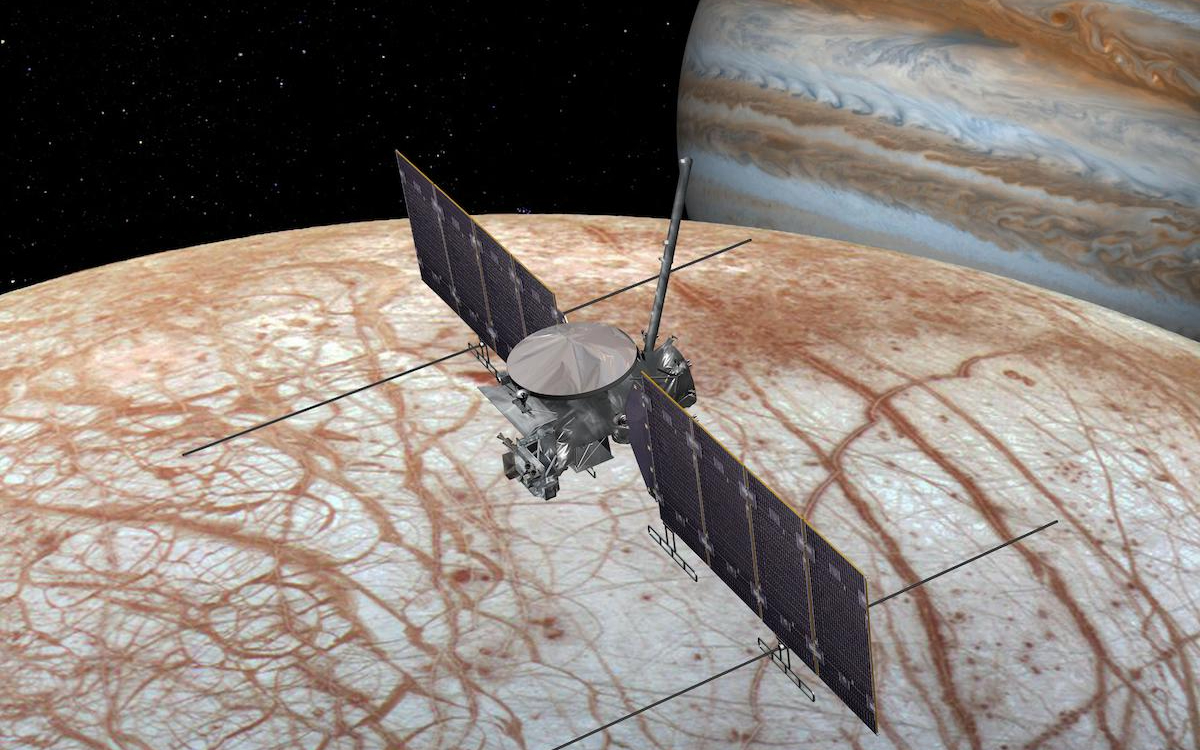
The Europa Clipper spacecraft will quickly be paying a go to to Europa to find if the icy Jovian moon might harbor the circumstances appropriate for all times. Specifically, astrobiologists wish to know if Europa’s icy shell hides subsurface lakes just like these beneath Antarctica’s ice sheet.

(opens in new tab)
The Europa Clipper is ready to launch in late 2024 arriving at Jupiter 5 years later when it’ll make 45 flybys of the large Jovian moon aiming to make use of its suite of 9 science devices to find out the depth and saltiness of Europa’s ocean.
Moreover, the spacecraft will even search for molecules within the ambiance of the Jovian moon deposited there by eruptions of icy water. Astrobiologists can be notably to find the presence of complicated natural molecules that might point out the processes related to easy types of life are occurring at Europa.
The moons of Jupiter’s fellow gas giant Saturn are additionally of nice curiosity to astrobiologists. In 2022 NASA-supported astrobiologists used geochemical fashions and information from the Cassini mission to search out Enceladus’ subsurface waters could be rich in dissolved phosphorus. As this ingredient is important for all times this means the oceans of Enceladus could possibly be liveable.
