2022 was one of many warmest years in recorded historical past regardless of cooling La Niña circumstances governing the tropical Pacific Ocean.
What’s worse, concentrations of warming greenhouse gases in Earth’s atmosphere reached new highs final yr, whereas polar areas continued warming at a breakneck tempo, in accordance with new knowledge launched by the world’s main climate-monitoring businesses.
Earlier this week, NASA, the U.S. Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European surroundings monitoring program Copernicus all launched their respective assessments of climate change‘s progress throughout 2022, revealing an unabated rise in common temperatures worldwide.
Globally, 2022 was the fifth warmest yr on document, according to NASA (opens in new tab) and Copernicus (opens in new tab). (NOAA (opens in new tab) locations the just lately concluded yr within the sixth spot with a marginal distinction.) However some elements of the world — together with western Europe, the Center East, Central Asia, China and north-western Africa — notched their hottest 12 months in historical past.
Associated: 10 devastating signs of climate change satellites can see from space
The final decade has had 9 of the ten hottest years in historical past
The entire hottest years on document have occurred since 2010, with the previous 9 years the warmest “since trendy record-keeping started in 1880,” NASA mentioned within the assertion.
“Whenever you take a look at 9 of the previous 10 years, they’re the warmest years within the trendy document since 1880, and that is fairly alarming,” NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson mentioned in a joint NASA/NOAA information convention on Thursday (Jan. 12), when the brand new knowledge was launched. “If we do not take it severely and have some actual motion to mitigate [the trend], there are going to be lethal results throughout the globe.”
In 2022, the planet was on common about 2 levels Fahrenheit (1.1 levels Celsius) hotter than within the late nineteenth century, simply 0.7 levels F (0.4 levels C) in need of the brink set by the worldwide local weather science group as a tipping level to keep away from as a way to stop extreme and unpredictable environmental penalties. In accordance with Europe’s Copernicus program, 2022 was additionally 0.54 levels F (0.3 levels C) hotter than the already heat common for the 1991 to 2020 interval.
“It is actually hotter now than most likely not less than through the previous 2,000 years, most likely for much longer,” Russel Vose, a NOAA bodily scientist, mentioned within the information convention. “And the speed of [temperature] enhance over the previous 50 years has been sooner than any time previously two millennia.”
File regardless of cooling La Niña
2022 scored within the high 10 hottest years on document, on par with 2015, even though the so-called La Niña impact ruled the tropical Pacific Ocean. Throughout La Niña years, floor water temperatures in jap elements of the central Pacific drop, which in flip leads to wetter and cooler climate circumstances throughout giant parts of the world.
Quite the opposite, 2015, which was as heat as 2022, in accordance with the newly launched knowledge, was an El Niño yr, that includes hotter tropical Pacific floor water temperatures and total drier and hotter climate circumstances throughout the globe.
“NASA scientists estimate that La Niña’s cooling affect might have lowered international temperatures barely (about 0.11 levels F, or 0.06 levels C) from what the common would have been below extra typical ocean circumstances,” NASA mentioned within the assertion.
Weak poles warming at breakneck tempo
The globe just isn’t warming evenly. Actually, among the most susceptible areas have already smashed by the two.7 degree-F (1.5 degrees-C) threshold. The delicate polar areas are warming exceptionally quick, with some areas in Antarctica and Siberia having logged temperatures 3.6 levels F (2 levels C) above the 1991-2020 averages in 2022, in accordance with Copernicus. The heat exacerbated annual sea ice loss, with the Antarctic area recording its second all-time lowest sea ice extent final yr. Solely 1987 noticed extra widespread sea ice loss through the peak of the Antarctic summer time.
Earlier NASA-backed research (opens in new tab) revealed that the Arctic, the floating ice cap protecting Earth’s north pole and the encircling areas of northern Europe and Asia, could also be warming at a mind-boggling fee, 4 instances sooner than the worldwide common. And this development just isn’t anticipated to subside, hinting at a way forward for accelerating ice sheet thawing and sea degree rise.

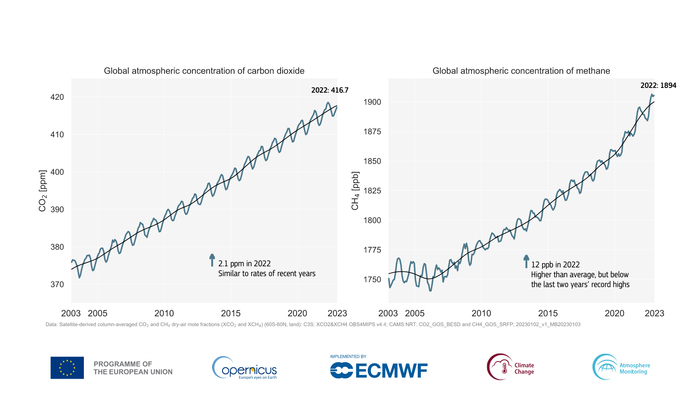
Greenhouse gasoline concentrations at new highs
Scientists are fairly sure that additional document and near-record years lie forward. Aside from making the highest 10 for highest temperatures, 2022 additionally noticed a rise in concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane within the environment, the 2 chief contributors to the ever-increasing warming. In accordance with Copernicus, there hasn’t been this a lot carbon dioxide within the air within the final 2 million years, whereas accessible scientific proof exhibits that concentrations of methane are at their highest in over 800,000 years.
“Preliminary evaluation of satellite knowledge averaged over the entire atmospheric column exhibits that carbon dioxide concentrations rose by roughly 2.1 ppm [parts per million], whereas methane rose by round 12 ppb [parts per billion],” Copernicus mentioned in a press release. “This resulted in an annual common for 2022 of roughly 417 ppm for carbon dioxide and 1,894 ppb for methane.”
The concentrations of carbon dioxide, which is usually launched by the burning of fossil fuels, have elevated by 50% for the reason that pre-industrial period, Vose mentioned.
In accordance with NOAA, international ocean warmth content material was at an all time excessive in 2022, that means that the general quantity of vitality accrued within the higher 6,500 ft (2,000 meters) of the world’s globally linked ocean has by no means been increased. The rising quantity of warmth is more likely to exacerbate many unfavorable results of local weather change, together with sea degree rise, additional thawing of polar ice sheets and degradation of marine ecosystems.
“Barring a serious volcanic eruption, there’s a 100% probability that in future years we’ll be within the high 10 once more,” Vose mentioned. “With El Niño doubtlessly brewing, the rising concentrations of heat-trapping greenhouse gases, we’re actually going to be near a document subsequent yr.”
Volcanic eruptions that Vose referred to typically briefly cut back international temperatures by injecting giant quantities of sunshine-reflecting ash into the stratosphere, the layer of Earth’s environment above the troposphere by which most climate happens. Some volcanic eruptions, akin to final yr’s Hunga Tonga explosion, however, can contribute to warming by injecting water vapor, which additionally traps warmth, into excessive atmospheric altitudes.
The Hunga Tonga contribution to the warmth of 2022 was, nonetheless, so tiny it was inconceivable to measure, Gavin Schmidt, NASA local weather scientists and director of the NASA Goddard Institute for Area Research, mentioned within the information convention.
Comply with Tereza Pultarova on Twitter @TerezaPultarova. Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.