Astrobiology and exoplanets

(opens in new tab)
Exterior the solar system, astrobiologists are starting to review the atmospheres of so-called ‘extrasolar planets’ or ‘exoplanets’ to find out the form of components and chemical compounds that comprise them.
The investigation of exoplanets is a comparatively new science however is rising at a staggering fee. That is exemplified by the truth that the primary exoplanet round a sun-like star was found in 1995 by the staff of Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz and in simply 17 years the “exoplanet catalog” had grown to over 5,000 confirmed worlds.
In December 2021 the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), probably the most highly effective telescope ever constructed by humanity launched and shortly started to revolutionize astronomy and space science.
NASA says the JWST’s impression on astrobiology comes from its capability to watch the formation of stars from their first phases to the formation of planetary programs thus permitting astrobiologists to watch the form of components which might be current as planets type. The JWST can also be able to measuring the bodily and chemical properties of planetary programs and thus permitting astrobiologists to analyze the potential for all times in these programs.
The primary JWST outcomes included a detailed investigation of the atmosphere of an exoplanet, the gas giant WASP-96 b, which was proven to own the distinct signature of water. The space telescope then examed the ambiance of the Saturn-like exoplanet WASP-39b returning what NASA says is “the primary molecular and chemical profile of a distant world’s skies.”
Although neither of those planets is able to internet hosting life, the outcomes set the stage for the JWST’s investigations of the atmospheres of rocky or terrestrial worlds just like Earth. The JWST adopted these exoplanet breakthroughs by discovering its first world orbiting another star in January 2023.
The research of exoplanets and their atmospheres and thus astrobiology acquired one other important enhance in the beginning of 2023 when NASA unveiled plans for a future telescope to succeed the JWST. The first objective of this telescope, the Liveable Worlds Observatory (HWO), can be to seek for the indicators of life on Earth-like worlds.
The brand new space telescope could possibly be operational as quickly because the 2040s and can be designed for robotic servicing and upgrades, which suggests not solely might it function for many years, however its observing energy might enhance with age.
The HWO ought to be able to detecting the indicators of life on 25 close by Earth-like worlds, the statistic minimal that astrobiologists and different scientists want to find out if life is frequent within the Milky Way.
Further sources
Comedian e book followers with a eager curiosity in space science could also be curious about NASA’s collection of Astrobiology graphic novels (opens in new tab). These publications discover a variety of astrobiology matters together with the research of the origin, evolution, and distribution of life within the universe. Discover the most recent discoveries and analysis in astrobiology with astrobiology.com (opens in new tab). Study extra concerning the Miller-Urey experiment with these sources from the online education website StudySmarter (opens in new tab).
Bibliography
What’s an astrobiologist?, CalTech, [Accessed 01/06/23], [https://coolcosmos.ipac.caltech.edu/ask/246-What-is-an-astrobiologist (opens in new tab).]
What Is Astrobiology? College of Washington, [Accessed 01/06/23], [https://depts.washington.edu/astrobio/wordpress/about-us/what-is-astrobiology/ (opens in new tab)]
G. S. Hubbard, What’s Astrobiology? NASA, [2008], [https://www.nasa.gov/feature/what-is-astrobiology (opens in new tab)]
Viking 1&2, NASA Mars Exploration Program, [Accessed 01/10/23], [https://mars.nasa.gov/mars-exploration/missions/viking-1-2/ (opens in new tab)]
E. Howell, 5,000 exoplanets! NASA confirms huge milestone for planetary science, Area, [2022], [https://www.space.com/nasa-confirms-5000-exoplanets-milestone (opens in new tab)]
Nobel Winners Modified Our Understanding with Exoplanet Discovery, [2019],[https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/news/1604/nobel-winners-changed-our-understanding-with-exoplanet-discovery/]
D. Clery, NASA unveils preliminary plan for multibillion-dollar telescope to search out life on alien worlds, Science, [2023], [https://www.science.org/content/article/nasa-unveils-initial-plan-multibillion-dollar-telescope-find-life-alien-worlds (opens in new tab)]